Zhongyi Han
DVLA-RL: Dual-Level Vision-Language Alignment with Reinforcement Learning Gating for Few-Shot Learning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Few-shot learning (FSL) aims to generalize to novel categories with only a few samples. Recent approaches incorporate large language models (LLMs) to enrich visual representations with semantic embeddings derived from class names. However, they overlook progressive and adaptive alignment between vision and language from low-level to high-level semantics, resulting in limited semantic gains. To address these challenges, we propose Dual-level Vision-Language Alignment with Reinforcement Learning gating (DVLA-RL), which consists of Dual-level Semantic Construction (DSC) and RL-gated Attention (RLA). Specifically, DSC conditions LLMs on both class names and support samples to generate discriminative attributes, progressively selects the most relevant ones, and then synthesizes them into coherent class descriptions. This process provides complementary low-level attributes and high-level descriptions, enabling both fine-grained grounding and holistic class understanding. To dynamically integrate dual-level semantics along with the visual network layers, RLA formulates cross-modal fusion as a sequential decision process. A lightweight policy trained with episodic REINFORCE adaptively adjusts the contributions of self-attention and cross-attention to integrate textual and visual tokens. As a result, shallow layers refine local attributes and deep layers emphasize global semantics, enabling more precise cross-modal alignment. This achieves class-specific discrimination and generalized representations with merely a few support samples. DVLA-RL achieves new state-of-the-art performance across nine benchmarks in three diverse FSL scenarios.
Revisiting Data Scaling Law for Medical Segmentation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:The population loss of trained deep neural networks often exhibits power law scaling with the size of the training dataset, guiding significant performance advancements in deep learning applications. In this study, we focus on the scaling relationship with data size in the context of medical anatomical segmentation, a domain that remains underexplored. We analyze scaling laws for anatomical segmentation across 15 semantic tasks and 4 imaging modalities, demonstrating that larger datasets significantly improve segmentation performance, following similar scaling trends. Motivated by the topological isomorphism in images sharing anatomical structures, we evaluate the impact of deformation-guided augmentation strategies on data scaling laws, specifically random elastic deformation and registration-guided deformation. We also propose a novel, scalable image augmentation approach that generates diffeomorphic mappings from geodesic subspace based on image registration to introduce realistic deformation. Our experimental results demonstrate that both registered and generated deformation-based augmentation considerably enhance data utilization efficiency. The proposed generated deformation method notably achieves superior performance and accelerated convergence, surpassing standard power law scaling trends without requiring additional data. Overall, this work provides insights into the understanding of segmentation scalability and topological variation impact in medical imaging, thereby leading to more efficient model development with reduced annotation and computational costs.
Unveiling the Superior Paradigm: A Comparative Study of Source-Free Domain Adaptation and Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Nov 24, 2024Abstract:In domain adaptation, there are two popular paradigms: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA), which aligns distributions using source data, and Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA), which leverages pre-trained source models without accessing source data. Evaluating the superiority of UDA versus SFDA is an open and timely question with significant implications for deploying adaptive algorithms in practical applications. In this study, we demonstrate through predictive coding theory and extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets that SFDA generally outperforms UDA in real-world scenarios. Specifically, SFDA offers advantages in time efficiency, storage requirements, targeted learning objectives, reduced risk of negative transfer, and increased robustness against overfitting. Notably, SFDA is particularly effective in mitigating negative transfer when there are substantial distribution discrepancies between source and target domains. Additionally, we introduce a novel data-model fusion scenario, where data sharing among stakeholders varies (e.g., some provide raw data while others provide only models), and reveal that traditional UDA and SFDA methods do not fully exploit their potential in this context. To address this limitation and capitalize on the strengths of SFDA, we propose a novel weight estimation method that effectively integrates available source data into multi-SFDA (MSFDA) approaches, thereby enhancing model performance within this scenario. This work provides a thorough analysis of UDA versus SFDA and advances a practical approach to model adaptation across diverse real-world environments.
Improving Representation of High-frequency Components for Medical Foundation Models
Jul 26, 2024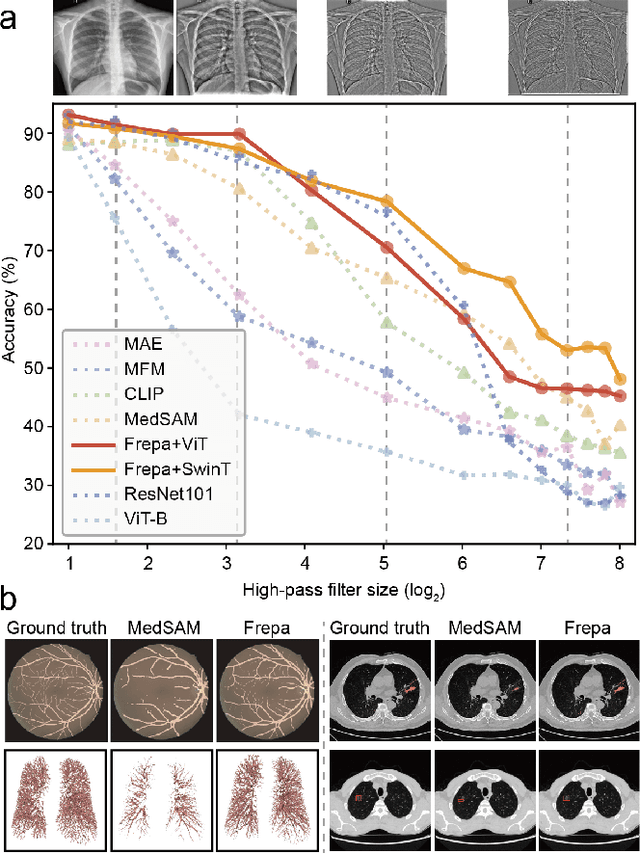

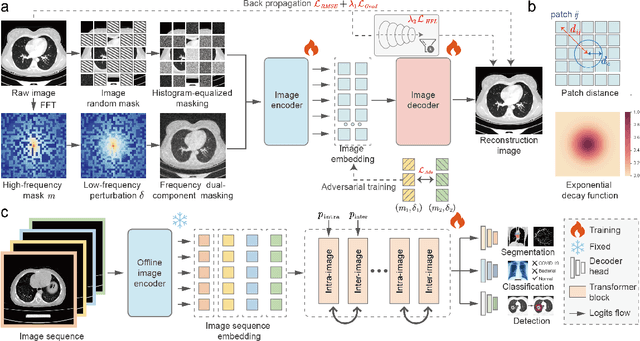

Abstract:Foundation models have recently attracted significant attention for their impressive generalizability across diverse downstream tasks. However, these models are demonstrated to exhibit great limitations in representing high-frequency components and fine-grained details. In many medical imaging tasks, the precise representation of such information is crucial due to the inherently intricate anatomical structures, sub-visual features, and complex boundaries involved. Consequently, the limited representation of prevalent foundation models can result in significant performance degradation or even failure in these tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a novel pretraining strategy, named Frequency-advanced Representation Autoencoder (Frepa). Through high-frequency masking and low-frequency perturbation combined with adversarial learning, Frepa encourages the encoder to effectively represent and preserve high-frequency components in the image embeddings. Additionally, we introduce an innovative histogram-equalized image masking strategy, extending the Masked Autoencoder approach beyond ViT to other architectures such as Swin Transformer and convolutional networks. We develop Frepa across nine medical modalities and validate it on 32 downstream tasks for both 2D images and 3D volume data. Without fine-tuning, Frepa can outperform other self-supervised pretraining methods and, in some cases, even surpasses task-specific trained models. This improvement is particularly significant for tasks involving fine-grained details, such as achieving up to a +15% increase in DSC for retina vessel segmentation and a +7% increase in IoU for lung nodule detection. Further experiments quantitatively reveal that Frepa enables superior high-frequency representations and preservation in the embeddings, underscoring its potential for developing more generalized and universal medical image foundation models.
SkinCAP: A Multi-modal Dermatology Dataset Annotated with Rich Medical Captions
May 28, 2024



Abstract:With the widespread application of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning (DL) and vision-based large language models (VLLMs), in skin disease diagnosis, the need for interpretability becomes crucial. However, existing dermatology datasets are limited in their inclusion of concept-level meta-labels, and none offer rich medical descriptions in natural language. This deficiency impedes the advancement of LLM-based methods in dermatological diagnosis. To address this gap and provide a meticulously annotated dermatology dataset with comprehensive natural language descriptions, we introduce SkinCAP: a multi-modal dermatology dataset annotated with rich medical captions. SkinCAP comprises 4,000 images sourced from the Fitzpatrick 17k skin disease dataset and the Diverse Dermatology Images dataset, annotated by board-certified dermatologists to provide extensive medical descriptions and captions. Notably, SkinCAP represents the world's first such dataset and is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/joshuachou/SkinCAP.
Can We Treat Noisy Labels as Accurate?
May 21, 2024



Abstract:Noisy labels significantly hinder the accuracy and generalization of machine learning models, particularly due to ambiguous instance features. Traditional techniques that attempt to correct noisy labels directly, such as those using transition matrices, often fail to address the inherent complexities of the problem sufficiently. In this paper, we introduce EchoAlign, a transformative paradigm shift in learning from noisy labels. Instead of focusing on label correction, EchoAlign treats noisy labels ($\tilde{Y}$) as accurate and modifies corresponding instance features ($X$) to achieve better alignment with $\tilde{Y}$. EchoAlign's core components are (1) EchoMod: Employing controllable generative models, EchoMod precisely modifies instances while maintaining their intrinsic characteristics and ensuring alignment with the noisy labels. (2) EchoSelect: Instance modification inevitably introduces distribution shifts between training and test sets. EchoSelect maintains a significant portion of clean original instances to mitigate these shifts. It leverages the distinct feature similarity distributions between original and modified instances as a robust tool for accurate sample selection. This integrated approach yields remarkable results. In environments with 30% instance-dependent noise, even at 99% selection accuracy, EchoSelect retains nearly twice the number of samples compared to the previous best method. Notably, on three datasets, EchoAlign surpasses previous state-of-the-art techniques with a substantial improvement.
Adapting Large Multimodal Models to Distribution Shifts: The Role of In-Context Learning
May 20, 2024Abstract:Recent studies indicate that large multimodal models (LMMs) are highly robust against natural distribution shifts, often surpassing previous baselines. Despite this, domain-specific adaptation is still necessary, particularly in specialized areas like healthcare. Due to the impracticality of fine-tuning LMMs given their vast parameter space, this work investigates in-context learning (ICL) as an effective alternative for enhancing LMMs' adaptability. We find that the success of ICL heavily relies on the choice of demonstration, mirroring challenges seen in large language models but introducing unique complexities for LMMs facing distribution shifts. Our study addresses this by evaluating an unsupervised ICL method, TopKNearestPR, which selects in-context examples through a nearest example search based on feature similarity. We uncover that its effectiveness is limited by the deficiencies of pre-trained vision encoders under distribution shift scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose InvariantSelectPR, a novel method leveraging Class-conditioned Contrastive Invariance (CCI) for more robust demonstration selection. Specifically, CCI enhances pre-trained vision encoders by improving their discriminative capabilities across different classes and ensuring invariance to domain-specific variations. This enhancement allows the encoders to effectively identify and retrieve the most informative examples, which are then used to guide LMMs in adapting to new query samples under varying distributions. Our experiments show that InvariantSelectPR substantially improves the adaptability of LMMs, achieving significant performance gains on benchmark datasets, with a 34.2%$\uparrow$ accuracy increase in 7-shot on Camelyon17 and 16.9%$\uparrow$ increase in 7-shot on HAM10000 compared to the baseline zero-shot performance.
CLIP-driven Outliers Synthesis for few-shot OOD detection
Mar 30, 2024
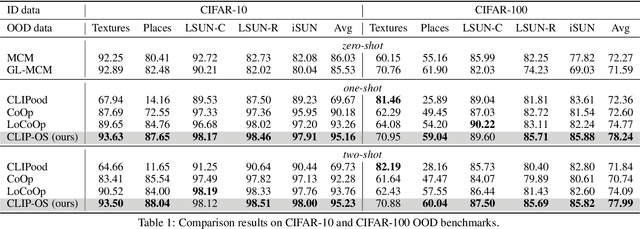
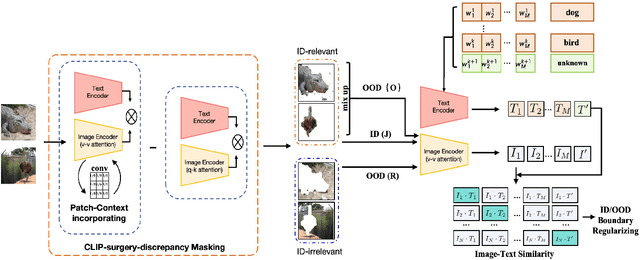
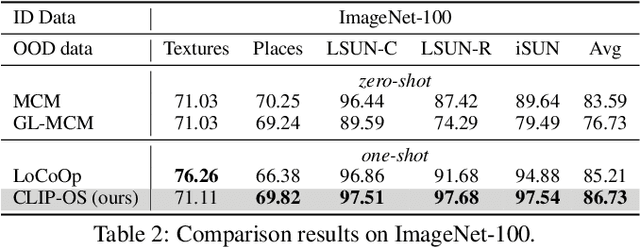
Abstract:Few-shot OOD detection focuses on recognizing out-of-distribution (OOD) images that belong to classes unseen during training, with the use of only a small number of labeled in-distribution (ID) images. Up to now, a mainstream strategy is based on large-scale vision-language models, such as CLIP. However, these methods overlook a crucial issue: the lack of reliable OOD supervision information, which can lead to biased boundaries between in-distribution (ID) and OOD. To tackle this problem, we propose CLIP-driven Outliers Synthesis~(CLIP-OS). Firstly, CLIP-OS enhances patch-level features' perception by newly proposed patch uniform convolution, and adaptively obtains the proportion of ID-relevant information by employing CLIP-surgery-discrepancy, thus achieving separation between ID-relevant and ID-irrelevant. Next, CLIP-OS synthesizes reliable OOD data by mixing up ID-relevant features from different classes to provide OOD supervision information. Afterward, CLIP-OS leverages synthetic OOD samples by unknown-aware prompt learning to enhance the separability of ID and OOD. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that CLIP-OS achieves superior few-shot OOD detection capability.
HCVP: Leveraging Hierarchical Contrastive Visual Prompt for Domain Generalization
Jan 18, 2024



Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) endeavors to create machine learning models that excel in unseen scenarios by learning invariant features. In DG, the prevalent practice of constraining models to a fixed structure or uniform parameterization to encapsulate invariant features can inadvertently blend specific aspects. Such an approach struggles with nuanced differentiation of inter-domain variations and may exhibit bias towards certain domains, hindering the precise learning of domain-invariant features. Recognizing this, we introduce a novel method designed to supplement the model with domain-level and task-specific characteristics. This approach aims to guide the model in more effectively separating invariant features from specific characteristics, thereby boosting the generalization. Building on the emerging trend of visual prompts in the DG paradigm, our work introduces the novel \textbf{H}ierarchical \textbf{C}ontrastive \textbf{V}isual \textbf{P}rompt (HCVP) methodology. This represents a significant advancement in the field, setting itself apart with a unique generative approach to prompts, alongside an explicit model structure and specialized loss functions. Differing from traditional visual prompts that are often shared across entire datasets, HCVP utilizes a hierarchical prompt generation network enhanced by prompt contrastive learning. These generative prompts are instance-dependent, catering to the unique characteristics inherent to different domains and tasks. Additionally, we devise a prompt modulation network that serves as a bridge, effectively incorporating the generated visual prompts into the vision transformer backbone. Experiments conducted on five DG datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of HCVP, outperforming both established DG algorithms and adaptation protocols.
How Well Does GPT-4V Adapt to Distribution Shifts? A Preliminary Investigation
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:In machine learning, generalization against distribution shifts -- where deployment conditions diverge from the training scenarios -- is crucial, particularly in fields like climate modeling, biomedicine, and autonomous driving. The emergence of foundation models, distinguished by their extensive pretraining and task versatility, has led to an increased interest in their adaptability to distribution shifts. GPT-4V(ision) acts as the most advanced publicly accessible multimodal foundation model, with extensive applications across various domains, including anomaly detection, video understanding, image generation, and medical diagnosis. However, its robustness against data distributions remains largely underexplored. Addressing this gap, this study rigorously evaluates GPT-4V's adaptability and generalization capabilities in dynamic environments, benchmarking against prominent models like CLIP and LLaVA. We delve into GPT-4V's zero-shot generalization across 13 diverse datasets spanning natural, medical, and molecular domains. We further investigate its adaptability to controlled data perturbations and examine the efficacy of in-context learning as a tool to enhance its adaptation. Our findings delineate GPT-4V's capability boundaries in distribution shifts, shedding light on its strengths and limitations across various scenarios. Importantly, this investigation contributes to our understanding of how AI foundation models generalize to distribution shifts, offering pivotal insights into their adaptability and robustness. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/jameszhou-gl/gpt-4v-distribution-shift.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge