Xiaonan He
Reward-Driven Interaction: Enhancing Proactive Dialogue Agents through User Satisfaction Prediction
May 24, 2025Abstract:Reward-driven proactive dialogue agents require precise estimation of user satisfaction as an intrinsic reward signal to determine optimal interaction strategies. Specifically, this framework triggers clarification questions when detecting potential user dissatisfaction during interactions in the industrial dialogue system. Traditional works typically rely on training a neural network model based on weak labels which are generated by a simple model trained on user actions after current turn. However, existing methods suffer from two critical limitations in real-world scenarios: (1) Noisy Reward Supervision, dependence on weak labels derived from post-hoc user actions introduces bias, particularly failing to capture satisfaction signals in ASR-error-induced utterances; (2) Long-Tail Feedback Sparsity, the power-law distribution of user queries causes reward prediction accuracy to drop in low-frequency domains. The noise in the weak labels and a power-law distribution of user utterances results in that the model is hard to learn good representation of user utterances and sessions. To address these limitations, we propose two auxiliary tasks to improve the representation learning of user utterances and sessions that enhance user satisfaction prediction. The first one is a contrastive self-supervised learning task, which helps the model learn the representation of rare user utterances and identify ASR errors. The second one is a domain-intent classification task, which aids the model in learning the representation of user sessions from long-tailed domains and improving the model's performance on such domains. The proposed method is evaluated on DuerOS, demonstrating significant improvements in the accuracy of error recognition on rare user utterances and long-tailed domains.
Leveraging Web-Crawled Data for High-Quality Fine-Tuning
Aug 15, 2024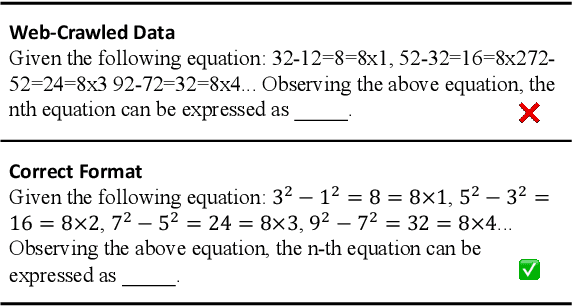


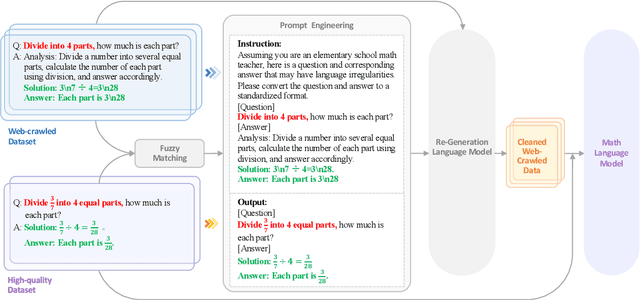
Abstract:Most large language models are fine-tuned using either expensive human-annotated data or GPT-4 generated data which cannot guarantee performance in certain domains. We argue that although the web-crawled data often has formatting errors causing semantic inaccuracies, it can still serve as a valuable source for high-quality supervised fine-tuning in specific domains without relying on advanced models like GPT-4. To this end, we create a paired training dataset automatically by aligning web-crawled data with a smaller set of high-quality data. By training a language model on this dataset, we can convert web data with irregular formats into high-quality ones. Our experiments show that training with the model-transformed data yields better results, surpassing training with only high-quality data by an average score of 9.4% in Chinese math problems. Additionally, our 7B model outperforms several open-source models larger than 32B and surpasses well-known closed-source models such as GPT-3.5, highlighting the efficacy of our approach.
SkinCAP: A Multi-modal Dermatology Dataset Annotated with Rich Medical Captions
May 28, 2024



Abstract:With the widespread application of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning (DL) and vision-based large language models (VLLMs), in skin disease diagnosis, the need for interpretability becomes crucial. However, existing dermatology datasets are limited in their inclusion of concept-level meta-labels, and none offer rich medical descriptions in natural language. This deficiency impedes the advancement of LLM-based methods in dermatological diagnosis. To address this gap and provide a meticulously annotated dermatology dataset with comprehensive natural language descriptions, we introduce SkinCAP: a multi-modal dermatology dataset annotated with rich medical captions. SkinCAP comprises 4,000 images sourced from the Fitzpatrick 17k skin disease dataset and the Diverse Dermatology Images dataset, annotated by board-certified dermatologists to provide extensive medical descriptions and captions. Notably, SkinCAP represents the world's first such dataset and is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/joshuachou/SkinCAP.
Dialogue State Distillation Network with Inter-Slot Contrastive Learning for Dialogue State Tracking
Feb 16, 2023



Abstract:In task-oriented dialogue systems, Dialogue State Tracking (DST) aims to extract users' intentions from the dialogue history. Currently, most existing approaches suffer from error propagation and are unable to dynamically select relevant information when utilizing previous dialogue states. Moreover, the relations between the updates of different slots provide vital clues for DST. However, the existing approaches rely only on predefined graphs to indirectly capture the relations. In this paper, we propose a Dialogue State Distillation Network (DSDN) to utilize relevant information of previous dialogue states and migrate the gap of utilization between training and testing. Thus, it can dynamically exploit previous dialogue states and avoid introducing error propagation simultaneously. Further, we propose an inter-slot contrastive learning loss to effectively capture the slot co-update relations from dialogue context. Experiments are conducted on the widely used MultiWOZ 2.0 and MultiWOZ 2.1 datasets. The experimental results show that our proposed model achieves the state-of-the-art performance for DST.
A Transformer-Based User Satisfaction Prediction for Proactive Interaction Mechanism in DuerOS
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:Recently, spoken dialogue systems have been widely deployed in a variety of applications, serving a huge number of end-users. A common issue is that the errors resulting from noisy utterances, semantic misunderstandings, or lack of knowledge make it hard for a real system to respond properly, possibly leading to an unsatisfactory user experience. To avoid such a case, we consider a proactive interaction mechanism where the system predicts the user satisfaction with the candidate response before giving it to the user. If the user is not likely to be satisfied according to the prediction, the system will ask the user a suitable question to determine the real intent of the user instead of providing the response directly. With such an interaction with the user, the system can give a better response to the user. Previous models that predict the user satisfaction are not applicable to DuerOS which is a large-scale commercial dialogue system. They are based on hand-crafted features and thus can hardly learn the complex patterns lying behind millions of conversations and temporal dependency in multiple turns of the conversation. Moreover, they are trained and evaluated on the benchmark datasets with adequate labels, which are expensive to obtain in a commercial dialogue system. To face these challenges, we propose a pipeline to predict the user satisfaction to help DuerOS decide whether to ask for clarification in each turn. Specifically, we propose to first generate a large number of weak labels and then train a transformer-based model to predict the user satisfaction with these weak labels. Empirically, we deploy and evaluate our model on DuerOS, and observe a 19% relative improvement on the accuracy of user satisfaction prediction and 2.3% relative improvement on user experience.
Inductive Matrix Completion Using Graph Autoencoder
Aug 25, 2021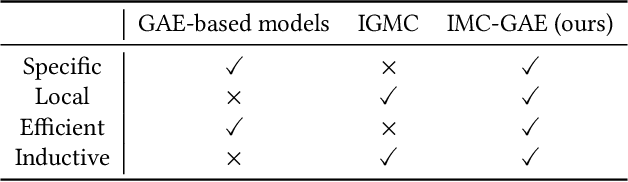
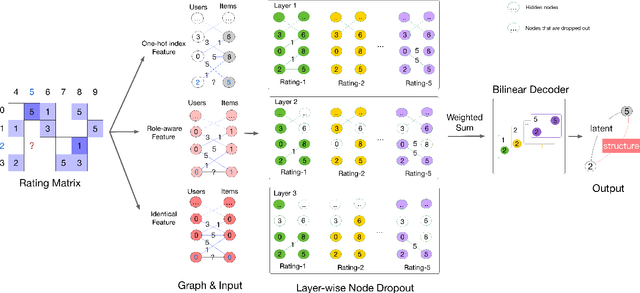

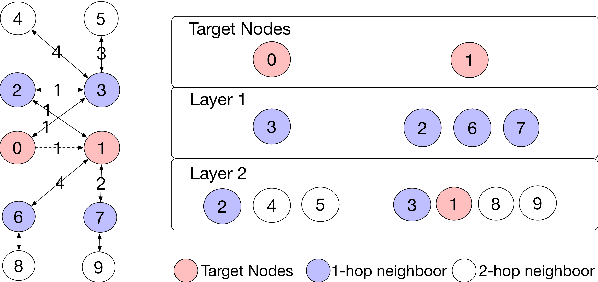
Abstract:Recently, the graph neural network (GNN) has shown great power in matrix completion by formulating a rating matrix as a bipartite graph and then predicting the link between the corresponding user and item nodes. The majority of GNN-based matrix completion methods are based on Graph Autoencoder (GAE), which considers the one-hot index as input, maps a user (or item) index to a learnable embedding, applies a GNN to learn the node-specific representations based on these learnable embeddings and finally aggregates the representations of the target users and its corresponding item nodes to predict missing links. However, without node content (i.e., side information) for training, the user (or item) specific representation can not be learned in the inductive setting, that is, a model trained on one group of users (or items) cannot adapt to new users (or items). To this end, we propose an inductive matrix completion method using GAE (IMC-GAE), which utilizes the GAE to learn both the user-specific (or item-specific) representation for personalized recommendation and local graph patterns for inductive matrix completion. Specifically, we design two informative node features and employ a layer-wise node dropout scheme in GAE to learn local graph patterns which can be generalized to unseen data. The main contribution of our paper is the capability to efficiently learn local graph patterns in GAE, with good scalability and superior expressiveness compared to previous GNN-based matrix completion methods. Furthermore, extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on several matrix completion benchmarks. Our official code is publicly available.
Auxiliary-task Based Deep Reinforcement Learning for Participant Selection Problem in Mobile Crowdsourcing
Aug 26, 2020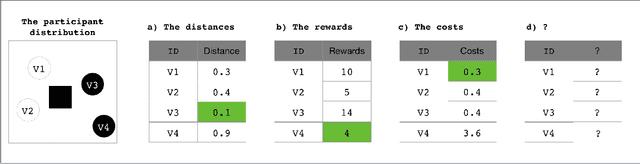

Abstract:In mobile crowdsourcing (MCS), the platform selects participants to complete location-aware tasks from the recruiters aiming to achieve multiple goals (e.g., profit maximization, energy efficiency, and fairness). However, different MCS systems have different goals and there are possibly conflicting goals even in one MCS system. Therefore, it is crucial to design a participant selection algorithm that applies to different MCS systems to achieve multiple goals. To deal with this issue, we formulate the participant selection problem as a reinforcement learning problem and propose to solve it with a novel method, which we call auxiliary-task based deep reinforcement learning (ADRL). We use transformers to extract representations from the context of the MCS system and a pointer network to deal with the combinatorial optimization problem. To improve the sample efficiency, we adopt an auxiliary-task training process that trains the network to predict the imminent tasks from the recruiters, which facilitates the embedding learning of the deep learning model. Additionally, we release a simulated environment on a specific MCS task, the ride-sharing task, and conduct extensive performance evaluations in this environment. The experimental results demonstrate that ADRL outperforms and improves sample efficiency over other well-recognized baselines in various settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge