Yixin Zhang
World Models for Policy Refinement in StarCraft II
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently shown strong reasoning and generalization capabilities, motivating their use as decision-making policies in complex environments. StarCraft II (SC2), with its massive state-action space and partial observability, is a challenging testbed. However, existing LLM-based SC2 agents primarily focus on improving the policy itself and overlook integrating a learnable, action-conditioned transition model into the decision loop. To bridge this gap, we propose StarWM, the first world model for SC2 that predicts future observations under partial observability. To facilitate learning SC2's hybrid dynamics, we introduce a structured textual representation that factorizes observations into five semantic modules, and construct SC2-Dynamics-50k, the first instruction-tuning dataset for SC2 dynamics prediction. We further develop a multi-dimensional offline evaluation framework for predicted structured observations. Offline results show StarWM's substantial gains over zero-shot baselines, including nearly 60% improvements in resource prediction accuracy and self-side macro-situation consistency. Finally, we propose StarWM-Agent, a world-model-augmented decision system that integrates StarWM into a Generate--Simulate--Refine decision loop for foresight-driven policy refinement. Online evaluation against SC2's built-in AI demonstrates consistent improvements, yielding win-rate gains of 30%, 15%, and 30% against Hard (LV5), Harder (LV6), and VeryHard (LV7), respectively, alongside improved macro-management stability and tactical risk assessment.
Evaluating an evidence-guided reinforcement learning framework in aligning light-parameter large language models with decision-making cognition in psychiatric clinical reasoning
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold transformative potential for medical decision support yet their application in psychiatry remains constrained by hallucinations and superficial reasoning. This limitation is particularly acute in light-parameter LLMs which are essential for privacy-preserving and efficient clinical deployment. Existing training paradigms prioritize linguistic fluency over structured clinical logic and result in a fundamental misalignment with professional diagnostic cognition. Here we introduce ClinMPO, a reinforcement learning framework designed to align the internal reasoning of LLMs with professional psychiatric practice. The framework employs a specialized reward model trained independently on a dataset derived from 4,474 psychiatry journal articles and structured according to evidence-based medicine principles. We evaluated ClinMPO on a unseen subset of the benchmark designed to isolate reasoning capabilities from rote memorization. This test set comprises items where leading large-parameter LLMs consistently fail. We compared the ClinMPO-aligned light LLM performance against a cohort of 300 medical students. The ClinMPO-tuned Qwen3-8B model achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 31.4% and surpassed the human benchmark of 30.8% on these complex cases. These results demonstrate that medical evidence-guided optimization enables light-parameter LLMs to master complex reasoning tasks. Our findings suggest that explicit cognitive alignment offers a scalable pathway to reliable and safe psychiatric decision support.
Speech-Aware Long Context Pruning and Integration for Contextualized Automatic Speech Recognition
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems have achieved remarkable performance in common conditions but often struggle to leverage long-context information in contextualized scenarios that require domain-specific knowledge, such as conference presentations. This challenge arises primarily due to constrained model context windows and the sparsity of relevant information within extensive contextual noise. To solve this, we propose the SAP$^{2}$ method, a novel framework that dynamically prunes and integrates relevant contextual keywords in two stages. Specifically, each stage leverages our proposed Speech-Driven Attention-based Pooling mechanism, enabling efficient compression of context embeddings while preserving speech-salient information. Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance of SAP$^{2}$ on the SlideSpeech and LibriSpeech datasets, achieving word error rates (WER) of 7.71% and 1.12%, respectively. On SlideSpeech, our method notably reduces biased keyword error rates (B-WER) by 41.1% compared to non-contextual baselines. SAP$^{2}$ also exhibits robust scalability, consistently maintaining performance under extensive contextual input conditions on both datasets.
MCOP: Multi-UAV Collaborative Occupancy Prediction
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarm systems necessitate efficient collaborative perception mechanisms for diverse operational scenarios. Current Bird's Eye View (BEV)-based approaches exhibit two main limitations: bounding-box representations fail to capture complete semantic and geometric information of the scene, and their performance significantly degrades when encountering undefined or occluded objects. To address these limitations, we propose a novel multi-UAV collaborative occupancy prediction framework. Our framework effectively preserves 3D spatial structures and semantics through integrating a Spatial-Aware Feature Encoder and Cross-Agent Feature Integration. To enhance efficiency, we further introduce Altitude-Aware Feature Reduction to compactly represent scene information, along with a Dual-Mask Perceptual Guidance mechanism to adaptively select features and reduce communication overhead. Due to the absence of suitable benchmark datasets, we extend three datasets for evaluation: two virtual datasets (Air-to-Pred-Occ and UAV3D-Occ) and one real-world dataset (GauUScene-Occ). Experiments results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, significantly outperforming existing collaborative methods while reducing communication overhead to only a fraction of previous approaches.
DAG-AFL:Directed Acyclic Graph-based Asynchronous Federated Learning
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Due to the distributed nature of federated learning (FL), the vulnerability of the global model and the need for coordination among many client devices pose significant challenges. As a promising decentralized, scalable and secure solution, blockchain-based FL methods have attracted widespread attention in recent years. However, traditional consensus mechanisms designed for Proof of Work (PoW) similar to blockchain incur substantial resource consumption and compromise the efficiency of FL, particularly when participating devices are wireless and resource-limited. To address asynchronous client participation and data heterogeneity in FL, while limiting the additional resource overhead introduced by blockchain, we propose the Directed Acyclic Graph-based Asynchronous Federated Learning (DAG-AFL) framework. We develop a tip selection algorithm that considers temporal freshness, node reachability and model accuracy, with a DAG-based trusted verification strategy. Extensive experiments on 3 benchmarking datasets against eight state-of-the-art approaches demonstrate that DAG-AFL significantly improves training efficiency and model accuracy by 22.7% and 6.5% on average, respectively.
LLM Agent for Hyper-Parameter Optimization
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Hyper-parameters are essential and critical for the performance of communication algorithms. However, current hyper-parameters tuning methods for warm-start particles swarm optimization with cross and mutation (WS-PSO-CM) algortihm for radio map-enabled unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) trajectory and communication are primarily heuristic-based, exhibiting low levels of automation and unsatisfactory performance. In this paper, we design an large language model (LLM) agent for automatic hyper-parameters-tuning, where an iterative framework and model context protocol (MCP) are applied. In particular, the LLM agent is first setup via a profile, which specifies the mission, background, and output format. Then, the LLM agent is driven by the prompt requirement, and iteratively invokes WS-PSO-CM algorithm for exploration. Finally, the LLM agent autonomously terminates the loop and returns a set of hyper-parameters. Our experiment results show that the minimal sum-rate achieved by hyper-parameters generated via our LLM agent is significantly higher than those by both human heuristics and random generation methods. This indicates that an LLM agent with PSO knowledge and WS-PSO-CM algorithm background is useful in finding high-performance hyper-parameters.
The Role of Machine Learning in Reducing Healthcare Costs: The Impact of Medication Adherence and Preventive Care on Hospitalization Expenses
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:This study reveals the important role of prevention care and medication adherence in reducing hospitalizations. By using a structured dataset of 1,171 patients, four machine learning models Logistic Regression, Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, and Artificial Neural Networks are applied to predict five-year hospitalization risk, with the Gradient Boosting model achieving the highest accuracy of 81.2%. The result demonstrated that patients with high medication adherence and consistent preventive care can reduce 38.3% and 37.7% in hospitalization risk. The finding also suggests that targeted preventive care can have positive Return on Investment (ROI), and therefore ML models can effectively direct personalized interventions and contribute to long-term medical savings.
LVC: A Lightweight Compression Framework for Enhancing VLMs in Long Video Understanding
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Long video understanding is a complex task that requires both spatial detail and temporal awareness. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) obtain frame-level understanding capabilities through multi-frame input, they suffer from information loss due to the sparse sampling strategy. In contrast, Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) capture temporal relationships within visual features but are limited by the scarcity of high-quality video-text datasets. To transfer long video understanding capabilities to VLMs with minimal data and computational cost, we propose Lightweight Video Compression (LVC), a novel method featuring the Query-Attention Video Compression mechanism, which effectively tackles the sparse sampling problem in VLMs. By training only the alignment layer with 10k short video-text pairs, LVC significantly enhances the temporal reasoning abilities of VLMs. Extensive experiments show that LVC provides consistent performance improvements across various models, including the InternVL2 series and Phi-3.5-Vision. Notably, the InternVL2-40B-LVC achieves scores of 68.2 and 65.9 on the long video understanding benchmarks MLVU and Video-MME, respectively, with relative improvements of 14.6% and 7.7%. The enhanced models and code will be publicly available soon.
Multipath Component-Aided Signal Processing for Integrated Sensing and Communication Systems
Dec 31, 2024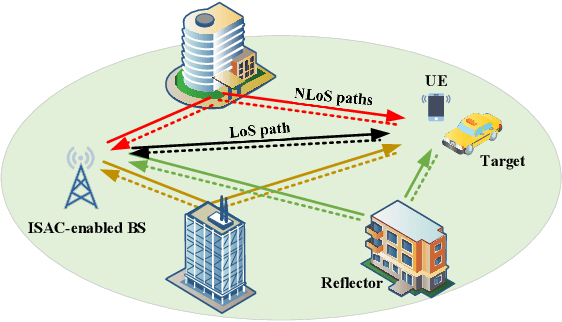
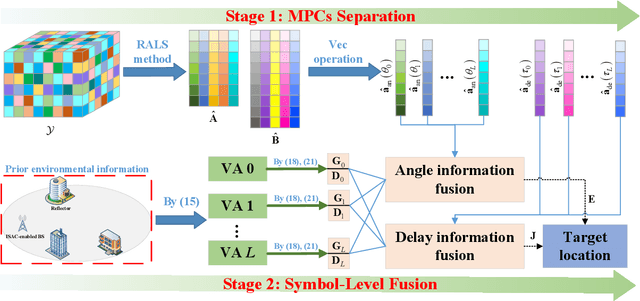
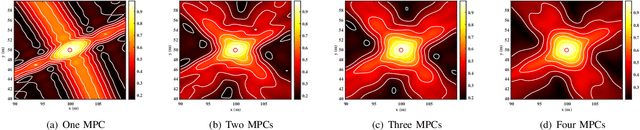
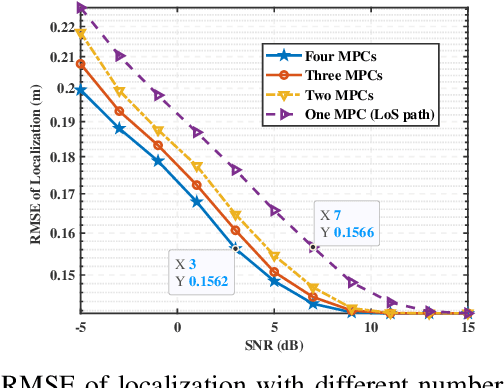
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has emerged as a pivotal enabling technology for sixth-generation (6G) mobile communication system. The ISAC research in dense urban areas has been plaguing by severe multipath interference, propelling the thorough research of ISAC multipath interference elimination. However, transforming the multipath component (MPC) from enemy into friend is a viable and mutually beneficial option. In this paper, we preliminarily explore the MPC-aided ISAC signal processing and apply a space-time code to improve the ISAC performance. Specifically, we propose a symbol-level fusion for MPC-aided localization (SFMC) scheme to achieve robust and high-accuracy localization, and apply a Khatri-Rao space-time (KRST) code to improve the communication and sensing performance in rich multipath environment. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed SFMC scheme has more robust localization performance with higher accuracy, compared with the existing state-of-the-art schemes. The proposed SFMC would benefit highly reliable communication and sub-meter level localization in rich multipath scenarios.
How to select slices for annotation to train best-performing deep learning segmentation models for cross-sectional medical images?
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Automated segmentation of medical images highly depends on the availability of accurate manual image annotations. Such annotations are very time-consuming and costly to generate, and often require specialized expertise, particularly for cross-sectional images which contain many slices for each patient. It is crucial to ensure the best use of annotation resources. In this paper, we systematically answer the question of how to select slices of cross-sectional medical images in order to maximize performance of the resulting deep learning segmentation models. We conducted experiments on 4 medical imaging segmentation tasks with varying annotation budgets, numbers of annotated cases, numbers of annotated slices per volume, slice selection techniques, and mask interpolations. We found that: 1) It is almost always preferable to annotate fewer slices per volume and more volumes given an annotation budget. 2) Selecting slices for annotation by unsupervised active learning (UAL) is not superior to selecting slices randomly or at fixed intervals, provided that each volume is allocated the same number of annotated slices. 3) Interpolating masks between annotated slices rarely enhances model performance, with exceptions of some specific configuration for 3D models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge