Zelei Liu
Federated Learning in Big Model Era: Domain-Specific Multimodal Large Models
Aug 24, 2023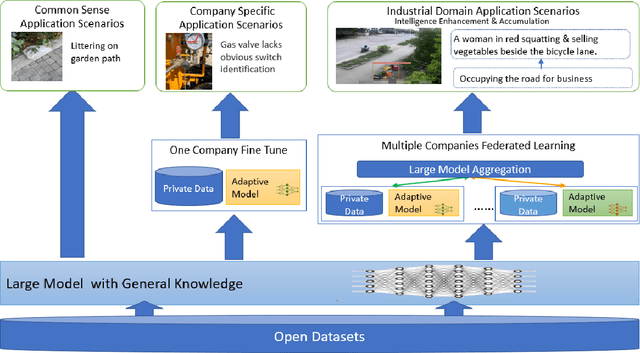
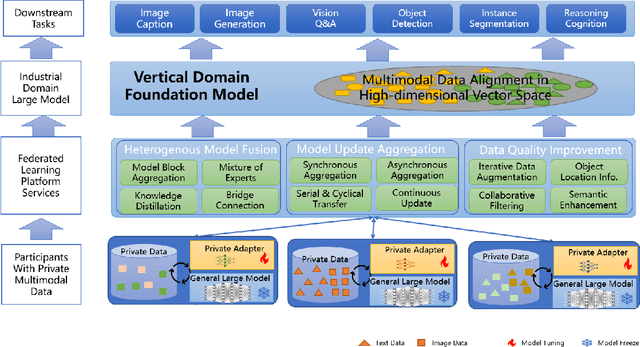
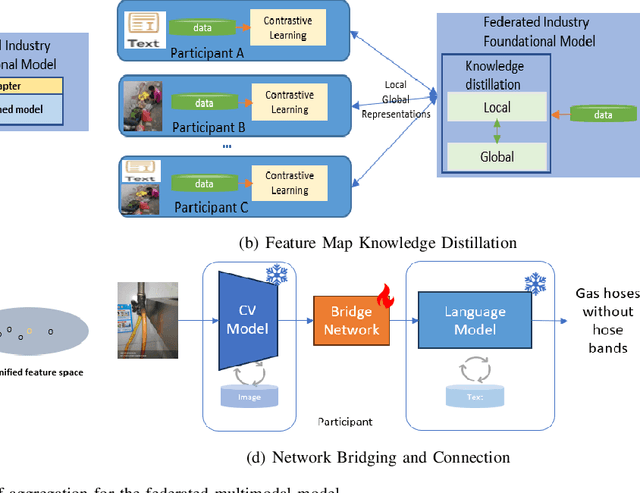
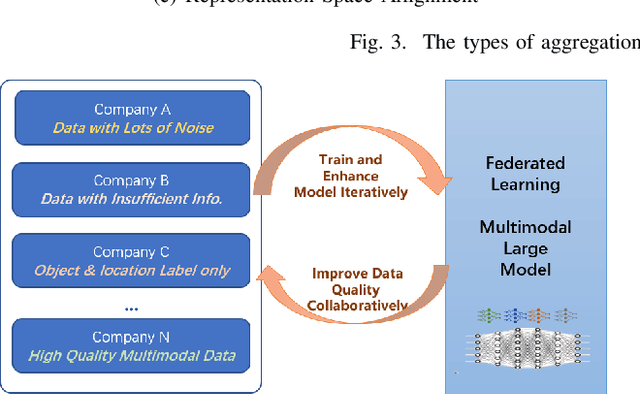
Abstract:Multimodal data, which can comprehensively perceive and recognize the physical world, has become an essential path towards general artificial intelligence. However, multimodal large models trained on public datasets often underperform in specific industrial domains. This paper proposes a multimodal federated learning framework that enables multiple enterprises to utilize private domain data to collaboratively train large models for vertical domains, achieving intelligent services across scenarios. The authors discuss in-depth the strategic transformation of federated learning in terms of intelligence foundation and objectives in the era of big model, as well as the new challenges faced in heterogeneous data, model aggregation, performance and cost trade-off, data privacy, and incentive mechanism. The paper elaborates a case study of leading enterprises contributing multimodal data and expert knowledge to city safety operation management , including distributed deployment and efficient coordination of the federated learning platform, technical innovations on data quality improvement based on large model capabilities and efficient joint fine-tuning approaches. Preliminary experiments show that enterprises can enhance and accumulate intelligent capabilities through multimodal model federated learning, thereby jointly creating an smart city model that provides high-quality intelligent services covering energy infrastructure safety, residential community security, and urban operation management. The established federated learning cooperation ecosystem is expected to further aggregate industry, academia, and research resources, realize large models in multiple vertical domains, and promote the large-scale industrial application of artificial intelligence and cutting-edge research on multimodal federated learning.
Fairness-Aware Client Selection for Federated Learning
Jul 20, 2023

Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has enabled multiple data owners (a.k.a. FL clients) to train machine learning models collaboratively without revealing private data. Since the FL server can only engage a limited number of clients in each training round, FL client selection has become an important research problem. Existing approaches generally focus on either enhancing FL model performance or enhancing the fair treatment of FL clients. The problem of balancing performance and fairness considerations when selecting FL clients remains open. To address this problem, we propose the Fairness-aware Federated Client Selection (FairFedCS) approach. Based on Lyapunov optimization, it dynamically adjusts FL clients' selection probabilities by jointly considering their reputations, times of participation in FL tasks and contributions to the resulting model performance. By not using threshold-based reputation filtering, it provides FL clients with opportunities to redeem their reputations after a perceived poor performance, thereby further enhancing fair client treatment. Extensive experiments based on real-world multimedia datasets show that FairFedCS achieves 19.6% higher fairness and 0.73% higher test accuracy on average than the best-performing state-of-the-art approach.
Efficient Training of Large-scale Industrial Fault Diagnostic Models through Federated Opportunistic Block Dropout
Feb 22, 2023Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI)-empowered industrial fault diagnostics is important in ensuring the safe operation of industrial applications. Since complex industrial systems often involve multiple industrial plants (possibly belonging to different companies or subsidiaries) with sensitive data collected and stored in a distributed manner, collaborative fault diagnostic model training often needs to leverage federated learning (FL). As the scale of the industrial fault diagnostic models are often large and communication channels in such systems are often not exclusively used for FL model training, existing deployed FL model training frameworks cannot train such models efficiently across multiple institutions. In this paper, we report our experience developing and deploying the Federated Opportunistic Block Dropout (FEDOBD) approach for industrial fault diagnostic model training. By decomposing large-scale models into semantic blocks and enabling FL participants to opportunistically upload selected important blocks in a quantized manner, it significantly reduces the communication overhead while maintaining model performance. Since its deployment in ENN Group in February 2022, FEDOBD has served two coal chemical plants across two cities in China to build industrial fault prediction models. It helped the company reduce the training communication overhead by over 70% compared to its previous AI Engine, while maintaining model performance at over 85% test F1 score. To our knowledge, it is the first successfully deployed dropout-based FL approach.
GTG-Shapley: Efficient and Accurate Participant Contribution Evaluation in Federated Learning
Sep 05, 2021



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) bridges the gap between collaborative machine learning and preserving data privacy. To sustain the long-term operation of an FL ecosystem, it is important to attract high quality data owners with appropriate incentive schemes. As an important building block of such incentive schemes, it is essential to fairly evaluate participants' contribution to the performance of the final FL model without exposing their private data. Shapley Value (SV)-based techniques have been widely adopted to provide fair evaluation of FL participant contributions. However, existing approaches incur significant computation costs, making them difficult to apply in practice. In this paper, we propose the Guided Truncation Gradient Shapley (GTG-Shapley) approach to address this challenge. It reconstructs FL models from gradient updates for SV calculation instead of repeatedly training with different combinations of FL participants. In addition, we design a guided Monte Carlo sampling approach combined with within-round and between-round truncation to further reduce the number of model reconstructions and evaluations required, through extensive experiments under diverse realistic data distribution settings. The results demonstrate that GTG-Shapley can closely approximate actual Shapley values, while significantly increasing computational efficiency compared to the state of the art, especially under non-i.i.d. settings.
FedCoin: A Peer-to-Peer Payment System for Federated Learning
Feb 26, 2020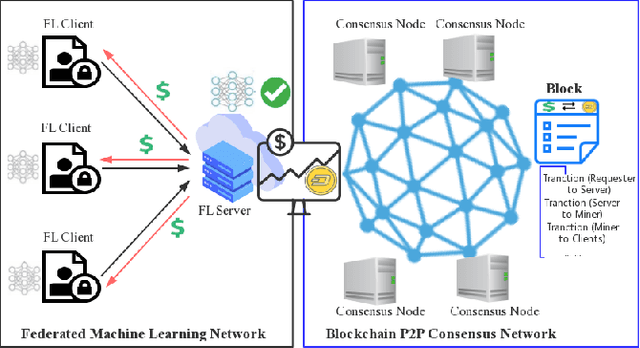
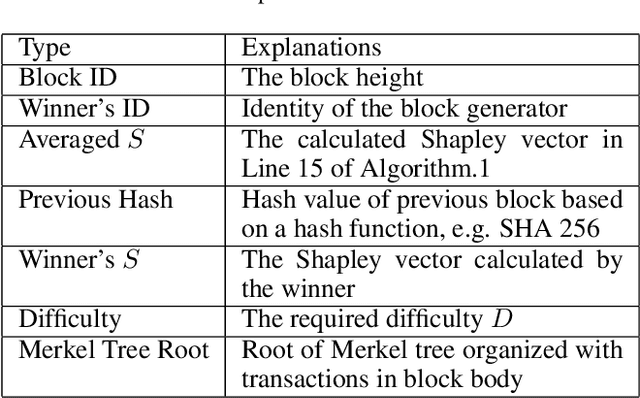
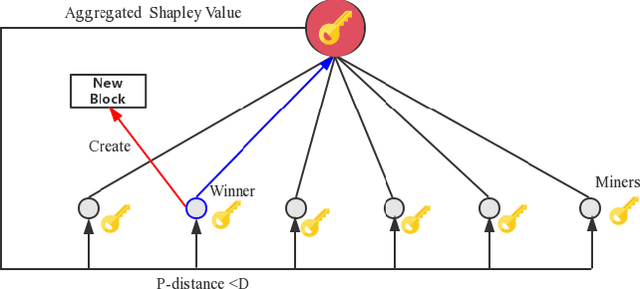
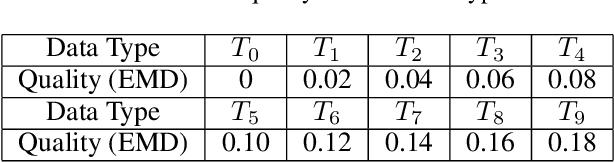
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is an emerging collaborative machine learning method to train models on distributed datasets with privacy concerns. To properly incentivize data owners to contribute their efforts, Shapley Value (SV) is often adopted to fairly assess their contribution. However, the calculation of SV is time-consuming and computationally costly. In this paper, we propose FedCoin, a blockchain-based peer-to-peer payment system for FL to enable a feasible SV based profit distribution. In FedCoin, blockchain consensus entities calculate SVs and a new block is created based on the proof of Shapley (PoSap) protocol. It is in contrast to the popular BitCoin network where consensus entities "mine" new blocks by solving meaningless puzzles. Based on the computed SVs, a scheme for dividing the incentive payoffs among FL clients with nonrepudiation and tamper-resistance properties is proposed. Experimental results based on real-world data show that FedCoin can promote high-quality data from FL clients through accurately computing SVs with an upper bound on the computational resources required for reaching consensus. It opens opportunities for non-data owners to play a role in FL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge