Longxi Zhou
Improving Representation of High-frequency Components for Medical Foundation Models
Jul 26, 2024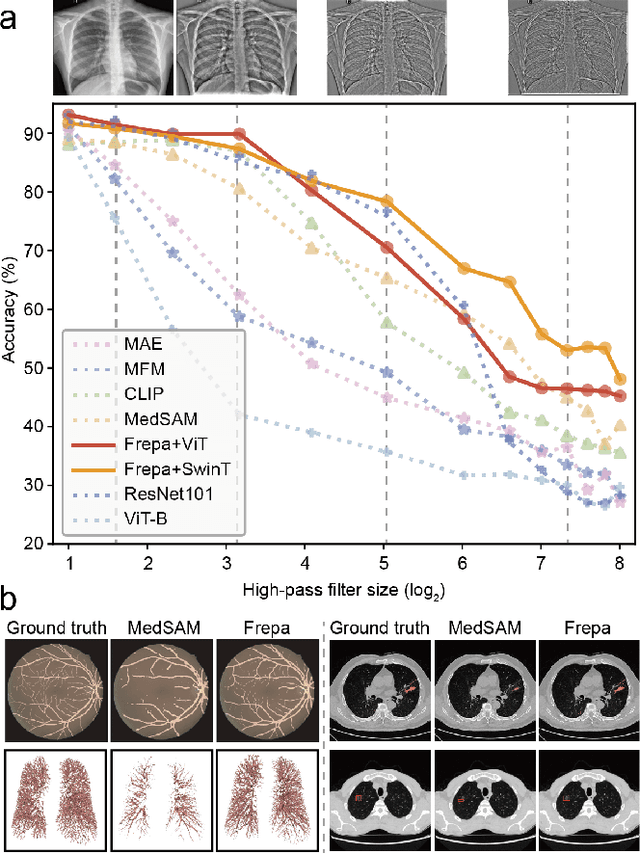

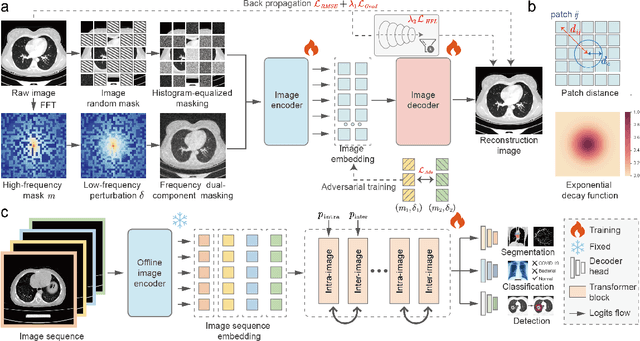

Abstract:Foundation models have recently attracted significant attention for their impressive generalizability across diverse downstream tasks. However, these models are demonstrated to exhibit great limitations in representing high-frequency components and fine-grained details. In many medical imaging tasks, the precise representation of such information is crucial due to the inherently intricate anatomical structures, sub-visual features, and complex boundaries involved. Consequently, the limited representation of prevalent foundation models can result in significant performance degradation or even failure in these tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a novel pretraining strategy, named Frequency-advanced Representation Autoencoder (Frepa). Through high-frequency masking and low-frequency perturbation combined with adversarial learning, Frepa encourages the encoder to effectively represent and preserve high-frequency components in the image embeddings. Additionally, we introduce an innovative histogram-equalized image masking strategy, extending the Masked Autoencoder approach beyond ViT to other architectures such as Swin Transformer and convolutional networks. We develop Frepa across nine medical modalities and validate it on 32 downstream tasks for both 2D images and 3D volume data. Without fine-tuning, Frepa can outperform other self-supervised pretraining methods and, in some cases, even surpasses task-specific trained models. This improvement is particularly significant for tasks involving fine-grained details, such as achieving up to a +15% increase in DSC for retina vessel segmentation and a +7% increase in IoU for lung nodule detection. Further experiments quantitatively reveal that Frepa enables superior high-frequency representations and preservation in the embeddings, underscoring its potential for developing more generalized and universal medical image foundation models.
Deep learning-driven pulmonary arteries and veins segmentation reveals demography-associated pulmonary vasculature anatomy
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:Pulmonary artery-vein segmentation is crucial for diagnosing pulmonary diseases and surgical planning, and is traditionally achieved by Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA). However, concerns regarding adverse health effects from contrast agents used in CTPA have constrained its clinical utility. In contrast, identifying arteries and veins using non-contrast CT, a conventional and low-cost clinical examination routine, has long been considered impossible. Here we propose a High-abundant Pulmonary Artery-vein Segmentation (HiPaS) framework achieving accurate artery-vein segmentation on both non-contrast CT and CTPA across various spatial resolutions. HiPaS first performs spatial normalization on raw CT scans via a super-resolution module, and then iteratively achieves segmentation results at different branch levels by utilizing the low-level vessel segmentation as a prior for high-level vessel segmentation. We trained and validated HiPaS on our established multi-centric dataset comprising 1,073 CT volumes with meticulous manual annotation. Both quantitative experiments and clinical evaluation demonstrated the superior performance of HiPaS, achieving a dice score of 91.8% and a sensitivity of 98.0%. Further experiments demonstrated the non-inferiority of HiPaS segmentation on non-contrast CT compared to segmentation on CTPA. Employing HiPaS, we have conducted an anatomical study of pulmonary vasculature on 10,613 participants in China (five sites), discovering a new association between pulmonary vessel abundance and sex and age: vessel abundance is significantly higher in females than in males, and slightly decreases with age, under the controlling of lung volumes (p < 0.0001). HiPaS realizing accurate artery-vein segmentation delineates a promising avenue for clinical diagnosis and understanding pulmonary physiology in a non-invasive manner.
Personalized and privacy-preserving federated heterogeneous medical image analysis with PPPML-HMI
Feb 20, 2023Abstract:Heterogeneous data is endemic due to the use of diverse models and settings of devices by hospitals in the field of medical imaging. However, there are few open-source frameworks for federated heterogeneous medical image analysis with personalization and privacy protection simultaneously without the demand to modify the existing model structures or to share any private data. In this paper, we proposed PPPML-HMI, an open-source learning paradigm for personalized and privacy-preserving federated heterogeneous medical image analysis. To our best knowledge, personalization and privacy protection were achieved simultaneously for the first time under the federated scenario by integrating the PerFedAvg algorithm and designing our novel cyclic secure aggregation with the homomorphic encryption algorithm. To show the utility of PPPML-HMI, we applied it to a simulated classification task namely the classification of healthy people and patients from the RAD-ChestCT Dataset, and one real-world segmentation task namely the segmentation of lung infections from COVID-19 CT scans. For the real-world task, PPPML-HMI achieved $\sim$5\% higher Dice score on average compared to conventional FL under the heterogeneous scenario. Meanwhile, we applied the improved deep leakage from gradients to simulate adversarial attacks and showed the solid privacy-preserving capability of PPPML-HMI. By applying PPPML-HMI to both tasks with different neural networks, a varied number of users, and sample sizes, we further demonstrated the strong robustness of PPPML-HMI.
Audit to Forget: A Unified Method to Revoke Patients' Private Data in Intelligent Healthcare
Feb 20, 2023Abstract:Revoking personal private data is one of the basic human rights, which has already been sheltered by several privacy-preserving laws in many countries. However, with the development of data science, machine learning and deep learning techniques, this right is usually neglected or violated as more and more patients' data are being collected and used for model training, especially in intelligent healthcare, thus making intelligent healthcare a sector where technology must meet the law, regulations, and privacy principles to ensure that the innovation is for the common good. In order to secure patients' right to be forgotten, we proposed a novel solution by using auditing to guide the forgetting process, where auditing means determining whether a dataset has been used to train the model and forgetting requires the information of a query dataset to be forgotten from the target model. We unified these two tasks by introducing a new approach called knowledge purification. To implement our solution, we developed AFS, a unified open-source software, which is able to evaluate and revoke patients' private data from pre-trained deep learning models. We demonstrated the generality of AFS by applying it to four tasks on different datasets with various data sizes and architectures of deep learning networks. The software is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/JoshuaChou2018/AFS}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge