Xinge You
VII: Visual Instruction Injection for Jailbreaking Image-to-Video Generation Models
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Image-to-Video (I2V) generation models, which condition video generation on reference images, have shown emerging visual instruction-following capability, allowing certain visual cues in reference images to act as implicit control signals for video generation. However, this capability also introduces a previously overlooked risk: adversaries may exploit visual instructions to inject malicious intent through the image modality. In this work, we uncover this risk by proposing Visual Instruction Injection (VII), a training-free and transferable jailbreaking framework that intentionally disguises the malicious intent of unsafe text prompts as benign visual instructions in the safe reference image. Specifically, VII coordinates a Malicious Intent Reprogramming module to distill malicious intent from unsafe text prompts while minimizing their static harmfulness, and a Visual Instruction Grounding module to ground the distilled intent onto a safe input image by rendering visual instructions that preserve semantic consistency with the original unsafe text prompt, thereby inducing harmful content during I2V generation. Empirically, our extensive experiments on four state-of-the-art commercial I2V models (Kling-v2.5-turbo, Gemini Veo-3.1, Seedance-1.5-pro, and PixVerse-V5) demonstrate that VII achieves Attack Success Rates of up to 83.5% while reducing Refusal Rates to near zero, significantly outperforming existing baselines.
Reverberation: Learning the Latencies Before Forecasting Trajectories
Nov 14, 2025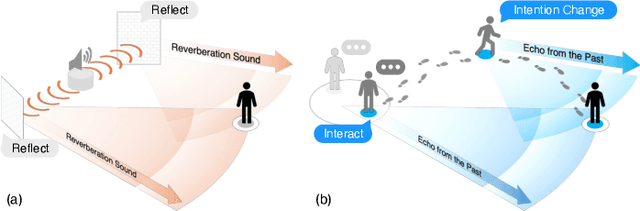
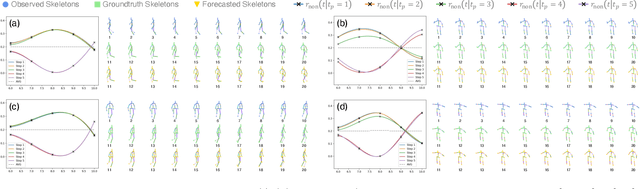
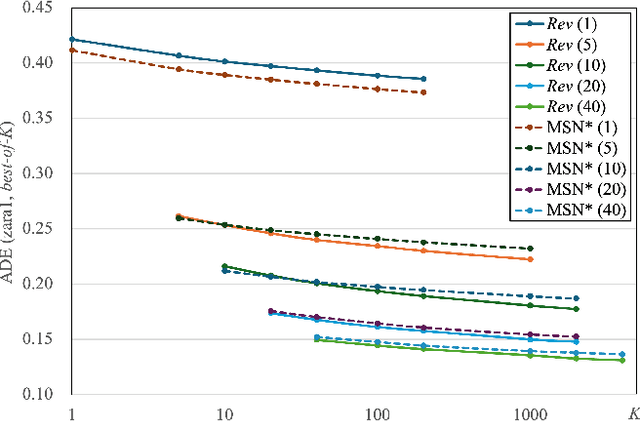
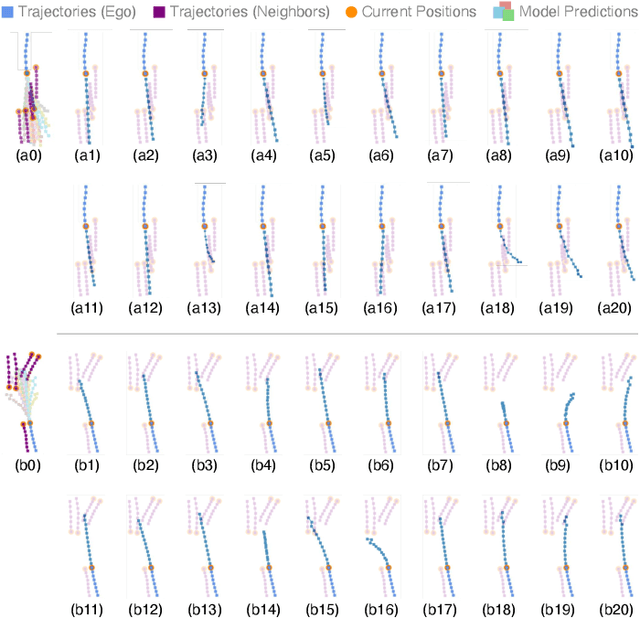
Abstract:Bridging the past to the future, connecting agents both spatially and temporally, lies at the core of the trajectory prediction task. Despite great efforts, it remains challenging to explicitly learn and predict latencies, the temporal delays with which agents respond to different trajectory-changing events and adjust their future paths, whether on their own or interactively. Different agents may exhibit distinct latency preferences for noticing, processing, and reacting to any specific trajectory-changing event. The lack of consideration of such latencies may undermine the causal continuity of the forecasting system and also lead to implausible or unintended trajectories. Inspired by the reverberation curves in acoustics, we propose a new reverberation transform and the corresponding Reverberation (short for Rev) trajectory prediction model, which simulates and predicts different latency preferences of each agent as well as their stochasticity by using two explicit and learnable reverberation kernels, allowing for the controllable trajectory prediction based on these forecasted latencies. Experiments on multiple datasets, whether pedestrians or vehicles, demonstrate that Rev achieves competitive accuracy while revealing interpretable latency dynamics across agents and scenarios. Qualitative analyses further verify the properties of the proposed reverberation transform, highlighting its potential as a general latency modeling approach.
Prototype-Guided Curriculum Learning for Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:In Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL), embedding-based methods enable knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes by learning a visual-semantic mapping from seen-class images to class-level semantic prototypes (e.g., attributes). However, these semantic prototypes are manually defined and may introduce noisy supervision for two main reasons: (i) instance-level mismatch: variations in perspective, occlusion, and annotation bias will cause discrepancies between individual sample and the class-level semantic prototypes; and (ii) class-level imprecision: the manually defined semantic prototypes may not accurately reflect the true semantics of the class. Consequently, the visual-semantic mapping will be misled, reducing the effectiveness of knowledge transfer to unseen classes. In this work, we propose a prototype-guided curriculum learning framework (dubbed as CLZSL), which mitigates instance-level mismatches through a Prototype-Guided Curriculum Learning (PCL) module and addresses class-level imprecision via a Prototype Update (PUP) module. Specifically, the PCL module prioritizes samples with high cosine similarity between their visual mappings and the class-level semantic prototypes, and progressively advances to less-aligned samples, thereby reducing the interference of instance-level mismatches to achieve accurate visual-semantic mapping. Besides, the PUP module dynamically updates the class-level semantic prototypes by leveraging the visual mappings learned from instances, thereby reducing class-level imprecision and further improving the visual-semantic mapping. Experiments were conducted on standard benchmark datasets-AWA2, SUN, and CUB-to verify the effectiveness of our method.
Toward Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection: Benchmarks and Method
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) primarily relies on semantic or instance segmentation methods. While these methods have made significant advancements in identifying the contours of camouflaged objects, they may be inefficient or cost-effective for tasks that only require the specific location of the object. Object detection algorithms offer an optimized solution for Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection (RCOD) in such cases. However, detecting camouflaged objects remains a formidable challenge due to the high degree of similarity between the features of the objects and their backgrounds. Unlike segmentation methods that perform pixel-wise comparisons to differentiate between foreground and background, object detectors omit this analysis, further aggravating the challenge. To solve this problem, we propose a camouflage-aware feature refinement (CAFR) strategy. Since camouflaged objects are not rare categories, CAFR fully utilizes a clear perception of the current object within the prior knowledge of large models to assist detectors in deeply understanding the distinctions between background and foreground. Specifically, in CAFR, we introduce the Adaptive Gradient Propagation (AGP) module that fine-tunes all feature extractor layers in large detection models to fully refine class-specific features from camouflaged contexts. We then design the Sparse Feature Refinement (SFR) module that optimizes the transformer-based feature extractor to focus primarily on capturing class-specific features in camouflaged scenarios. To facilitate the assessment of RCOD tasks, we manually annotate the labels required for detection on three existing segmentation COD datasets, creating a new benchmark for RCOD tasks. Code and datasets are available at: https://github.com/zhimengXin/RCOD.
Discriminative Image Generation with Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Learning
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Generative Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) methods synthesize class-related features based on predefined class semantic prototypes, showcasing superior performance. However, this feature generation paradigm falls short of providing interpretable insights. In addition, existing approaches rely on semantic prototypes annotated by human experts, which exhibit a significant limitation in their scalability to generalized scenes. To overcome these deficiencies, a natural solution is to generate images for unseen classes using text prompts. To this end, We present DIG-ZSL, a novel Discriminative Image Generation framework for Zero-Shot Learning. Specifically, to ensure the generation of discriminative images for training an effective ZSL classifier, we learn a discriminative class token (DCT) for each unseen class under the guidance of a pre-trained category discrimination model (CDM). Harnessing DCTs, we can generate diverse and high-quality images, which serve as informative unseen samples for ZSL tasks. In this paper, the extensive experiments and visualizations on four datasets show that our DIG-ZSL: (1) generates diverse and high-quality images, (2) outperforms previous state-of-the-art nonhuman-annotated semantic prototype-based methods by a large margin, and (3) achieves comparable or better performance than baselines that leverage human-annotated semantic prototypes. The codes will be made available upon acceptance of the paper.
Resonance: Learning to Predict Social-Aware Pedestrian Trajectories as Co-Vibrations
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Learning to forecast the trajectories of intelligent agents like pedestrians has caught more researchers' attention. Despite researchers' efforts, it remains a challenge to accurately account for social interactions among agents when forecasting, and in particular, to simulate such social modifications to future trajectories in an explainable and decoupled way. Inspired by the resonance phenomenon of vibration systems, we propose the Resonance (short for Re) model to forecast pedestrian trajectories as co-vibrations, and regard that social interactions are associated with spectral properties of agents' trajectories. It forecasts future trajectories as three distinct vibration terms to represent agents' future plans from different perspectives in a decoupled way. Also, agents' social interactions and how they modify scheduled trajectories will be considered in a resonance-like manner by learning the similarities of their trajectory spectrums. Experiments on multiple datasets, whether pedestrian or vehicle, have verified the usefulness of our method both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Who Walks With You Matters: Perceiving Social Interactions with Groups for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Dec 03, 2024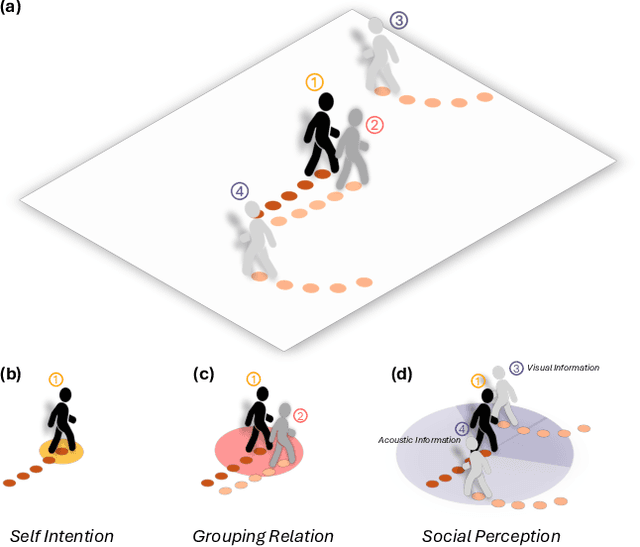
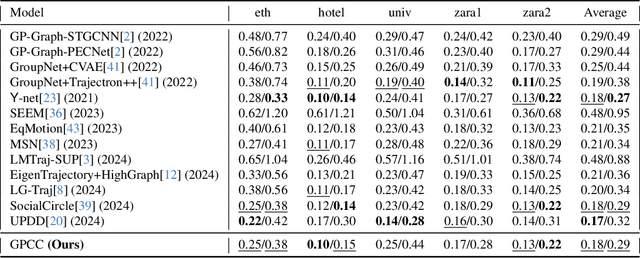
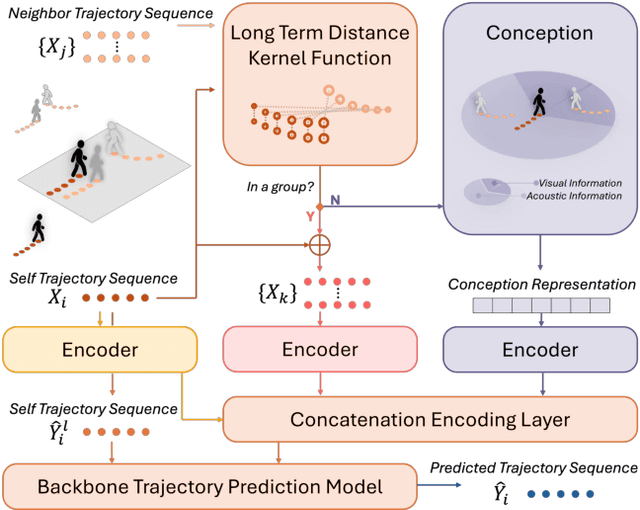
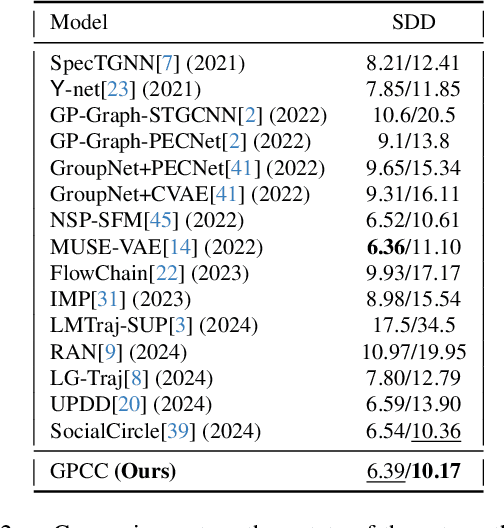
Abstract:Understanding and anticipating human movement has become more critical and challenging in diverse applications such as autonomous driving and surveillance. The complex interactions brought by different relations between agents are a crucial reason that poses challenges to this task. Researchers have put much effort into designing a system using rule-based or data-based models to extract and validate the patterns between pedestrian trajectories and these interactions, which has not been adequately addressed yet. Inspired by how humans perceive social interactions with different level of relations to themself, this work proposes the GrouP ConCeption (short for GPCC) model composed of the Group method, which categorizes nearby agents into either group members or non-group members based on a long-term distance kernel function, and the Conception module, which perceives both visual and acoustic information surrounding the target agent. Evaluated across multiple datasets, the GPCC model demonstrates significant improvements in trajectory prediction accuracy, validating its effectiveness in modeling both social and individual dynamics. The qualitative analysis also indicates that the GPCC framework successfully leverages grouping and perception cues human-like intuitively to validate the proposed model's explainability in pedestrian trajectory forecasting.
Generalized Sparse Additive Model with Unknown Link Function
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Generalized additive models (GAM) have been successfully applied to high dimensional data analysis. However, most existing methods cannot simultaneously estimate the link function, the component functions and the variable interaction. To alleviate this problem, we propose a new sparse additive model, named generalized sparse additive model with unknown link function (GSAMUL), in which the component functions are estimated by B-spline basis and the unknown link function is estimated by a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network. Furthermore, $\ell_{2,1}$-norm regularizer is used for variable selection. The proposed GSAMUL can realize both variable selection and hidden interaction. We integrate this estimation into a bilevel optimization problem, where the data is split into training set and validation set. In theory, we provide the guarantees about the convergence of the approximate procedure. In applications, experimental evaluations on both synthetic and real world data sets consistently validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
What Happens Without Background? Constructing Foreground-Only Data for Fine-Grained Tasks
Aug 04, 2024



Abstract:Fine-grained recognition, a pivotal task in visual signal processing, aims to distinguish between similar subclasses based on discriminative information present in samples. However, prevailing methods often erroneously focus on background areas, neglecting the capture of genuinely effective discriminative information from the subject, thus impeding practical application. To facilitate research into the impact of background noise on models and enhance their ability to concentrate on the subject's discriminative features, we propose an engineered pipeline that leverages the capabilities of SAM and Detic to create fine-grained datasets with only foreground subjects, devoid of background. Extensive cross-experiments validate this approach as a preprocessing step prior to training, enhancing algorithmic performance and holding potential for further modal expansion of the data.
Optimal Kernel Choice for Score Function-based Causal Discovery
Jul 14, 2024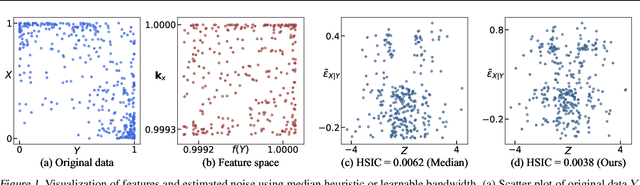

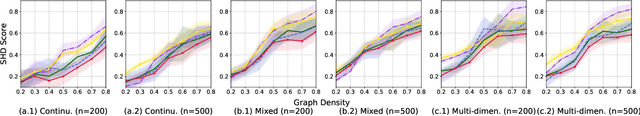
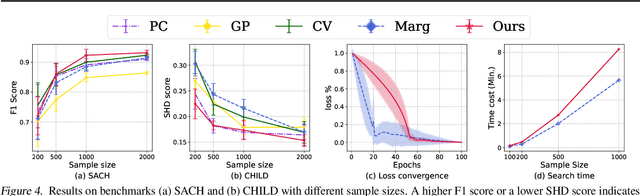
Abstract:Score-based methods have demonstrated their effectiveness in discovering causal relationships by scoring different causal structures based on their goodness of fit to the data. Recently, Huang et al. proposed a generalized score function that can handle general data distributions and causal relationships by modeling the relations in reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS). The selection of an appropriate kernel within this score function is crucial for accurately characterizing causal relationships and ensuring precise causal discovery. However, the current method involves manual heuristic selection of kernel parameters, making the process tedious and less likely to ensure optimality. In this paper, we propose a kernel selection method within the generalized score function that automatically selects the optimal kernel that best fits the data. Specifically, we model the generative process of the variables involved in each step of the causal graph search procedure as a mixture of independent noise variables. Based on this model, we derive an automatic kernel selection method by maximizing the marginal likelihood of the variables involved in each search step. We conduct experiments on both synthetic data and real-world benchmarks, and the results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms heuristic kernel selection methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge