Zhe Kong
InfiniteTalk: Audio-driven Video Generation for Sparse-Frame Video Dubbing
Aug 19, 2025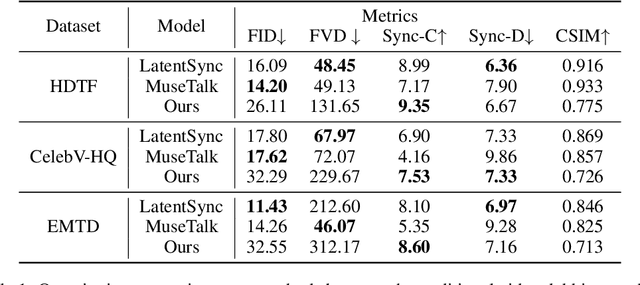
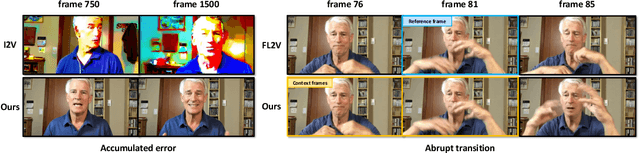
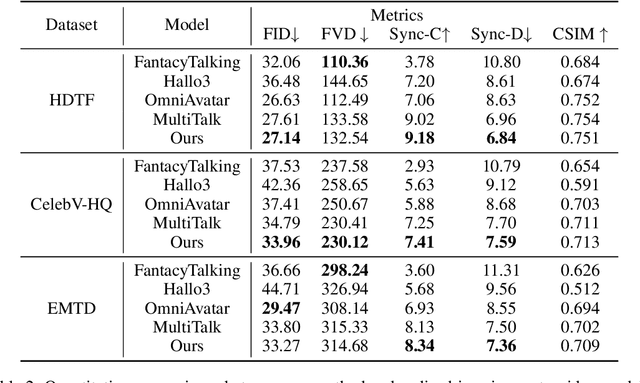
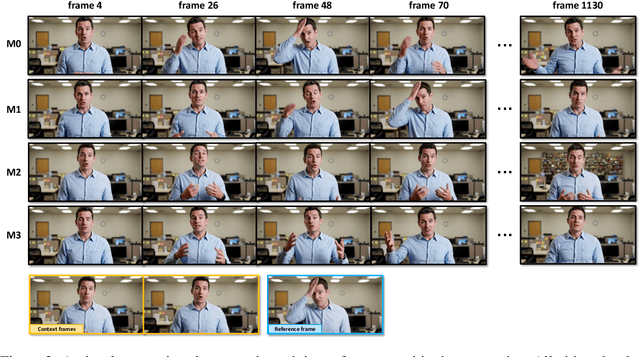
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in video AIGC have ushered in a transformative era for audio-driven human animation. However, conventional video dubbing techniques remain constrained to mouth region editing, resulting in discordant facial expressions and body gestures that compromise viewer immersion. To overcome this limitation, we introduce sparse-frame video dubbing, a novel paradigm that strategically preserves reference keyframes to maintain identity, iconic gestures, and camera trajectories while enabling holistic, audio-synchronized full-body motion editing. Through critical analysis, we identify why naive image-to-video models fail in this task, particularly their inability to achieve adaptive conditioning. Addressing this, we propose InfiniteTalk, a streaming audio-driven generator designed for infinite-length long sequence dubbing. This architecture leverages temporal context frames for seamless inter-chunk transitions and incorporates a simple yet effective sampling strategy that optimizes control strength via fine-grained reference frame positioning. Comprehensive evaluations on HDTF, CelebV-HQ, and EMTD datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Quantitative metrics confirm superior visual realism, emotional coherence, and full-body motion synchronization.
DAM-VSR: Disentanglement of Appearance and Motion for Video Super-Resolution
Jul 01, 2025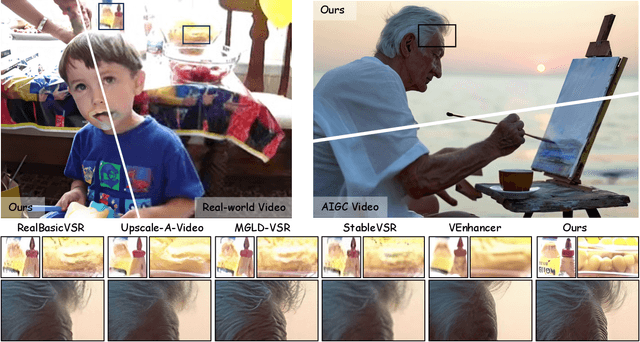


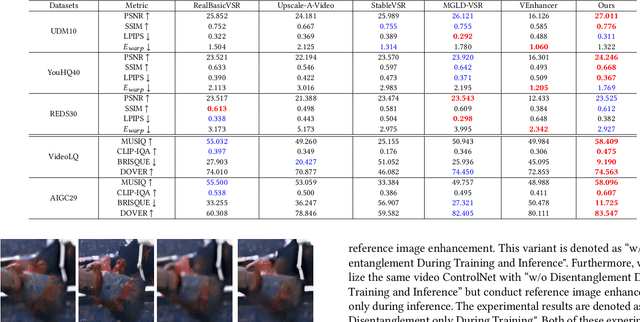
Abstract:Real-world video super-resolution (VSR) presents significant challenges due to complex and unpredictable degradations. Although some recent methods utilize image diffusion models for VSR and have shown improved detail generation capabilities, they still struggle to produce temporally consistent frames. We attempt to use Stable Video Diffusion (SVD) combined with ControlNet to address this issue. However, due to the intrinsic image-animation characteristics of SVD, it is challenging to generate fine details using only low-quality videos. To tackle this problem, we propose DAM-VSR, an appearance and motion disentanglement framework for VSR. This framework disentangles VSR into appearance enhancement and motion control problems. Specifically, appearance enhancement is achieved through reference image super-resolution, while motion control is achieved through video ControlNet. This disentanglement fully leverages the generative prior of video diffusion models and the detail generation capabilities of image super-resolution models. Furthermore, equipped with the proposed motion-aligned bidirectional sampling strategy, DAM-VSR can conduct VSR on longer input videos. DAM-VSR achieves state-of-the-art performance on real-world data and AIGC data, demonstrating its powerful detail generation capabilities.
Let Them Talk: Audio-Driven Multi-Person Conversational Video Generation
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Audio-driven human animation methods, such as talking head and talking body generation, have made remarkable progress in generating synchronized facial movements and appealing visual quality videos. However, existing methods primarily focus on single human animation and struggle with multi-stream audio inputs, facing incorrect binding problems between audio and persons. Additionally, they exhibit limitations in instruction-following capabilities. To solve this problem, in this paper, we propose a novel task: Multi-Person Conversational Video Generation, and introduce a new framework, MultiTalk, to address the challenges during multi-person generation. Specifically, for audio injection, we investigate several schemes and propose the Label Rotary Position Embedding (L-RoPE) method to resolve the audio and person binding problem. Furthermore, during training, we observe that partial parameter training and multi-task training are crucial for preserving the instruction-following ability of the base model. MultiTalk achieves superior performance compared to other methods on several datasets, including talking head, talking body, and multi-person datasets, demonstrating the powerful generation capabilities of our approach.
MG-MotionLLM: A Unified Framework for Motion Comprehension and Generation across Multiple Granularities
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Recent motion-aware large language models have demonstrated promising potential in unifying motion comprehension and generation. However, existing approaches primarily focus on coarse-grained motion-text modeling, where text describes the overall semantics of an entire motion sequence in just a few words. This limits their ability to handle fine-grained motion-relevant tasks, such as understanding and controlling the movements of specific body parts. To overcome this limitation, we pioneer MG-MotionLLM, a unified motion-language model for multi-granular motion comprehension and generation. We further introduce a comprehensive multi-granularity training scheme by incorporating a set of novel auxiliary tasks, such as localizing temporal boundaries of motion segments via detailed text as well as motion detailed captioning, to facilitate mutual reinforcement for motion-text modeling across various levels of granularity. Extensive experiments show that our MG-MotionLLM achieves superior performance on classical text-to-motion and motion-to-text tasks, and exhibits potential in novel fine-grained motion comprehension and editing tasks. Project page: CVI-SZU/MG-MotionLLM
StereoCrafter: Diffusion-based Generation of Long and High-fidelity Stereoscopic 3D from Monocular Videos
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a novel framework for converting 2D videos to immersive stereoscopic 3D, addressing the growing demand for 3D content in immersive experience. Leveraging foundation models as priors, our approach overcomes the limitations of traditional methods and boosts the performance to ensure the high-fidelity generation required by the display devices. The proposed system consists of two main steps: depth-based video splatting for warping and extracting occlusion mask, and stereo video inpainting. We utilize pre-trained stable video diffusion as the backbone and introduce a fine-tuning protocol for the stereo video inpainting task. To handle input video with varying lengths and resolutions, we explore auto-regressive strategies and tiled processing. Finally, a sophisticated data processing pipeline has been developed to reconstruct a large-scale and high-quality dataset to support our training. Our framework demonstrates significant improvements in 2D-to-3D video conversion, offering a practical solution for creating immersive content for 3D devices like Apple Vision Pro and 3D displays. In summary, this work contributes to the field by presenting an effective method for generating high-quality stereoscopic videos from monocular input, potentially transforming how we experience digital media.
OMG: Occlusion-friendly Personalized Multi-concept Generation in Diffusion Models
Mar 16, 2024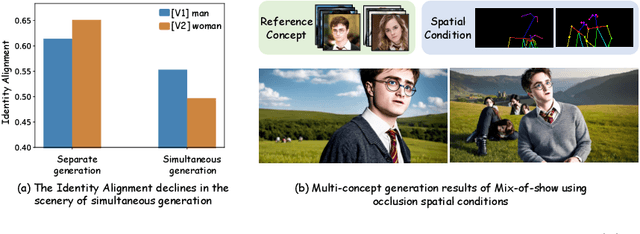
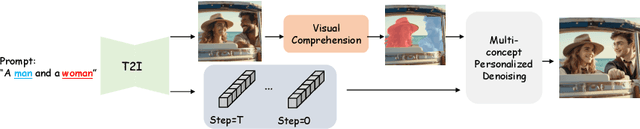
Abstract:Personalization is an important topic in text-to-image generation, especially the challenging multi-concept personalization. Current multi-concept methods are struggling with identity preservation, occlusion, and the harmony between foreground and background. In this work, we propose OMG, an occlusion-friendly personalized generation framework designed to seamlessly integrate multiple concepts within a single image. We propose a novel two-stage sampling solution. The first stage takes charge of layout generation and visual comprehension information collection for handling occlusions. The second one utilizes the acquired visual comprehension information and the designed noise blending to integrate multiple concepts while considering occlusions. We also observe that the initiation denoising timestep for noise blending is the key to identity preservation and layout. Moreover, our method can be combined with various single-concept models, such as LoRA and InstantID without additional tuning. Especially, LoRA models on civitai.com can be exploited directly. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OMG exhibits superior performance in multi-concept personalization.
Dual Teacher Knowledge Distillation with Domain Alignment for Face Anti-spoofing
Jan 02, 2024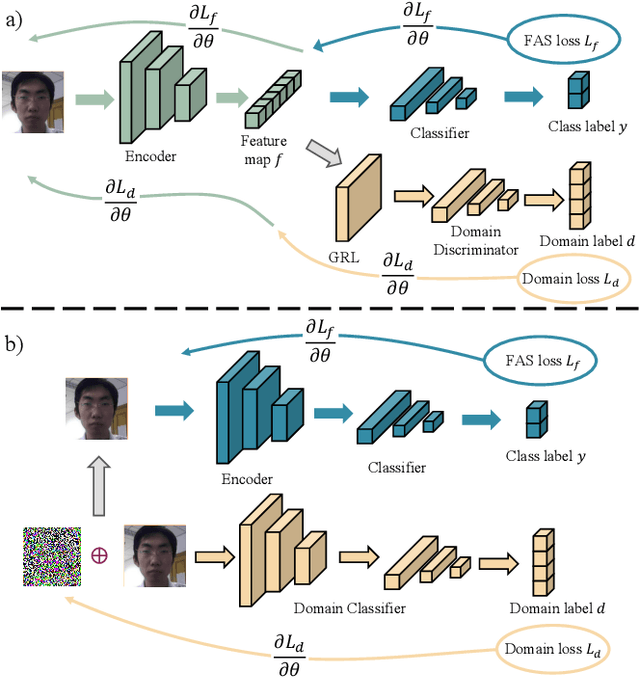
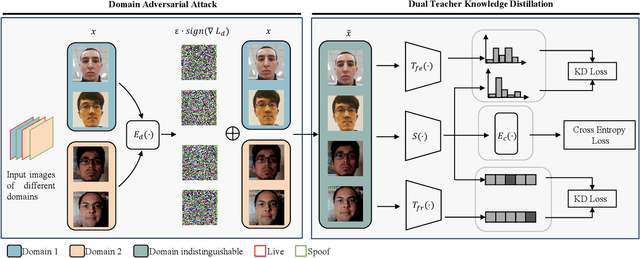
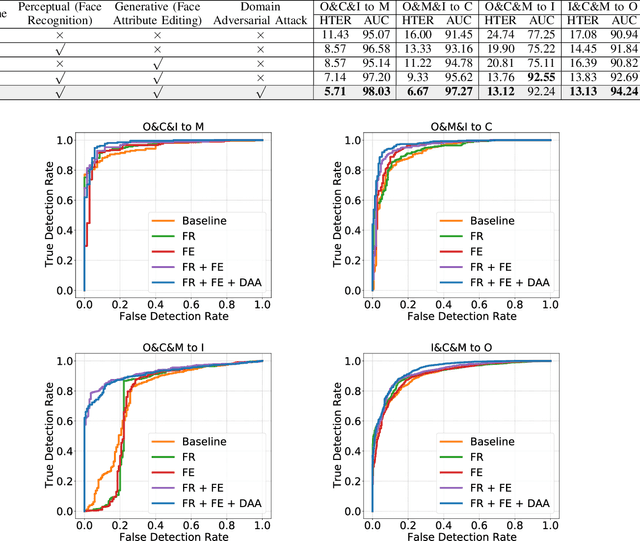
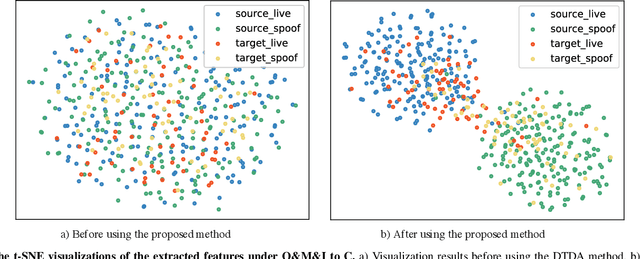
Abstract:Face recognition systems have raised concerns due to their vulnerability to different presentation attacks, and system security has become an increasingly critical concern. Although many face anti-spoofing (FAS) methods perform well in intra-dataset scenarios, their generalization remains a challenge. To address this issue, some methods adopt domain adversarial training (DAT) to extract domain-invariant features. However, the competition between the encoder and the domain discriminator can cause the network to be difficult to train and converge. In this paper, we propose a domain adversarial attack (DAA) method to mitigate the training instability problem by adding perturbations to the input images, which makes them indistinguishable across domains and enables domain alignment. Moreover, since models trained on limited data and types of attacks cannot generalize well to unknown attacks, we propose a dual perceptual and generative knowledge distillation framework for face anti-spoofing that utilizes pre-trained face-related models containing rich face priors. Specifically, we adopt two different face-related models as teachers to transfer knowledge to the target student model. The pre-trained teacher models are not from the task of face anti-spoofing but from perceptual and generative tasks, respectively, which implicitly augment the data. By combining both DAA and dual-teacher knowledge distillation, we develop a dual teacher knowledge distillation with domain alignment framework (DTDA) for face anti-spoofing. The advantage of our proposed method has been verified through extensive ablation studies and comparison with state-of-the-art methods on public datasets across multiple protocols.
Fingerprint Presentation Attack Detection by Channel-wise Feature Denoising
Nov 15, 2021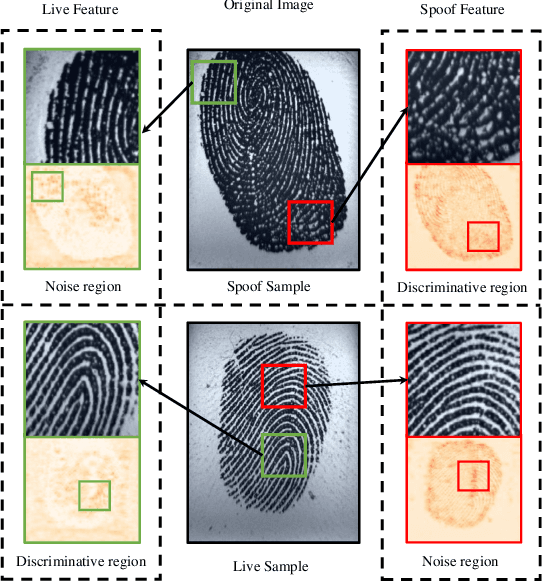
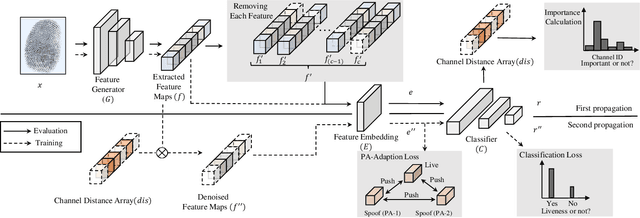
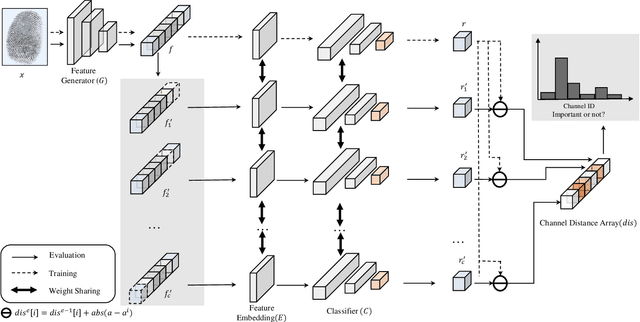

Abstract:Due to the diversity of attack materials, fingerprint recognition systems (AFRSs) are vulnerable to malicious attacks. It is of great importance to propose effective Fingerprint Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) methods for the safety and reliability of AFRSs. However, current PAD methods often have poor robustness under new attack materials or sensor settings. This paper thus proposes a novel Channel-wise Feature Denoising fingerprint PAD (CFD-PAD) method by considering handling the redundant "noise" information which ignored in previous works. The proposed method learned important features of fingerprint images by weighting the importance of each channel and finding those discriminative channels and "noise" channels. Then, the propagation of "noise" channels is suppressed in the feature map to reduce interference. Specifically, a PA-Adaption loss is designed to constrain the feature distribution so as to make the feature distribution of live fingerprints more aggregate and spoof fingerprints more disperse. Our experimental results evaluated on LivDet 2017 showed that our proposed CFD-PAD can achieve 2.53% ACE and 93.83% True Detection Rate when the False Detection Rate equals to 1.0% (TDR@FDR=1%) and it outperforms the best single model based methods in terms of ACE (2.53% vs. 4.56%) and TDR@FDR=1%(93.83% vs. 73.32\%) significantly, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed method. Although we have achieved a comparable result compared with the state-of-the-art multiple model based method, there still achieves an increase of TDR@FDR=1% from 91.19% to 93.83% by our method. Besides, our model is simpler, lighter and, more efficient and has achieved a 74.76% reduction in time-consuming compared with the state-of-the-art multiple model based method. Code will be publicly available.
Taming Self-Supervised Learning for Presentation Attack Detection: In-Image De-Folding and Out-of-Image De-Mixing
Sep 09, 2021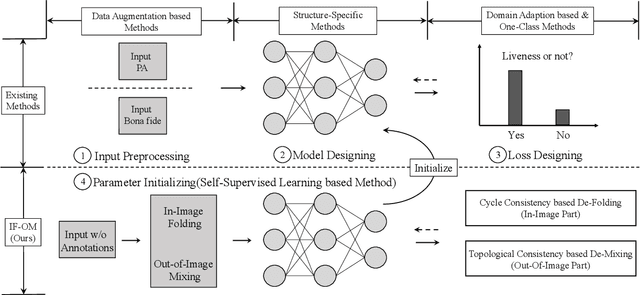
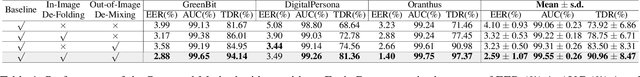
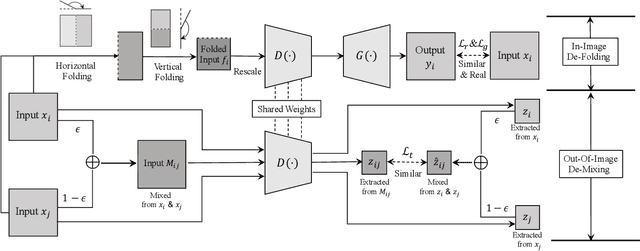
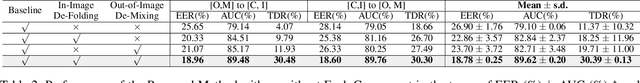
Abstract:Biometric systems are vulnerable to the Presentation Attacks (PA) performed using various Presentation Attack Instruments (PAIs). Even though there are numerous Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) techniques based on both deep learning and hand-crafted features, the generalization of PAD for unknown PAI is still a challenging problem. The common problem with existing deep learning-based PAD techniques is that they may struggle with local optima, resulting in weak generalization against different PAs. In this work, we propose to use self-supervised learning to find a reasonable initialization against local trap, so as to improve the generalization ability in detecting PAs on the biometric system.The proposed method, denoted as IF-OM, is based on a global-local view coupled with De-Folding and De-Mixing to derive the task-specific representation for PAD.During De-Folding, the proposed technique will learn region-specific features to represent samples in a local pattern by explicitly maximizing cycle consistency. While, De-Mixing drives detectors to obtain the instance-specific features with global information for more comprehensive representation by maximizing topological consistency. Extensive experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve significant improvements in terms of both face and fingerprint PAD in more complicated and hybrid datasets, when compared with the state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, when training in CASIA-FASD and Idiap Replay-Attack, the proposed method can achieve 18.60% Equal Error Rate (EER) in OULU-NPU and MSU-MFSD, exceeding baseline performance by 9.54%. Code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge