Junkai Ji
RIGA-Fold: A General Framework for Protein Inverse Folding via Recurrent Interaction and Geometric Awareness
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Protein inverse folding, the task of predicting amino acid sequences for desired structures, is pivotal for de novo protein design. However, existing GNN-based methods typically suffer from restricted receptive fields that miss long-range dependencies and a "single-pass" inference paradigm that leads to error accumulation. To address these bottlenecks, we propose RIGA-Fold, a framework that synergizes Recurrent Interaction with Geometric Awareness. At the micro-level, we introduce a Geometric Attention Update (GAU) module where edge features explicitly serve as attention keys, ensuring strictly SE(3)-invariant local encoding. At the macro-level, we design an attention-based Global Context Bridge that acts as a soft gating mechanism to dynamically inject global topological information. Furthermore, to bridge the gap between structural and sequence modalities, we introduce an enhanced variant, RIGA-Fold*, which integrates trainable geometric features with frozen evolutionary priors from ESM-2 and ESM-IF via a dual-stream architecture. Finally, a biologically inspired ``predict-recycle-refine'' strategy is implemented to iteratively denoise sequence distributions. Extensive experiments on CATH 4.2, TS50, and TS500 benchmarks demonstrate that our geometric framework is highly competitive, while RIGA-Fold* significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both sequence recovery and structural consistency.
Unveiling Scaling Behaviors in Molecular Language Models: Effects of Model Size, Data, and Representation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Molecular generative models, often employing GPT-style language modeling on molecular string representations, have shown promising capabilities when scaled to large datasets and model sizes. However, it remains unclear and subject to debate whether these models adhere to predictable scaling laws under fixed computational budgets, which is a crucial understanding for optimally allocating resources between model size, data volume, and molecular representation. In this study, we systematically investigate the scaling behavior of molecular language models across both pretraining and downstream tasks. We train 300 models and conduct over 10,000 experiments, rigorously controlling compute budgets while independently varying model size, number of training tokens, and molecular representation. Our results demonstrate clear scaling laws in molecular models for both pretraining and downstream transfer, reveal the substantial impact of molecular representation on performance, and explain previously observed inconsistencies in scaling behavior for molecular generation. Additionally, we publicly release the largest library of molecular language models to date to facilitate future research and development. Code and models are available at https://github.com/SZU-ADDG/MLM-Scaling.
From Tokens to Blocks: A Block-Diffusion Perspective on Molecular Generation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Drug discovery can be viewed as a combinatorial search over an immense chemical space, motivating the development of deep generative models for de novo molecular design. Among these, GPT-based molecular language models (MLM) have shown strong molecular design performance by learning chemical syntax and semantics from large-scale data. However, existing MLMs face two fundamental limitations: they inadequately capture the graph-structured nature of molecules when formulated as next-token prediction problems, and they typically lack explicit mechanisms for target-aware generation. Here, we propose SoftMol, a unified framework that co-designs molecular representation, model architecture, and search strategy for target-aware molecular generation. SoftMol introduces soft fragments, a rule-free block representation of SMILES that enables diffusion-native modeling, and develops SoftBD, the first block-diffusion molecular language model that combines local bidirectional diffusion with autoregressive generation under molecular structural constraints. To favor generated molecules with high drug-likeness and synthetic accessibility, SoftBD is trained on a carefully curated dataset named ZINC-Curated. SoftMol further integrates a gated Monte Carlo tree search to assemble fragments in a target-aware manner. Experimental results show that, compared with current state-of-the-art models, SoftMol achieves 100% chemical validity, improves binding affinity by 9.7%, yields a 2-3x increase in molecular diversity, and delivers a 6.6x speedup in inference efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/szu-aicourse/softmol
Rethinking Drug-Drug Interaction Modeling as Generalizable Relation Learning
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Drug-drug interaction (DDI) prediction is central to drug discovery and clinical development, particularly in the context of increasingly prevalent polypharmacy. Although existing computational methods achieve strong performance on standard benchmarks, they often fail to generalize to realistic deployment scenarios, where most candidate drug pairs involve previously unseen drugs and validated interactions are scarce. We demonstrate that proximity in the embedding spaces of prevailing molecule-centric DDI models does not reliably correspond to interaction labels, and that simply scaling up model capacity therefore fails to improve generalization. To address these limitations, we propose GenRel-DDI, a generalizable relation learning framework that reformulates DDI prediction as a relation-centric learning problem, in which interaction representations are learned independently of drug identities. This relation-level abstraction enables the capture of transferable interaction patterns that generalize to unseen drugs and novel drug pairs. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark demonstrate that GenRel-DDI consistently and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with particularly large gains on strict entity-disjoint evaluations, highlighting the effectiveness and practical utility of relation learning for robust DDI prediction. The code is available at https://github.com/SZU-ADDG/GenRel-DDI.
Toward Closed-loop Molecular Discovery via Language Model, Property Alignment and Strategic Search
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Drug discovery is a time-consuming and expensive process, with traditional high-throughput and docking-based virtual screening hampered by low success rates and limited scalability. Recent advances in generative modelling, including autoregressive, diffusion, and flow-based approaches, have enabled de novo ligand design beyond the limits of enumerative screening. Yet these models often suffer from inadequate generalization, limited interpretability, and an overemphasis on binding affinity at the expense of key pharmacological properties, thereby restricting their translational utility. Here we present Trio, a molecular generation framework integrating fragment-based molecular language modeling, reinforcement learning, and Monte Carlo tree search, for effective and interpretable closed-loop targeted molecular design. Through the three key components, Trio enables context-aware fragment assembly, enforces physicochemical and synthetic feasibility, and guides a balanced search between the exploration of novel chemotypes and the exploitation of promising intermediates within protein binding pockets. Experimental results show that Trio reliably achieves chemically valid and pharmacologically enhanced ligands, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches with improved binding affinity (+7.85%), drug-likeness (+11.10%) and synthetic accessibility (+12.05%), while expanding molecular diversity more than fourfold. By combining generalization, plausibility, and interpretability, Trio establishes a closed-loop generative paradigm that redefines how chemical space can be navigated, offering a transformative foundation for the next era of AI-driven drug discovery.
MODA: A Unified 3D Diffusion Framework for Multi-Task Target-Aware Molecular Generation
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Three-dimensional molecular generators based on diffusion models can now reach near-crystallographic accuracy, yet they remain fragmented across tasks. SMILES-only inputs, two-stage pretrain-finetune pipelines, and one-task-one-model practices hinder stereochemical fidelity, task alignment, and zero-shot transfer. We introduce MODA, a diffusion framework that unifies fragment growing, linker design, scaffold hopping, and side-chain decoration with a Bayesian mask scheduler. During training, a contiguous spatial fragment is masked and then denoised in one pass, enabling the model to learn shared geometric and chemical priors across tasks. Multi-task training yields a universal backbone that surpasses six diffusion baselines and three training paradigms on substructure, chemical property, interaction, and geometry. Model-C reduces ligand-protein clashes and substructure divergences while maintaining Lipinski compliance, whereas Model-B preserves similarity but trails in novelty and binding affinity. Zero-shot de novo design and lead-optimisation tests confirm stable negative Vina scores and high improvement rates without force-field refinement. These results demonstrate that a single-stage multi-task diffusion routine can replace two-stage workflows for structure-based molecular design.
Reimagining Target-Aware Molecular Generation through Retrieval-Enhanced Aligned Diffusion
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Breakthroughs in high-accuracy protein structure prediction, such as AlphaFold, have established receptor-based molecule design as a critical driver for rapid early-phase drug discovery. However, most approaches still struggle to balance pocket-specific geometric fit with strict valence and synthetic constraints. To resolve this trade-off, a Retrieval-Enhanced Aligned Diffusion termed READ is introduced, which is the first to merge molecular Retrieval-Augmented Generation with an SE(3)-equivariant diffusion model. Specifically, a contrastively pre-trained encoder aligns atom-level representations during training, then retrieves graph embeddings of pocket-matched scaffolds to guide each reverse-diffusion step at inference. This single mechanism can inject real-world chemical priors exactly where needed, producing valid, diverse, and shape-complementary ligands. Experimental results demonstrate that READ can achieve very competitive performance in CBGBench, surpassing state-of-the-art generative models and even native ligands. That suggests retrieval and diffusion can be co-optimized for faster, more reliable structure-based drug design.
Dockformer: A transformer-based molecular docking paradigm for large-scale virtual screening
Nov 15, 2024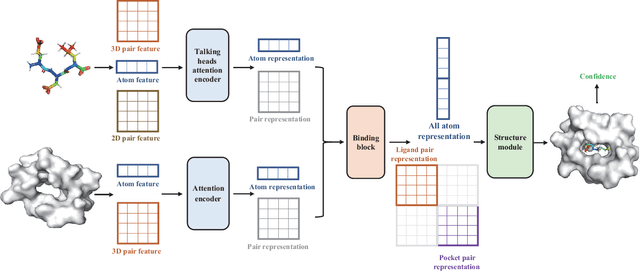
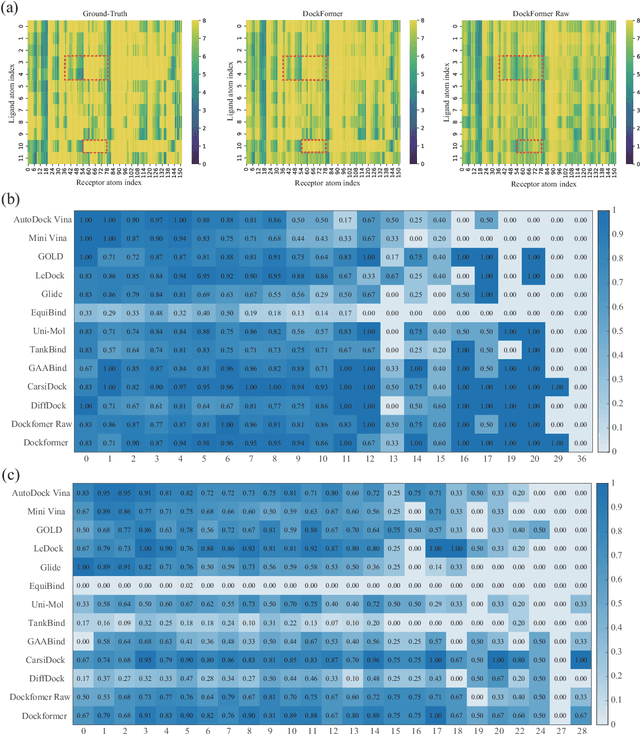
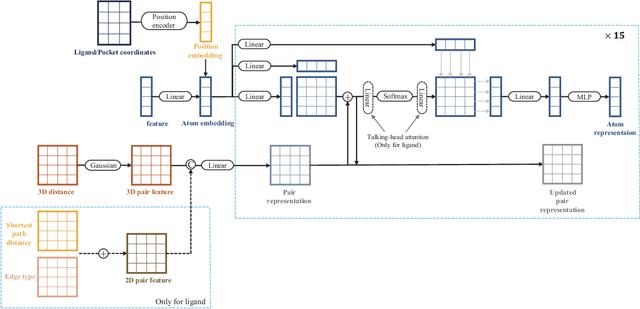
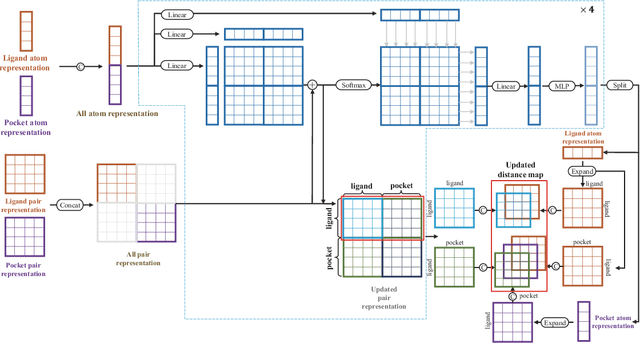
Abstract:Molecular docking enables virtual screening of compound libraries to identify potential ligands that target proteins of interest, a crucial step in drug development; however, as the size of the compound library increases, the computational complexity of traditional docking models increases. Deep learning algorithms can provide data-driven research and development models to increase the speed of the docking process. Unfortunately, few models can achieve superior screening performance compared to that of traditional models. Therefore, a novel deep learning-based docking approach named Dockformer is introduced in this study. Dockformer leverages multimodal information to capture the geometric topology and structural knowledge of molecules and can directly generate binding conformations with the corresponding confidence measures in an end-to-end manner. The experimental results show that Dockformer achieves success rates of 90.53\% and 82.71\% on the PDBbind core set and PoseBusters benchmarks, respectively, and more than a 100-fold increase in the inference process speed, outperforming almost all state-of-the-art docking methods. In addition, the ability of Dockformer to identify the main protease inhibitors of coronaviruses is demonstrated in a real-world virtual screening scenario. Considering its high docking accuracy and screening efficiency, Dockformer can be regarded as a powerful and robust tool in the field of drug design.
TransMUSIC: A Transformer-Aided Subspace Method for DOA Estimation with Low-Resolution ADCs
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Direction of arrival (DOA) estimation employing low-resolution analog-to-digital convertors (ADCs) has emerged as a challenging and intriguing problem, particularly with the rise in popularity of large-scale arrays. The substantial quantization distortion complicates the extraction of signal and noise subspaces from the quantized data. To address this issue, this paper introduces a novel approach that leverages the Transformer model to aid the subspace estimation. In this model, multiple snapshots are processed in parallel, enabling the capture of global correlations that span them. The learned subspace empowers us to construct the MUSIC spectrum and perform gridless DOA estimation using a neural network-based peak finder. Additionally, the acquired subspace encodes the vital information of model order, allowing us to determine the exact number of sources. These integrated components form a unified algorithmic framework referred to as TransMUSIC. Numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the TransMUSIC algorithm, even when dealing with one-bit quantized data. The results highlight the potential of Transformer-based techniques in DOA estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge