TS-LIF: A Temporal Segment Spiking Neuron Network for Time Series Forecasting
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2025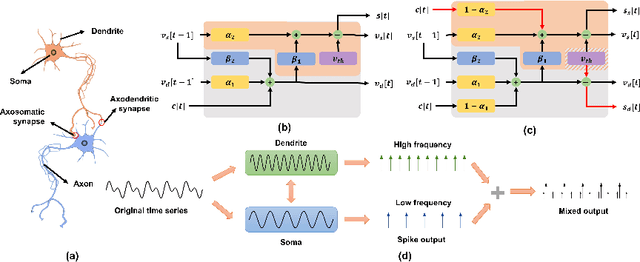



Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a promising, biologically inspired approach for processing spatiotemporal data, particularly for time series forecasting. However, conventional neuron models like the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) struggle to capture long-term dependencies and effectively process multi-scale temporal dynamics. To overcome these limitations, we introduce the Temporal Segment Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (TS-LIF) model, featuring a novel dual-compartment architecture. The dendritic and somatic compartments specialize in capturing distinct frequency components, providing functional heterogeneity that enhances the neuron's ability to process both low- and high-frequency information. Furthermore, the newly introduced direct somatic current injection reduces information loss during intra-neuronal transmission, while dendritic spike generation improves multi-scale information extraction. We provide a theoretical stability analysis of the TS-LIF model and explain how each compartment contributes to distinct frequency response characteristics. Experimental results show that TS-LIF outperforms traditional SNNs in time series forecasting, demonstrating better accuracy and robustness, even with missing data. TS-LIF advances the application of SNNs in time-series forecasting, providing a biologically inspired approach that captures complex temporal dynamics and offers potential for practical implementation in diverse forecasting scenarios. The source code is available at https://github.com/kkking-kk/TS-LIF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge