Zhiqi Shen
Following the TRAIL: Predicting and Explaining Tomorrow's Hits with a Fine-Tuned LLM
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been widely applied across multiple domains for their broad knowledge and strong reasoning capabilities. However, applying them to recommendation systems is challenging since it is hard for LLMs to extract user preferences from large, sparse user-item logs, and real-time per-user ranking over the full catalog is too time-consuming to be practical. Moreover, many existing recommender systems focus solely on ranking items while overlooking explanations, which could help improve predictive accuracy and make recommendations more convincing to users. Inspired by recent works that achieve strong recommendation performance by forecasting near-term item popularity, we propose TRAIL (TRend and explAnation Integrated Learner). TRAIL is a fine-tuned LLM that jointly predicts short-term item popularity and generates faithful natural-language explanations. It employs contrastive learning with positive and negative pairs to align its scores and explanations with structured trend signals, yielding accurate and explainable popularity predictions. Extensive experiments show that TRAIL outperforms strong baselines and produces coherent, well-grounded explanations.
Towards Comprehensive Stage-wise Benchmarking of Large Language Models in Fact-Checking
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world fact-checking systems, yet existing evaluations focus predominantly on claim verification and overlook the broader fact-checking workflow, including claim extraction and evidence retrieval. This narrow focus prevents current benchmarks from revealing systematic reasoning failures, factual blind spots, and robustness limitations of modern LLMs. To bridge this gap, we present FactArena, a fully automated arena-style evaluation framework that conducts comprehensive, stage-wise benchmarking of LLMs across the complete fact-checking pipeline. FactArena integrates three key components: (i) an LLM-driven fact-checking process that standardizes claim decomposition, evidence retrieval via tool-augmented interactions, and justification-based verdict prediction; (ii) an arena-styled judgment mechanism guided by consolidated reference guidelines to ensure unbiased and consistent pairwise comparisons across heterogeneous judge agents; and (iii) an arena-driven claim-evolution module that adaptively generates more challenging and semantically controlled claims to probe LLMs' factual robustness beyond fixed seed data. Across 16 state-of-the-art LLMs spanning seven model families, FactArena produces stable and interpretable rankings. Our analyses further reveal significant discrepancies between static claim-verification accuracy and end-to-end fact-checking competence, highlighting the necessity of holistic evaluation. The proposed framework offers a scalable and trustworthy paradigm for diagnosing LLMs' factual reasoning, guiding future model development, and advancing the reliable deployment of LLMs in safety-critical fact-checking applications.
MCP-SafetyBench: A Benchmark for Safety Evaluation of Large Language Models with Real-World MCP Servers
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are evolving into agentic systems that reason, plan, and operate external tools. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a key enabler of this transition, offering a standardized interface for connecting LLMs with heterogeneous tools and services. Yet MCP's openness and multi-server workflows introduce new safety risks that existing benchmarks fail to capture, as they focus on isolated attacks or lack real-world coverage. We present MCP-SafetyBench, a comprehensive benchmark built on real MCP servers that supports realistic multi-turn evaluation across five domains: browser automation, financial analysis, location navigation, repository management, and web search. It incorporates a unified taxonomy of 20 MCP attack types spanning server, host, and user sides, and includes tasks requiring multi-step reasoning and cross-server coordination under uncertainty. Using MCP-SafetyBench, we systematically evaluate leading open- and closed-source LLMs, revealing large disparities in safety performance and escalating vulnerabilities as task horizons and server interactions grow. Our results highlight the urgent need for stronger defenses and establish MCP-SafetyBench as a foundation for diagnosing and mitigating safety risks in real-world MCP deployments.
EHRStruct: A Comprehensive Benchmark Framework for Evaluating Large Language Models on Structured Electronic Health Record Tasks
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Structured Electronic Health Record (EHR) data stores patient information in relational tables and plays a central role in clinical decision-making. Recent advances have explored the use of large language models (LLMs) to process such data, showing promise across various clinical tasks.However, the absence of standardized evaluation frameworks and clearly defined tasks makes it difficult to systematically assess and compare LLM performance on structured EHR data.To address these evaluation challenges, we introduce EHRStruct, a benchmark specifically designed to evaluate LLMs on structured EHR tasks.EHRStruct defines 11 representative tasks spanning diverse clinical needs and includes 2,200 task-specific evaluation samples derived from two widely used EHR datasets.We use EHRStruct to evaluate 20 advanced and representative LLMs, covering both general and medical models.We further analyze key factors influencing model performance, including input formats, few-shot generalisation, and finetuning strategies, and compare results with 11 state-of-the-art LLM-based enhancement methods for structured data reasoning. Our results indicate that many structured EHR tasks place high demands on the understanding and reasoning capabilities of LLMs.In response, we propose EHRMaster, a code-augmented method that achieves state-of-the-art performance and offers practical
Is Meta-Learning Out? Rethinking Unsupervised Few-Shot Classification with Limited Entropy
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:Meta-learning is a powerful paradigm for tackling few-shot tasks. However, recent studies indicate that models trained with the whole-class training strategy can achieve comparable performance to those trained with meta-learning in few-shot classification tasks. To demonstrate the value of meta-learning, we establish an entropy-limited supervised setting for fair comparisons. Through both theoretical analysis and experimental validation, we establish that meta-learning has a tighter generalization bound compared to whole-class training. We unravel that meta-learning is more efficient with limited entropy and is more robust to label noise and heterogeneous tasks, making it well-suited for unsupervised tasks. Based on these insights, We propose MINO, a meta-learning framework designed to enhance unsupervised performance. MINO utilizes the adaptive clustering algorithm DBSCAN with a dynamic head for unsupervised task construction and a stability-based meta-scaler for robustness against label noise. Extensive experiments confirm its effectiveness in multiple unsupervised few-shot and zero-shot tasks.
MCP-Universe: Benchmarking Large Language Models with Real-World Model Context Protocol Servers
Aug 20, 2025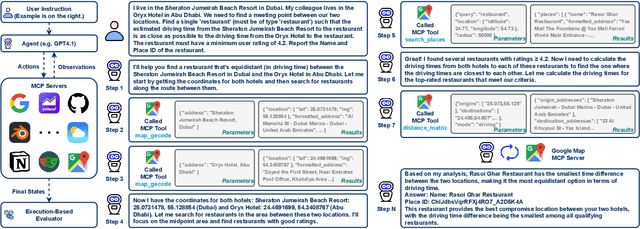
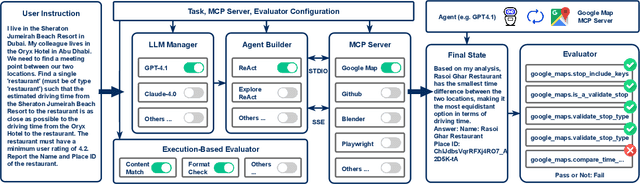
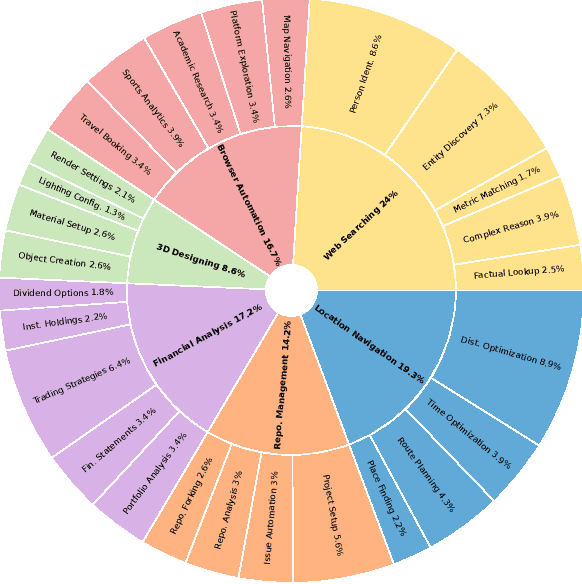
Abstract:The Model Context Protocol has emerged as a transformative standard for connecting large language models to external data sources and tools, rapidly gaining adoption across major AI providers and development platforms. However, existing benchmarks are overly simplistic and fail to capture real application challenges such as long-horizon reasoning and large, unfamiliar tool spaces. To address this critical gap, we introduce MCP-Universe, the first comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to evaluate LLMs in realistic and hard tasks through interaction with real-world MCP servers. Our benchmark encompasses 6 core domains spanning 11 different MCP servers: Location Navigation, Repository Management, Financial Analysis, 3D Design, Browser Automation, and Web Searching. To ensure rigorous evaluation, we implement execution-based evaluators, including format evaluators for agent format compliance, static evaluators for time-invariant content matching, and dynamic evaluators that automatically retrieve real-time ground truth for temporally sensitive tasks. Through extensive evaluation of leading LLMs, we find that even SOTA models such as GPT-5 (43.72%), Grok-4 (33.33%) and Claude-4.0-Sonnet (29.44%) exhibit significant performance limitations. In addition, our benchmark poses a significant long-context challenge for LLM agents, as the number of input tokens increases rapidly with the number of interaction steps. Moreover, it introduces an unknown-tools challenge, as LLM agents often lack familiarity with the precise usage of the MCP servers. Notably, enterprise-level agents like Cursor cannot achieve better performance than standard ReAct frameworks. Beyond evaluation, we open-source our extensible evaluation framework with UI support, enabling researchers and practitioners to seamlessly integrate new agents and MCP servers while fostering innovation in the rapidly evolving MCP ecosystem.
Semantic Item Graph Enhancement for Multimodal Recommendation
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Multimodal recommendation systems have attracted increasing attention for their improved performance by leveraging items' multimodal information. Prior methods often build modality-specific item-item semantic graphs from raw modality features and use them as supplementary structures alongside the user-item interaction graph to enhance user preference learning. However, these semantic graphs suffer from semantic deficiencies, including (1) insufficient modeling of collaborative signals among items and (2) structural distortions introduced by noise in raw modality features, ultimately compromising performance. To address these issues, we first extract collaborative signals from the interaction graph and infuse them into each modality-specific item semantic graph to enhance semantic modeling. Then, we design a modulus-based personalized embedding perturbation mechanism that injects perturbations with modulus-guided personalized intensity into embeddings to generate contrastive views. This enables the model to learn noise-robust representations through contrastive learning, thereby reducing the effect of structural noise in semantic graphs. Besides, we propose a dual representation alignment mechanism that first aligns multiple semantic representations via a designed Anchor-based InfoNCE loss using behavior representations as anchors, and then aligns behavior representations with the fused semantics by standard InfoNCE, to ensure representation consistency. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of our framework.
Does Multimodality Improve Recommender Systems as Expected? A Critical Analysis and Future Directions
Aug 07, 2025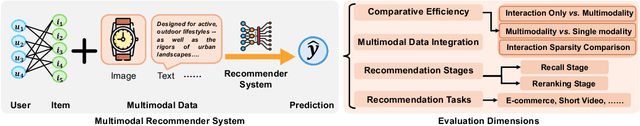
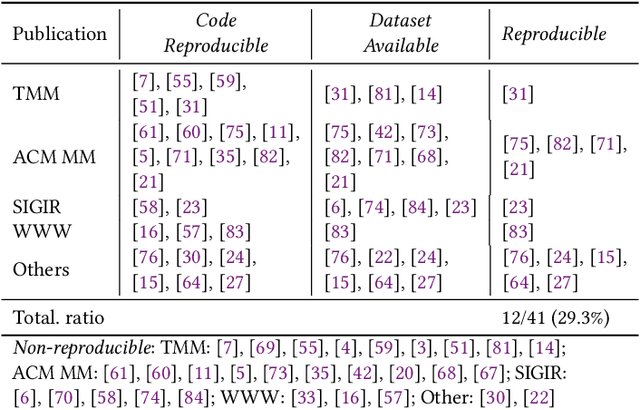
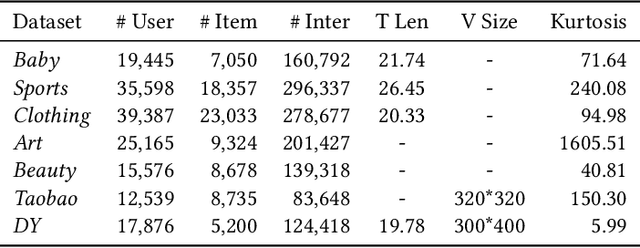
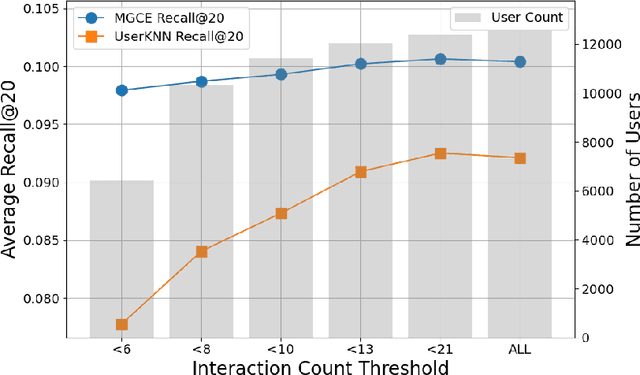
Abstract:Multimodal recommendation systems are increasingly popular for their potential to improve performance by integrating diverse data types. However, the actual benefits of this integration remain unclear, raising questions about when and how it truly enhances recommendations. In this paper, we propose a structured evaluation framework to systematically assess multimodal recommendations across four dimensions: Comparative Efficiency, Recommendation Tasks, Recommendation Stages, and Multimodal Data Integration. We benchmark a set of reproducible multimodal models against strong traditional baselines and evaluate their performance on different platforms. Our findings show that multimodal data is particularly beneficial in sparse interaction scenarios and during the recall stage of recommendation pipelines. We also observe that the importance of each modality is task-specific, where text features are more useful in e-commerce and visual features are more effective in short-video recommendations. Additionally, we explore different integration strategies and model sizes, finding that Ensemble-Based Learning outperforms Fusion-Based Learning, and that larger models do not necessarily deliver better results. To deepen our understanding, we include case studies and review findings from other recommendation domains. Our work provides practical insights for building efficient and effective multimodal recommendation systems, emphasizing the need for thoughtful modality selection, integration strategies, and model design.
Response Uncertainty and Probe Modeling: Two Sides of the Same Coin in LLM Interpretability?
May 24, 2025Abstract:Probing techniques have shown promise in revealing how LLMs encode human-interpretable concepts, particularly when applied to curated datasets. However, the factors governing a dataset's suitability for effective probe training are not well-understood. This study hypothesizes that probe performance on such datasets reflects characteristics of both the LLM's generated responses and its internal feature space. Through quantitative analysis of probe performance and LLM response uncertainty across a series of tasks, we find a strong correlation: improved probe performance consistently corresponds to a reduction in response uncertainty, and vice versa. Subsequently, we delve deeper into this correlation through the lens of feature importance analysis. Our findings indicate that high LLM response variance is associated with a larger set of important features, which poses a greater challenge for probe models and often results in diminished performance. Moreover, leveraging the insights from response uncertainty analysis, we are able to identify concrete examples where LLM representations align with human knowledge across diverse domains, offering additional evidence of interpretable reasoning in LLMs.
Knowledge Retrieval in LLM Gaming: A Shift from Entity-Centric to Goal-Oriented Graphs
May 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive general capabilities but often struggle with step-by-step reasoning, especially in complex applications such as games. While retrieval-augmented methods like GraphRAG attempt to bridge this gap through cross-document extraction and indexing, their fragmented entity-relation graphs and overly dense local connectivity hinder the construction of coherent reasoning. In this paper, we propose a novel framework based on Goal-Oriented Graphs (GoGs), where each node represents a goal and its associated attributes, and edges encode logical dependencies between goals. This structure enables explicit retrieval of reasoning paths by first identifying high-level goals and recursively retrieving their subgoals, forming coherent reasoning chains to guide LLM prompting. Our method significantly enhances the reasoning ability of LLMs in game-playing tasks, as demonstrated by extensive experiments on the Minecraft testbed, outperforming GraphRAG and other baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge