Jingcheng Ni
VideoGPA: Distilling Geometry Priors for 3D-Consistent Video Generation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:While recent video diffusion models (VDMs) produce visually impressive results, they fundamentally struggle to maintain 3D structural consistency, often resulting in object deformation or spatial drift. We hypothesize that these failures arise because standard denoising objectives lack explicit incentives for geometric coherence. To address this, we introduce VideoGPA (Video Geometric Preference Alignment), a data-efficient self-supervised framework that leverages a geometry foundation model to automatically derive dense preference signals that guide VDMs via Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). This approach effectively steers the generative distribution toward inherent 3D consistency without requiring human annotations. VideoGPA significantly enhances temporal stability, physical plausibility, and motion coherence using minimal preference pairs, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art baselines in extensive experiments.
Coffee: Controllable Diffusion Fine-tuning
Nov 18, 2025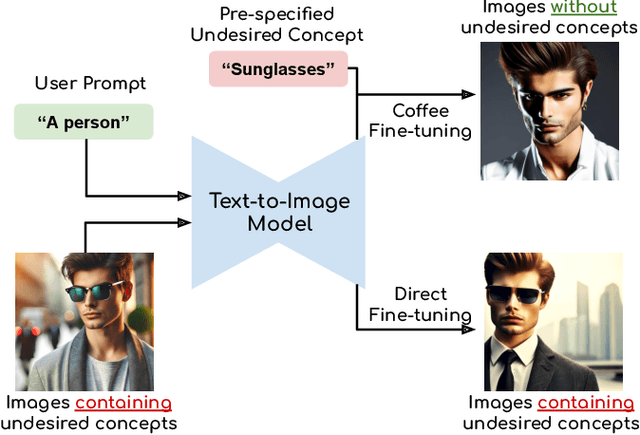
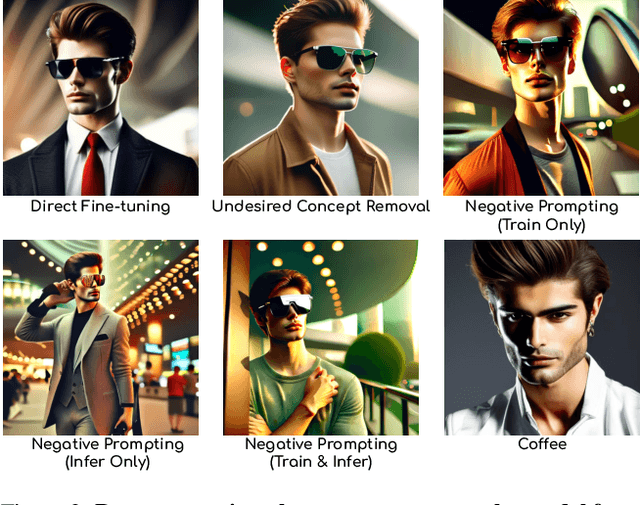
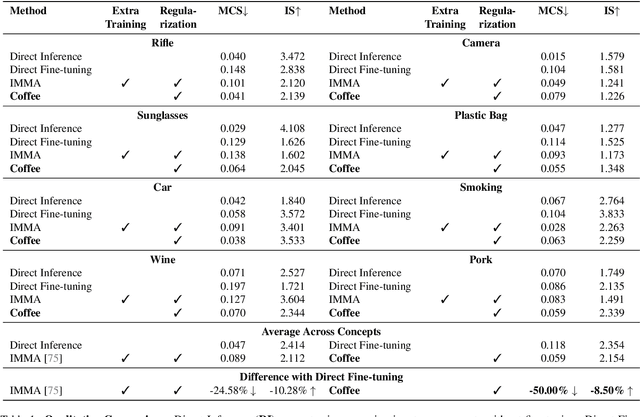

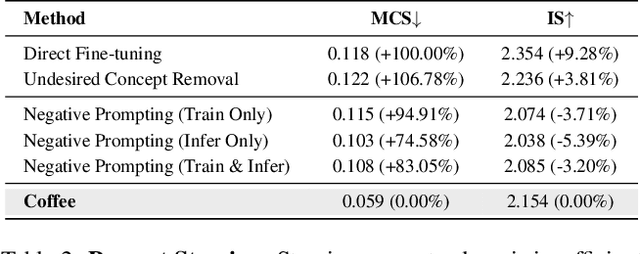
Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models can generate diverse content with flexible prompts, which makes them well-suited for customization through fine-tuning with a small amount of user-provided data. However, controllable fine-tuning that prevents models from learning undesired concepts present in the fine-tuning data, and from entangling those concepts with user prompts, remains an open challenge. It is crucial for downstream tasks like bias mitigation, preventing malicious adaptation, attribute disentanglement, and generalizable fine-tuning of diffusion policy. We propose Coffee that allows using language to specify undesired concepts to regularize the adaptation process. The crux of our method lies in keeping the embeddings of the user prompt from aligning with undesired concepts. Crucially, Coffee requires no additional training and enables flexible modification of undesired concepts by modifying textual descriptions. We evaluate Coffee by fine-tuning on images associated with user prompts paired with undesired concepts. Experimental results demonstrate that Coffee can prevent text-to-image models from learning specified undesired concepts during fine-tuning and outperforms existing methods. Code will be released upon acceptance.
CVD-STORM: Cross-View Video Diffusion with Spatial-Temporal Reconstruction Model for Autonomous Driving
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Generative models have been widely applied to world modeling for environment simulation and future state prediction. With advancements in autonomous driving, there is a growing demand not only for high-fidelity video generation under various controls, but also for producing diverse and meaningful information such as depth estimation. To address this, we propose CVD-STORM, a cross-view video diffusion model utilizing a spatial-temporal reconstruction Variational Autoencoder (VAE) that generates long-term, multi-view videos with 4D reconstruction capabilities under various control inputs. Our approach first fine-tunes the VAE with an auxiliary 4D reconstruction task, enhancing its ability to encode 3D structures and temporal dynamics. Subsequently, we integrate this VAE into the video diffusion process to significantly improve generation quality. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves substantial improvements in both FID and FVD metrics. Additionally, the jointly-trained Gaussian Splatting Decoder effectively reconstructs dynamic scenes, providing valuable geometric information for comprehensive scene understanding.
MaskGWM: A Generalizable Driving World Model with Video Mask Reconstruction
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:World models that forecast environmental changes from actions are vital for autonomous driving models with strong generalization. The prevailing driving world model mainly build on video prediction model. Although these models can produce high-fidelity video sequences with advanced diffusion-based generator, they are constrained by their predictive duration and overall generalization capabilities. In this paper, we explore to solve this problem by combining generation loss with MAE-style feature-level context learning. In particular, we instantiate this target with three key design: (1) A more scalable Diffusion Transformer (DiT) structure trained with extra mask construction task. (2) we devise diffusion-related mask tokens to deal with the fuzzy relations between mask reconstruction and generative diffusion process. (3) we extend mask construction task to spatial-temporal domain by utilizing row-wise mask for shifted self-attention rather than masked self-attention in MAE. Then, we adopt a row-wise cross-view module to align with this mask design. Based on above improvement, we propose MaskGWM: a Generalizable driving World Model embodied with Video Mask reconstruction. Our model contains two variants: MaskGWM-long, focusing on long-horizon prediction, and MaskGWM-mview, dedicated to multi-view generation. Comprehensive experiments on standard benchmarks validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which contain normal validation of Nuscene dataset, long-horizon rollout of OpenDV-2K dataset and zero-shot validation of Waymo dataset. Quantitative metrics on these datasets show our method notably improving state-of-the-art driving world model.
Efficient Interactive 3D Multi-Object Removal
Jan 30, 2025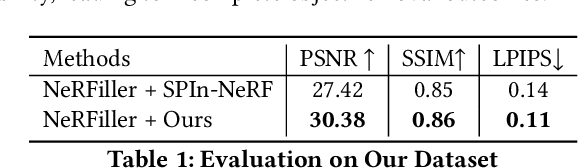
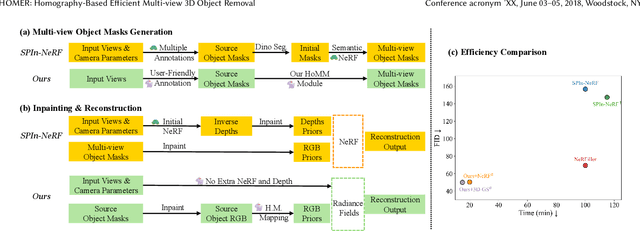
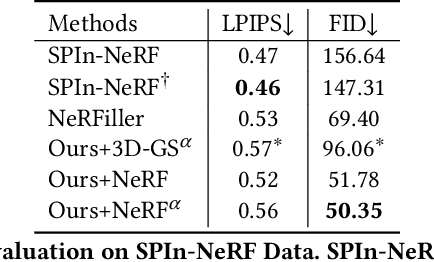
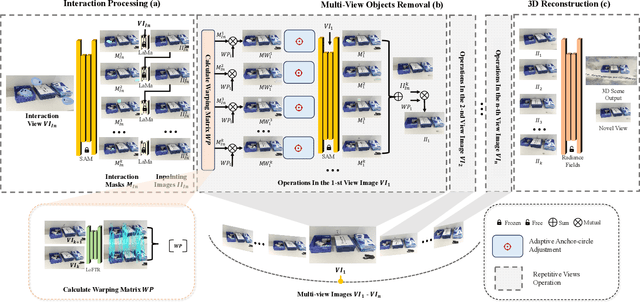
Abstract:Object removal is of great significance to 3D scene understanding, essential for applications in content filtering and scene editing. Current mainstream methods primarily focus on removing individual objects, with a few methods dedicated to eliminating an entire area or all objects of a certain category. They however confront the challenge of insufficient granularity and flexibility for real-world applications, where users demand tailored excision and preservation of objects within defined zones. In addition, most of the current methods require kinds of priors when addressing multi-view inpainting, which is time-consuming. To address these limitations, we propose an efficient and user-friendly pipeline for 3D multi-object removal, enabling users to flexibly select areas and define objects for removal or preservation. Concretely, to ensure object consistency and correspondence across multiple views, we propose a novel mask matching and refinement module, which integrates homography-based warping with high-confidence anchor points for segmentation. By leveraging the IoU joint shape context distance loss, we enhance the accuracy of warped masks and improve subsequent inpainting processes. Considering the current immaturity of 3D multi-object removal, we provide a new evaluation dataset to bridge the developmental void. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly reduces computational costs, achieving processing speeds more than 80% faster than state-of-the-art methods while maintaining equivalent or higher reconstruction quality.
UniMLVG: Unified Framework for Multi-view Long Video Generation with Comprehensive Control Capabilities for Autonomous Driving
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:The creation of diverse and realistic driving scenarios has become essential to enhance perception and planning capabilities of the autonomous driving system. However, generating long-duration, surround-view consistent driving videos remains a significant challenge. To address this, we present UniMLVG, a unified framework designed to generate extended street multi-perspective videos under precise control. By integrating single- and multi-view driving videos into the training data, our approach updates cross-frame and cross-view modules across three stages with different training objectives, substantially boosting the diversity and quality of generated visual content. Additionally, we employ the explicit viewpoint modeling in multi-view video generation to effectively improve motion transition consistency. Capable of handling various input reference formats (e.g., text, images, or video), our UniMLVG generates high-quality multi-view videos according to the corresponding condition constraints such as 3D bounding boxes or frame-level text descriptions. Compared to the best models with similar capabilities, our framework achieves improvements of 21.4% in FID and 36.5% in FVD.
HoloDrive: Holistic 2D-3D Multi-Modal Street Scene Generation for Autonomous Driving
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Generative models have significantly improved the generation and prediction quality on either camera images or LiDAR point clouds for autonomous driving. However, a real-world autonomous driving system uses multiple kinds of input modality, usually cameras and LiDARs, where they contain complementary information for generation, while existing generation methods ignore this crucial feature, resulting in the generated results only covering separate 2D or 3D information. In order to fill the gap in 2D-3D multi-modal joint generation for autonomous driving, in this paper, we propose our framework, \emph{HoloDrive}, to jointly generate the camera images and LiDAR point clouds. We employ BEV-to-Camera and Camera-to-BEV transform modules between heterogeneous generative models, and introduce a depth prediction branch in the 2D generative model to disambiguate the un-projecting from image space to BEV space, then extend the method to predict the future by adding temporal structure and carefully designed progressive training. Further, we conduct experiments on single frame generation and world model benchmarks, and demonstrate our method leads to significant performance gains over SOTA methods in terms of generation metrics.
PriorDiffusion: Leverage Language Prior in Diffusion Models for Monocular Depth Estimation
Nov 24, 2024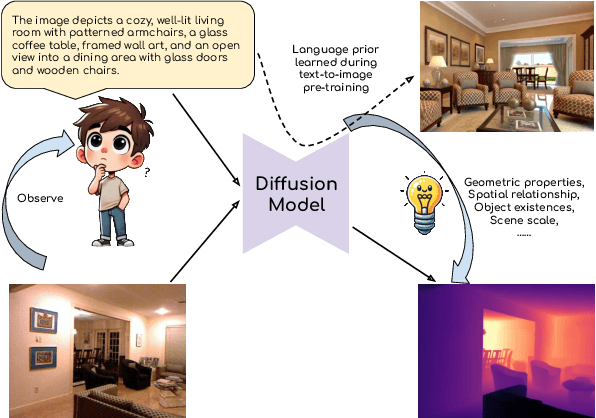
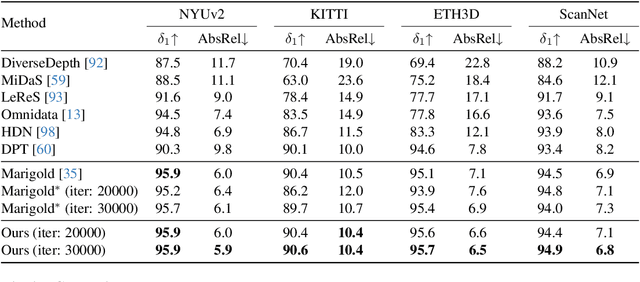
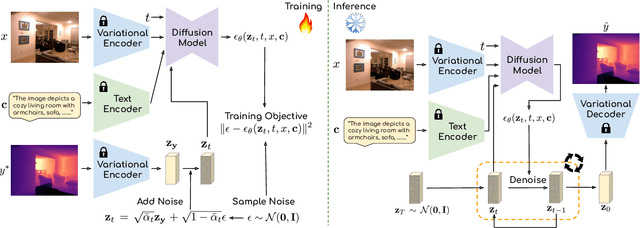
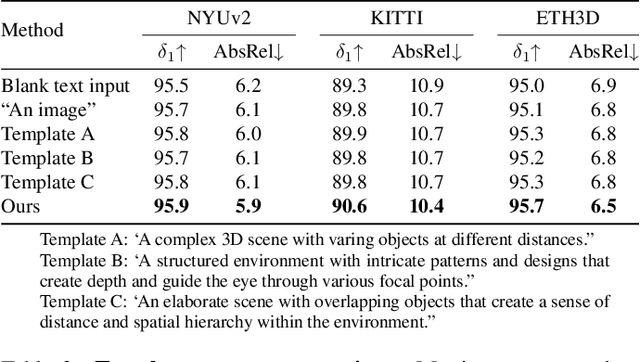
Abstract:This paper explores the potential of leveraging language priors learned by text-to-image diffusion models to address ambiguity and visual nuisance in monocular depth estimation. Particularly, traditional monocular depth estimation suffers from inherent ambiguity due to the absence of stereo or multi-view depth cues, and nuisance due to lack of robustness of vision. We argue that language prior in diffusion models can enhance monocular depth estimation by leveraging the geometric prior aligned with the language description, which is learned during text-to-image pre-training. To generate images that reflect the text properly, the model must comprehend the size and shape of specified objects, their spatial relationship, and the scale of the scene. Thus, we propose PriorDiffusion, using a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model that takes both image and text description that aligned with the scene to infer affine-invariant depth through a denoising process. We also show that language priors can guide the model's attention to specific regions and help it perceive the 3D scene in alignment with user intent. Simultaneously, it acts as a constraint to accelerate the convergence of the diffusion trajectory, since learning 3D properties from a condensed, low-dimensional language feature is more efficient compared with learning from a redundant, high-dimensional image feature. By training on HyperSim and Virtual KITTI, we achieve state-of-the-art zero-shot performance and a faster convergence speed, compared with other diffusion-based depth estimators, across NYUv2, KITTI, ETH3D, and ScanNet.
GaitFormer: Revisiting Intrinsic Periodicity for Gait Recognition
Jul 25, 2023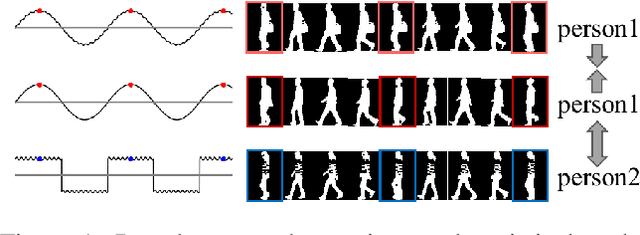
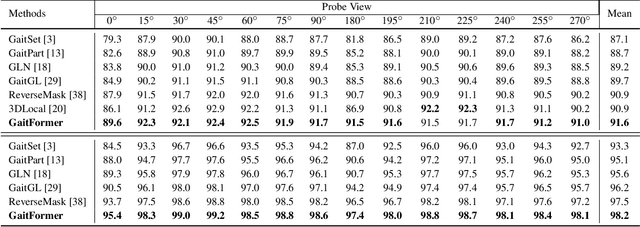
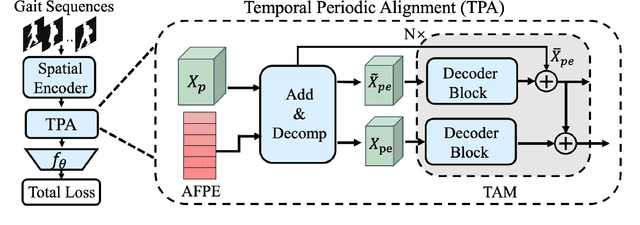
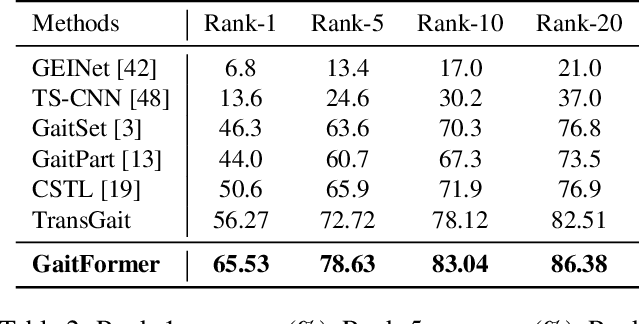
Abstract:Gait recognition aims to distinguish different walking patterns by analyzing video-level human silhouettes, rather than relying on appearance information. Previous research on gait recognition has primarily focused on extracting local or global spatial-temporal representations, while overlooking the intrinsic periodic features of gait sequences, which, when fully utilized, can significantly enhance performance. In this work, we propose a plug-and-play strategy, called Temporal Periodic Alignment (TPA), which leverages the periodic nature and fine-grained temporal dependencies of gait patterns. The TPA strategy comprises two key components. The first component is Adaptive Fourier-transform Position Encoding (AFPE), which adaptively converts features and discrete-time signals into embeddings that are sensitive to periodic walking patterns. The second component is the Temporal Aggregation Module (TAM), which separates embeddings into trend and seasonal components, and extracts meaningful temporal correlations to identify primary components, while filtering out random noise. We present a simple and effective baseline method for gait recognition, based on the TPA strategy. Extensive experiments conducted on three popular public datasets (CASIA-B, OU-MVLP, and GREW) demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmark tests.
Motion Sensitive Contrastive Learning for Self-supervised Video Representation
Aug 12, 2022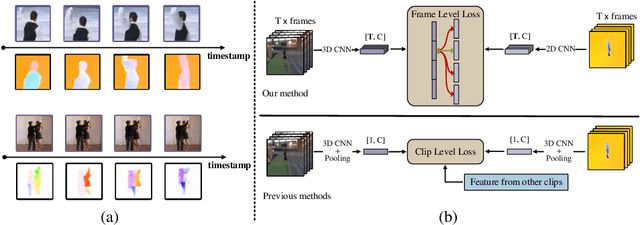
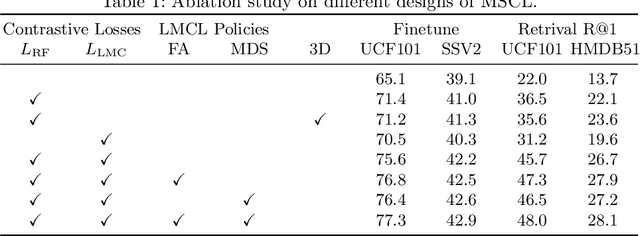
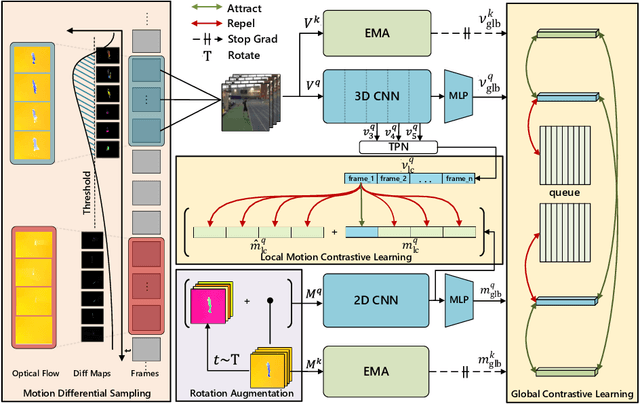
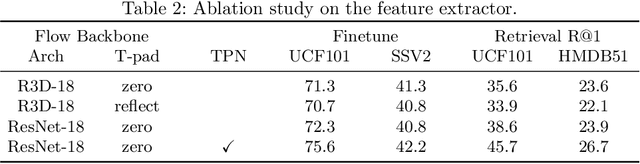
Abstract:Contrastive learning has shown great potential in video representation learning. However, existing approaches fail to sufficiently exploit short-term motion dynamics, which are crucial to various down-stream video understanding tasks. In this paper, we propose Motion Sensitive Contrastive Learning (MSCL) that injects the motion information captured by optical flows into RGB frames to strengthen feature learning. To achieve this, in addition to clip-level global contrastive learning, we develop Local Motion Contrastive Learning (LMCL) with frame-level contrastive objectives across the two modalities. Moreover, we introduce Flow Rotation Augmentation (FRA) to generate extra motion-shuffled negative samples and Motion Differential Sampling (MDS) to accurately screen training samples. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. With the commonly-used 3D ResNet-18 as the backbone, we achieve the top-1 accuracies of 91.5\% on UCF101 and 50.3\% on Something-Something v2 for video classification, and a 65.6\% Top-1 Recall on UCF101 for video retrieval, notably improving the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge