Ruibin Bai
Toward Closed-loop Molecular Discovery via Language Model, Property Alignment and Strategic Search
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Drug discovery is a time-consuming and expensive process, with traditional high-throughput and docking-based virtual screening hampered by low success rates and limited scalability. Recent advances in generative modelling, including autoregressive, diffusion, and flow-based approaches, have enabled de novo ligand design beyond the limits of enumerative screening. Yet these models often suffer from inadequate generalization, limited interpretability, and an overemphasis on binding affinity at the expense of key pharmacological properties, thereby restricting their translational utility. Here we present Trio, a molecular generation framework integrating fragment-based molecular language modeling, reinforcement learning, and Monte Carlo tree search, for effective and interpretable closed-loop targeted molecular design. Through the three key components, Trio enables context-aware fragment assembly, enforces physicochemical and synthetic feasibility, and guides a balanced search between the exploration of novel chemotypes and the exploitation of promising intermediates within protein binding pockets. Experimental results show that Trio reliably achieves chemically valid and pharmacologically enhanced ligands, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches with improved binding affinity (+7.85%), drug-likeness (+11.10%) and synthetic accessibility (+12.05%), while expanding molecular diversity more than fourfold. By combining generalization, plausibility, and interpretability, Trio establishes a closed-loop generative paradigm that redefines how chemical space can be navigated, offering a transformative foundation for the next era of AI-driven drug discovery.
MeLA: A Metacognitive LLM-Driven Architecture for Automatic Heuristic Design
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces MeLA, a Metacognitive LLM-Driven Architecture that presents a new paradigm for Automatic Heuristic Design (AHD). Traditional evolutionary methods operate directly on heuristic code; in contrast, MeLA evolves the instructional prompts used to guide a Large Language Model (LLM) in generating these heuristics. This process of "prompt evolution" is driven by a novel metacognitive framework where the system analyzes performance feedback to systematically refine its generative strategy. MeLA's architecture integrates a problem analyzer to construct an initial strategic prompt, an error diagnosis system to repair faulty code, and a metacognitive search engine that iteratively optimizes the prompt based on heuristic effectiveness. In comprehensive experiments across both benchmark and real-world problems, MeLA consistently generates more effective and robust heuristics, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Ultimately, this research demonstrates the profound potential of using cognitive science as a blueprint for AI architecture, revealing that by enabling an LLM to metacognitively regulate its problem-solving process, we unlock a more robust and interpretable path to AHD.
PGU-SGP: A Pheno-Geno Unified Surrogate Genetic Programming For Real-life Container Terminal Truck Scheduling
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Data-driven genetic programming (GP) has proven highly effective in solving combinatorial optimization problems under dynamic and uncertain environments. A central challenge lies in fast fitness evaluations on large training datasets, especially for complex real-world problems involving time-consuming simulations. Surrogate models, like phenotypic characterization (PC)-based K-nearest neighbors (KNN), have been applied to reduce computational cost. However, the PC-based similarity measure is confined to behavioral characteristics, overlooking genotypic differences, which can limit surrogate quality and impair performance. To address these issues, this paper proposes a pheno-geno unified surrogate GP algorithm, PGU-SGP, integrating phenotypic and genotypic characterization (GC) to enhance surrogate sample selection and fitness prediction. A novel unified similarity metric combining PC and GC distances is proposed, along with an effective and efficient GC representation. Experimental results of a real-life vehicle scheduling problem demonstrate that PGU-SGP reduces training time by approximately 76% while achieving comparable performance to traditional GP. With the same training time, PGU-SGP significantly outperforms traditional GP and the state-of-the-art algorithm on most datasets. Additionally, PGU-SGP shows faster convergence and improved surrogate quality by maintaining accurate fitness rankings and appropriate selection pressure, further validating its effectiveness.
ERL-MPP: Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning with Multi-head Puzzle Perception for Solving Large-scale Jigsaw Puzzles of Eroded Gaps
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Solving jigsaw puzzles has been extensively studied. While most existing models focus on solving either small-scale puzzles or puzzles with no gap between fragments, solving large-scale puzzles with gaps presents distinctive challenges in both image understanding and combinatorial optimization. To tackle these challenges, we propose a framework of Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning with Multi-head Puzzle Perception (ERL-MPP) to derive a better set of swapping actions for solving the puzzles. Specifically, to tackle the challenges of perceiving the puzzle with gaps, a Multi-head Puzzle Perception Network (MPPN) with a shared encoder is designed, where multiple puzzlet heads comprehensively perceive the local assembly status, and a discriminator head provides a global assessment of the puzzle. To explore the large swapping action space efficiently, an Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning (EvoRL) agent is designed, where an actor recommends a set of suitable swapping actions from a large action space based on the perceived puzzle status, a critic updates the actor using the estimated rewards and the puzzle status, and an evaluator coupled with evolutionary strategies evolves the actions aligning with the historical assembly experience. The proposed ERL-MPP is comprehensively evaluated on the JPLEG-5 dataset with large gaps and the MIT dataset with large-scale puzzles. It significantly outperforms all state-of-the-art models on both datasets.
Genetic Programming with Reinforcement Learning Trained Transformer for Real-World Dynamic Scheduling Problems
Apr 10, 2025
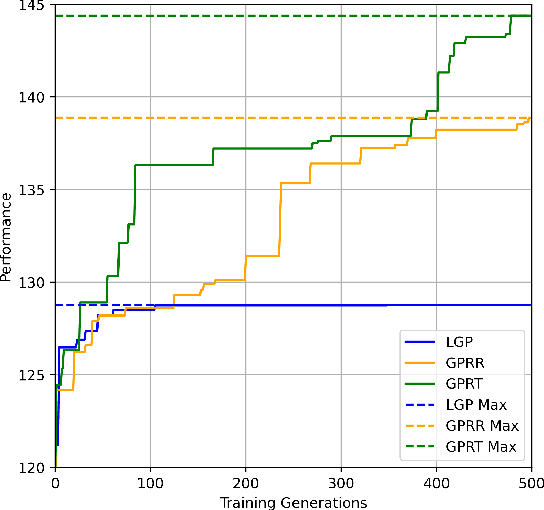


Abstract:Dynamic scheduling in real-world environments often struggles to adapt to unforeseen disruptions, making traditional static scheduling methods and human-designed heuristics inadequate. This paper introduces an innovative approach that combines Genetic Programming (GP) with a Transformer trained through Reinforcement Learning (GPRT), specifically designed to tackle the complexities of dynamic scheduling scenarios. GPRT leverages the Transformer to refine heuristics generated by GP while also seeding and guiding the evolution of GP. This dual functionality enhances the adaptability and effectiveness of the scheduling heuristics, enabling them to better respond to the dynamic nature of real-world tasks. The efficacy of this integrated approach is demonstrated through a practical application in container terminal truck scheduling, where the GPRT method outperforms traditional GP, standalone Transformer methods, and other state-of-the-art competitors. The key contribution of this research is the development of the GPRT method, which showcases a novel combination of GP and Reinforcement Learning (RL) to produce robust and efficient scheduling solutions. Importantly, GPRT is not limited to container port truck scheduling; it offers a versatile framework applicable to various dynamic scheduling challenges. Its practicality, coupled with its interpretability and ease of modification, makes it a valuable tool for diverse real-world scenarios.
MG-MotionLLM: A Unified Framework for Motion Comprehension and Generation across Multiple Granularities
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Recent motion-aware large language models have demonstrated promising potential in unifying motion comprehension and generation. However, existing approaches primarily focus on coarse-grained motion-text modeling, where text describes the overall semantics of an entire motion sequence in just a few words. This limits their ability to handle fine-grained motion-relevant tasks, such as understanding and controlling the movements of specific body parts. To overcome this limitation, we pioneer MG-MotionLLM, a unified motion-language model for multi-granular motion comprehension and generation. We further introduce a comprehensive multi-granularity training scheme by incorporating a set of novel auxiliary tasks, such as localizing temporal boundaries of motion segments via detailed text as well as motion detailed captioning, to facilitate mutual reinforcement for motion-text modeling across various levels of granularity. Extensive experiments show that our MG-MotionLLM achieves superior performance on classical text-to-motion and motion-to-text tasks, and exhibits potential in novel fine-grained motion comprehension and editing tasks. Project page: CVI-SZU/MG-MotionLLM
Towards Constraint-Based Adaptive Hypergraph Learning for Solving Vehicle Routing: An End-to-End Solution
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:The application of learning based methods to vehicle routing problems has emerged as a pivotal area of research in combinatorial optimization. These problems are characterized by vast solution spaces and intricate constraints, making traditional approaches such as exact mathematical models or heuristic methods prone to high computational overhead or reliant on the design of complex heuristic operators to achieve optimal or near optimal solutions. Meanwhile, although some recent learning-based methods can produce good performance for VRP with straightforward constraint scenarios, they often fail to effectively handle hard constraints that are common in practice. This study introduces a novel end-to-end framework that combines constraint-oriented hypergraphs with reinforcement learning to address vehicle routing problems. A central innovation of this work is the development of a constraint-oriented dynamic hyperedge reconstruction strategy within an encoder, which significantly enhances hypergraph representation learning. Additionally, the decoder leverages a double-pointer attention mechanism to iteratively generate solutions. The proposed model is trained by incorporating asynchronous parameter updates informed by hypergraph constraints and optimizing a dual loss function comprising constraint loss and policy gradient loss. The experiment results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach not only eliminates the need for sophisticated heuristic operators but also achieves substantial improvements in solution quality.
Dockformer: A transformer-based molecular docking paradigm for large-scale virtual screening
Nov 15, 2024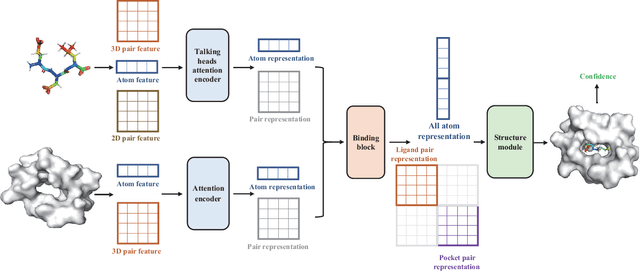
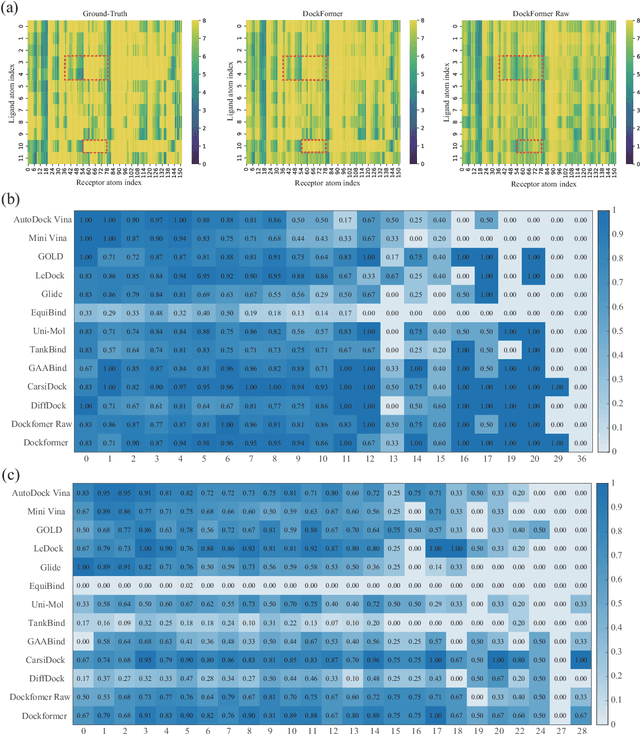
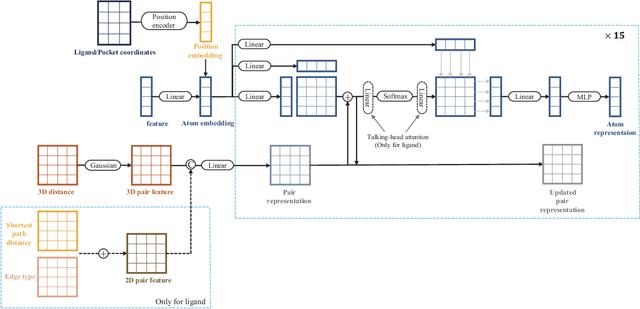
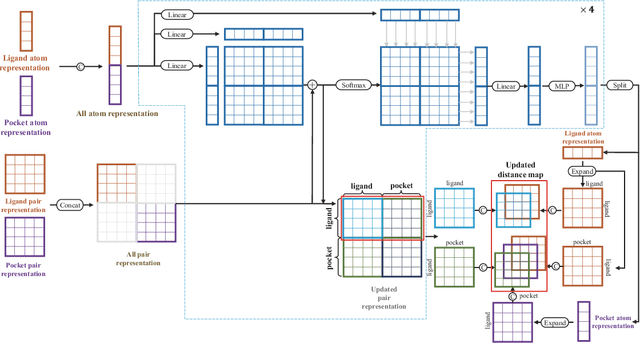
Abstract:Molecular docking enables virtual screening of compound libraries to identify potential ligands that target proteins of interest, a crucial step in drug development; however, as the size of the compound library increases, the computational complexity of traditional docking models increases. Deep learning algorithms can provide data-driven research and development models to increase the speed of the docking process. Unfortunately, few models can achieve superior screening performance compared to that of traditional models. Therefore, a novel deep learning-based docking approach named Dockformer is introduced in this study. Dockformer leverages multimodal information to capture the geometric topology and structural knowledge of molecules and can directly generate binding conformations with the corresponding confidence measures in an end-to-end manner. The experimental results show that Dockformer achieves success rates of 90.53\% and 82.71\% on the PDBbind core set and PoseBusters benchmarks, respectively, and more than a 100-fold increase in the inference process speed, outperforming almost all state-of-the-art docking methods. In addition, the ability of Dockformer to identify the main protease inhibitors of coronaviruses is demonstrated in a real-world virtual screening scenario. Considering its high docking accuracy and screening efficiency, Dockformer can be regarded as a powerful and robust tool in the field of drug design.
Pattern based learning and optimisation through pricing for bin packing problem
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:As a popular form of knowledge and experience, patterns and their identification have been critical tasks in most data mining applications. However, as far as we are aware, no study has systematically examined the dynamics of pattern values and their reuse under varying conditions. We argue that when problem conditions such as the distributions of random variables change, the patterns that performed well in previous circumstances may become less effective and adoption of these patterns would result in sub-optimal solutions. In response, we make a connection between data mining and the duality theory in operations research and propose a novel scheme to efficiently identify patterns and dynamically quantify their values for each specific condition. Our method quantifies the value of patterns based on their ability to satisfy stochastic constraints and their effects on the objective value, allowing high-quality patterns and their combinations to be detected. We use the online bin packing problem to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme and illustrate the online packing procedure with the guidance of patterns that address the inherent uncertainty of the problem. Results show that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. We also analysed in detail the distinctive features of the proposed methods that lead to performance improvement and the special cases where our method can be further improved.
GASE: Graph Attention Sampling with Edges Fusion for Solving Vehicle Routing Problems
May 21, 2024



Abstract:Learning-based methods have become increasingly popular for solving vehicle routing problems due to their near-optimal performance and fast inference speed. Among them, the combination of deep reinforcement learning and graph representation allows for the abstraction of node topology structures and features in an encoder-decoder style. Such an approach makes it possible to solve routing problems end-to-end without needing complicated heuristic operators designed by domain experts. Existing research studies have been focusing on novel encoding and decoding structures via various neural network models to enhance the node embedding representation. Despite the sophisticated approaches applied, there is a noticeable lack of consideration for the graph-theoretic properties inherent to routing problems. Moreover, the potential ramifications of inter-nodal interactions on the decision-making efficacy of the models have not been adequately explored. To bridge this gap, we propose an adaptive Graph Attention Sampling with the Edges Fusion framework (GASE),where nodes' embedding is determined through attention calculation from certain highly correlated neighbourhoods and edges, utilizing a filtered adjacency matrix. In detail, the selections of particular neighbours and adjacency edges are led by a multi-head attention mechanism, contributing directly to the message passing and node embedding in graph attention sampling networks. Furthermore, we incorporate an adaptive actor-critic algorithm with policy improvements to expedite the training convergence. We then conduct comprehensive experiments against baseline methods on learning-based VRP tasks from different perspectives. Our proposed model outperforms the existing methods by 2.08\%-6.23\% and shows stronger generalization ability, achieving state-of-the-art performance on randomly generated instances and real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge