Ziqian Zou
Reverberation: Learning the Latencies Before Forecasting Trajectories
Nov 14, 2025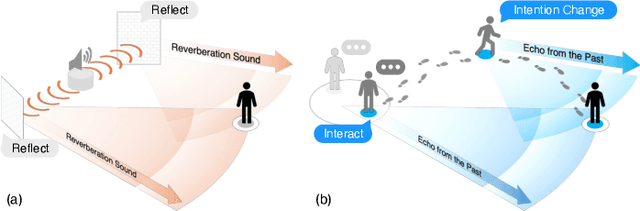
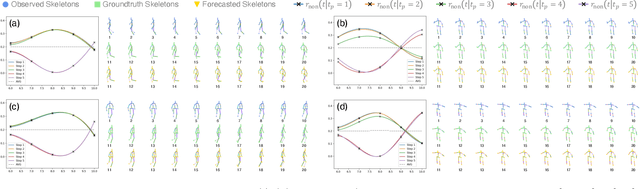
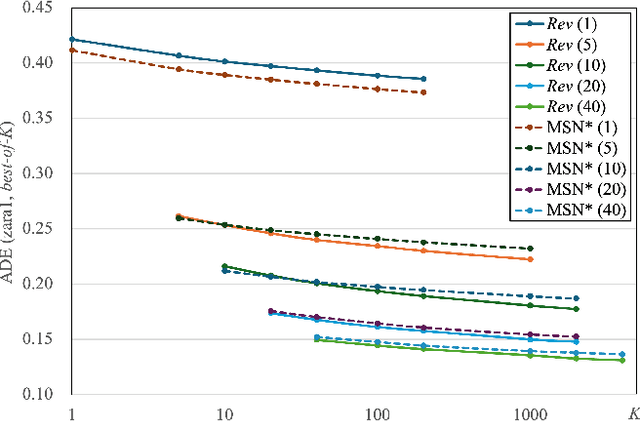
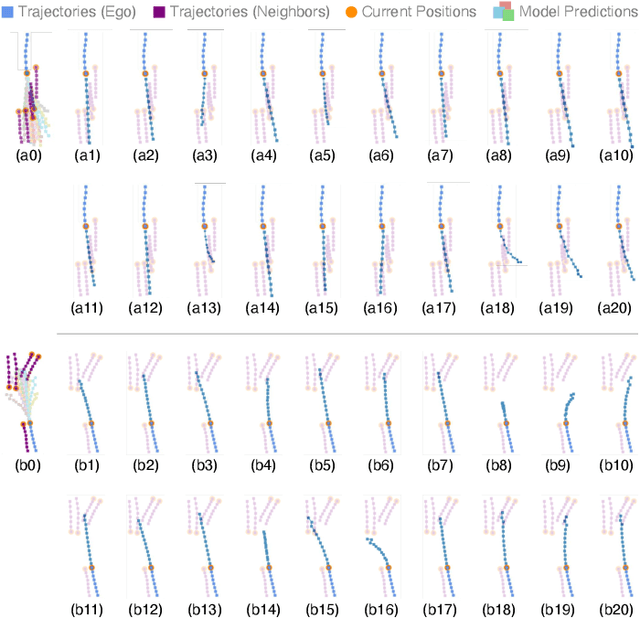
Abstract:Bridging the past to the future, connecting agents both spatially and temporally, lies at the core of the trajectory prediction task. Despite great efforts, it remains challenging to explicitly learn and predict latencies, the temporal delays with which agents respond to different trajectory-changing events and adjust their future paths, whether on their own or interactively. Different agents may exhibit distinct latency preferences for noticing, processing, and reacting to any specific trajectory-changing event. The lack of consideration of such latencies may undermine the causal continuity of the forecasting system and also lead to implausible or unintended trajectories. Inspired by the reverberation curves in acoustics, we propose a new reverberation transform and the corresponding Reverberation (short for Rev) trajectory prediction model, which simulates and predicts different latency preferences of each agent as well as their stochasticity by using two explicit and learnable reverberation kernels, allowing for the controllable trajectory prediction based on these forecasted latencies. Experiments on multiple datasets, whether pedestrians or vehicles, demonstrate that Rev achieves competitive accuracy while revealing interpretable latency dynamics across agents and scenarios. Qualitative analyses further verify the properties of the proposed reverberation transform, highlighting its potential as a general latency modeling approach.
Who Walks With You Matters: Perceiving Social Interactions with Groups for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Dec 03, 2024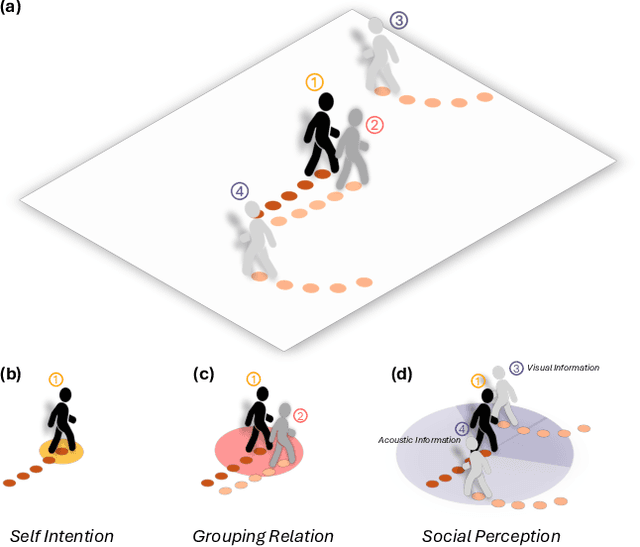
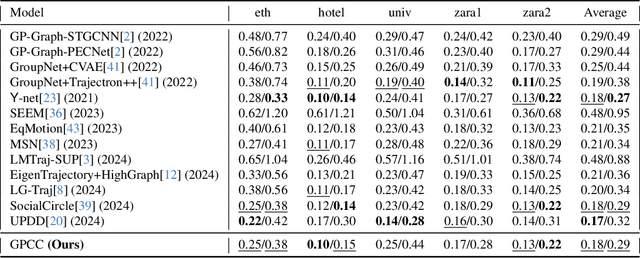
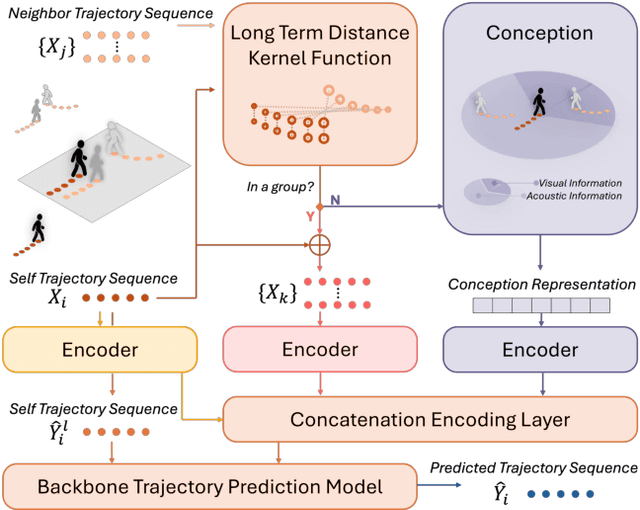
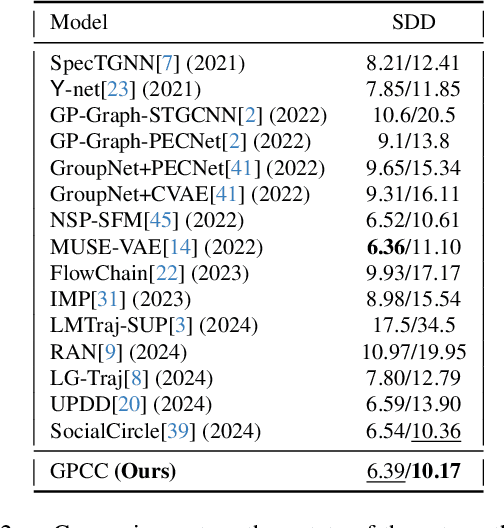
Abstract:Understanding and anticipating human movement has become more critical and challenging in diverse applications such as autonomous driving and surveillance. The complex interactions brought by different relations between agents are a crucial reason that poses challenges to this task. Researchers have put much effort into designing a system using rule-based or data-based models to extract and validate the patterns between pedestrian trajectories and these interactions, which has not been adequately addressed yet. Inspired by how humans perceive social interactions with different level of relations to themself, this work proposes the GrouP ConCeption (short for GPCC) model composed of the Group method, which categorizes nearby agents into either group members or non-group members based on a long-term distance kernel function, and the Conception module, which perceives both visual and acoustic information surrounding the target agent. Evaluated across multiple datasets, the GPCC model demonstrates significant improvements in trajectory prediction accuracy, validating its effectiveness in modeling both social and individual dynamics. The qualitative analysis also indicates that the GPCC framework successfully leverages grouping and perception cues human-like intuitively to validate the proposed model's explainability in pedestrian trajectory forecasting.
Resonance: Learning to Predict Social-Aware Pedestrian Trajectories as Co-Vibrations
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Learning to forecast the trajectories of intelligent agents like pedestrians has caught more researchers' attention. Despite researchers' efforts, it remains a challenge to accurately account for social interactions among agents when forecasting, and in particular, to simulate such social modifications to future trajectories in an explainable and decoupled way. Inspired by the resonance phenomenon of vibration systems, we propose the Resonance (short for Re) model to forecast pedestrian trajectories as co-vibrations, and regard that social interactions are associated with spectral properties of agents' trajectories. It forecasts future trajectories as three distinct vibration terms to represent agents' future plans from different perspectives in a decoupled way. Also, agents' social interactions and how they modify scheduled trajectories will be considered in a resonance-like manner by learning the similarities of their trajectory spectrums. Experiments on multiple datasets, whether pedestrian or vehicle, have verified the usefulness of our method both quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge