CLIP-driven Outliers Synthesis for few-shot OOD detection
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2024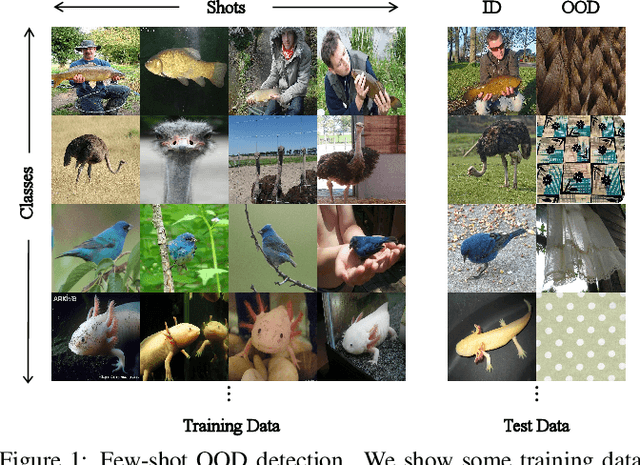
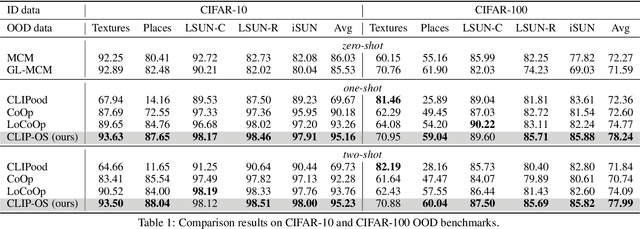
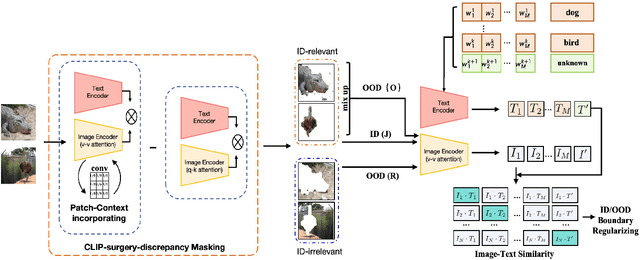
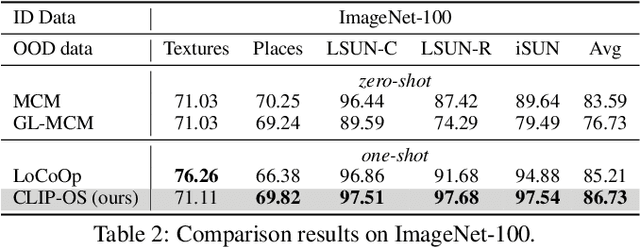
Few-shot OOD detection focuses on recognizing out-of-distribution (OOD) images that belong to classes unseen during training, with the use of only a small number of labeled in-distribution (ID) images. Up to now, a mainstream strategy is based on large-scale vision-language models, such as CLIP. However, these methods overlook a crucial issue: the lack of reliable OOD supervision information, which can lead to biased boundaries between in-distribution (ID) and OOD. To tackle this problem, we propose CLIP-driven Outliers Synthesis~(CLIP-OS). Firstly, CLIP-OS enhances patch-level features' perception by newly proposed patch uniform convolution, and adaptively obtains the proportion of ID-relevant information by employing CLIP-surgery-discrepancy, thus achieving separation between ID-relevant and ID-irrelevant. Next, CLIP-OS synthesizes reliable OOD data by mixing up ID-relevant features from different classes to provide OOD supervision information. Afterward, CLIP-OS leverages synthetic OOD samples by unknown-aware prompt learning to enhance the separability of ID and OOD. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that CLIP-OS achieves superior few-shot OOD detection capability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge