Zhendong Li
Beamforming for Transmissive RIS Transmitter Enabled Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer Systems
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates a novel transmissive reconfigurable intelligent surface (TRIS) transceiver-empowered simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) system with multiple information decoding (ID) and energy harvesting (EH) users. Under the considered system model, we formulate an optimization problem that maximizes the sum-rate of all ID users via the design of the TRIS transceiver's active beamforming. The design is constrained by per-antenna power limits at the TRIS transceiver and by the minimum harvested energy demand of all EH users. Due to the non-convexity of the objective function and the energy harvesting constraint, the sum-rate problem is difficult to tackle. To solve this challenging optimization problem, by leveraging the weighted minimum mean squared error (WMMSE) framework and the majorization-minimization (MM) method, we propose a second-order cone programming (SOCP)-based algorithm. Per-element power constraints introduce a large number of constraints, making the problem considerably more difficult. By applying the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) method, we successfully develop an analytical, computationally efficient, and highly parallelizable algorithm to address this challenge. Numerical results are provided to validate the convergence and effectiveness of the proposed algorithms. Furthermore, the low-complexity algorithm significantly reduces computational complexity without performance degradation.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-Scale Learning: An Efficient and User-Friendly Scaling Library
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce ROLL, an efficient, scalable, and user-friendly library designed for Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-scale Learning. ROLL caters to three primary user groups: tech pioneers aiming for cost-effective, fault-tolerant large-scale training, developers requiring flexible control over training workflows, and researchers seeking agile experimentation. ROLL is built upon several key modules to serve these user groups effectively. First, a single-controller architecture combined with an abstraction of the parallel worker simplifies the development of the training pipeline. Second, the parallel strategy and data transfer modules enable efficient and scalable training. Third, the rollout scheduler offers fine-grained management of each sample's lifecycle during the rollout stage. Fourth, the environment worker and reward worker support rapid and flexible experimentation with agentic RL algorithms and reward designs. Finally, AutoDeviceMapping allows users to assign resources to different models flexibly across various stages.
Movable Antennas Enabled ISAC Systems: Fundamentals, Opportunities, and Future Directions
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:The movable antenna (MA)-enabled integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system attracts widespread attention as an innovative framework. The ISAC system integrates sensing and communication functions, achieving resource sharing across various domains, significantly enhancing communication and sensing performance, and promoting the intelligent interconnection of everything. Meanwhile, MA utilizes the spatial variations of wireless channels by dynamically adjusting the positions of MA elements at the transmitter and receiver to improve the channel and further enhance the performance of the ISAC systems. In this paper, we first outline the fundamental principles of MA and introduce the application scenarios of MA-enabled ISAC systems. Then, we summarize the advantages of MA-enabled ISAC systems in enhancing spectral efficiency, achieving flexible and precise beamforming, and making the signal coverage range adjustable. Besides, a specific case is studied to show the performance gains in terms of transmit power that MA brings to ISAC systems. Finally, we discuss the challenges of MA-enabled ISAC and future research directions, aiming to provide insights for future research on MA-enabled ISAC systems.
UniLoc: Towards Universal Place Recognition Using Any Single Modality
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:To date, most place recognition methods focus on single-modality retrieval. While they perform well in specific environments, cross-modal methods offer greater flexibility by allowing seamless switching between map and query sources. It also promises to reduce computation requirements by having a unified model, and achieving greater sample efficiency by sharing parameters. In this work, we develop a universal solution to place recognition, UniLoc, that works with any single query modality (natural language, image, or point cloud). UniLoc leverages recent advances in large-scale contrastive learning, and learns by matching hierarchically at two levels: instance-level matching and scene-level matching. Specifically, we propose a novel Self-Attention based Pooling (SAP) module to evaluate the importance of instance descriptors when aggregated into a place-level descriptor. Experiments on the KITTI-360 dataset demonstrate the benefits of cross-modality for place recognition, achieving superior performance in cross-modal settings and competitive results also for uni-modal scenarios. Our project page is publicly available at https://yan-xia.github.io/projects/UniLoc/.
Joint Discrete Antenna Positioning and Beamforming Optimization in Movable Antenna Enabled Full-Duplex ISAC Networks
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a full-duplex integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system enabled by a movable antenna (MA). By leveraging the characteristic of MA that can increase the spatial diversity gain, the performance of the system can be enhanced. We formulate a problem of minimizing the total transmit power consumption via jointly optimizing the discrete position of MA elements, beamforming vectors, sensing signal covariance matrix and user transmit power. Given the significant coupling of optimization variables, the formulated problem presents a non-convex optimization challenge that poses difficulties for direct resolution. To address this challenging issue, the discrete binary particle swarm optimization (BPSO) algorithm framework is employed to solve the formulated problem. Specifically, the discrete positions of MA elements are first obtained by iteratively solving the fitness function. The difference-of-convex (DC) programming and successive convex approximation (SCA) are used to handle non-convex and rank-1 terms in the fitness function. Once the BPSO iteration is complete, the discrete positions of MA elements can be determined, and we can obtain the solutions for beamforming vectors, sensing signal covariance matrix and user transmit power. Numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed system in reducing the total transmit power consumption compared with fixed antenna arrays.
Model Predictive Control Enabled UAV Trajectory Optimization and Secure Resource Allocation
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a secure communication architecture based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), which enhances the security performance of the communication system through UAV trajectory optimization. We formulate a control problem of minimizing the UAV flight path and power consumption while maximizing secure communication rate over infinite horizon by jointly optimizing UAV trajectory, transmit beamforming vector, and artificial noise (AN) vector. Given the non-uniqueness of optimization objective and significant coupling of the optimization variables, the problem is a non-convex optimization problem which is difficult to solve directly. To address this complex issue, an alternating-iteration technique is employed to decouple the optimization variables. Specifically, the problem is divided into three subproblems, i.e., UAV trajectory, transmit beamforming vector, and AN vector, which are solved alternately. Additionally, considering the susceptibility of UAV trajectory to disturbances, the model predictive control (MPC) approach is applied to obtain UAV trajectory and enhance the system robustness. Numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed optimization algorithm in maintaining accurate UAV trajectory and high secure communication rate compared with other benchmark schemes.
Towards TMA-Based Transmissive RIS Transceiver Enabled Downlink Communication Networks: A Consensus-ADMM Approach
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel multi-stream downlink communication system that utilizes a transmissive reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) transceiver. Specifically, we elaborate the downlink communication scheme using time-modulated array (TMA) technology, which enables high order modulation and multi-stream beamforming. Then, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize the minimum signal-to-interference-plusnoise ratio (SINR) with user fairness, which takes into account the constraint of the maximum available power for each transmissive element. Due to the non-convex nature of the formulated problem,finding optimal solution is challenging. To mitigate the complexity,we propose a linear-complexity beamforming algorithm based on consensus alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM).Specifically, by introducing a set of auxiliary variables, the problem can be decomposed into multiple sub-problems that are amenable to parallel computation, where the each sub-problem can yield closed-form expressions, bringing a significant reduction in the computational complexity. The overall problem achieves convergence by iteratively addressing these sub-problems in an alternating manner. Finally, the convergence of the proposed algorithm and the impact of various parameter configurations on the system performance are validated through numerical simulations.
Transmissive RIS Enabled Transceiver Systems:Architecture, Design Issues and Opportunities
Aug 24, 2024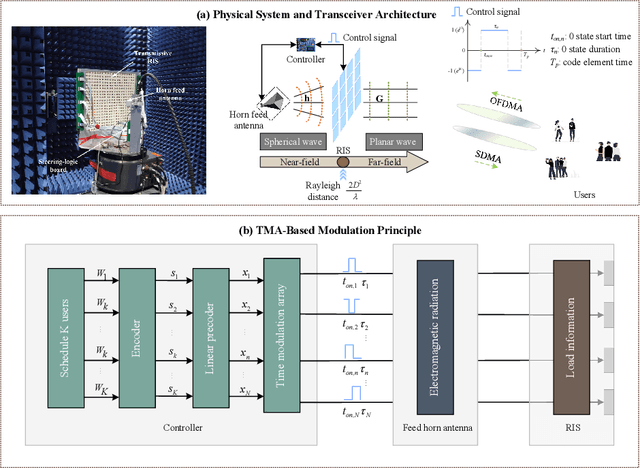
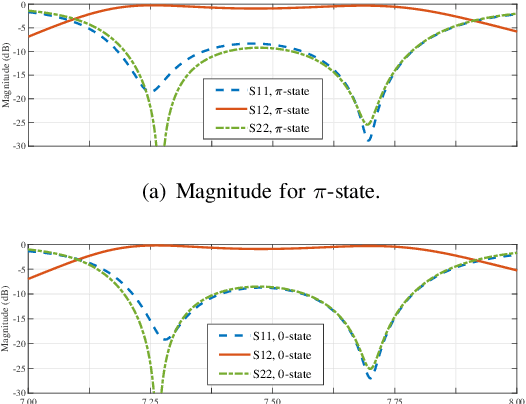
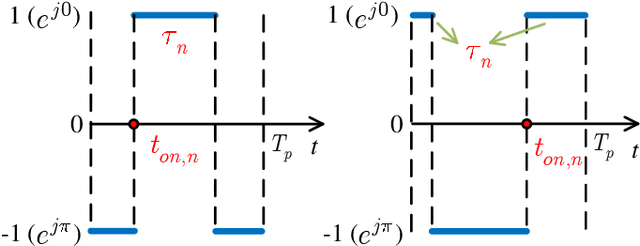
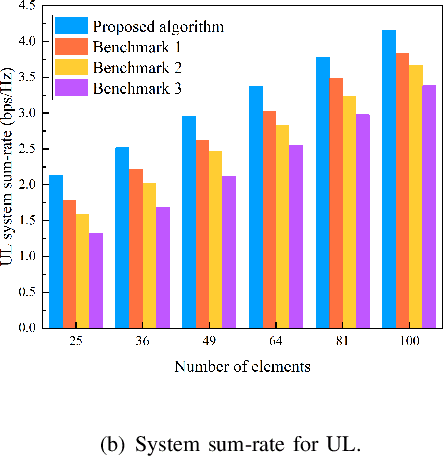
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is anticipated to augment the performance of beyond fifth-generation (B5G) and sixth-generation (6G) networks by intelligently manipulating the state of its components. Rather than employing reflective RIS for aided communications, this paper proposes an innovative transmissive RIS-enabled transceiver (TRTC) architecture that can accomplish the functions of traditional multi-antenna systems in a cost-effective and energy-efficient manner. First, the proposed network architecture and its corresponding transmission scheme are elaborated from the perspectives of downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) transmissions. Then, we illustrate several significant advantages and differences of TRTC compared to other multiantenna systems. Furthermore, the downlink modulation and extraction principle based on time-modulation array (TMA) is introduced in detail to tackle the multi-stream communications. Moreover, a near-far field channel model appropriate for this architecture is proposed. Based on the channel model, we summarize some state-of-the-art channel estimation schemes, and the channel estimation scheme of TRTC is also provided. Considering the optimization for DL and UL communications, we present numerical simulations that confirm the superiority of the proposed optimization algorithm. Lastly, numerous prospective research avenues for TRTC systems are delineated to inspire further exploration.
Cramer-Rao Bound Minimization for Movable Antenna-Assisted Multiuser Integrated Sensing and Communications
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates a movable antenna (MA)-assisted multiuser integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) system, where the base station (BS) and communication users are all equipped with MA for improving both the sensing and communication performance. We employ the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) as the performance metric of sensing, thus a joint beamforming design and MAs' position optimizing problem is formulated to minimize the CRB. However the resulting optimization problem is NP-hard and the variables are highly coupled. To tackle this problem, we propose an alternating optimization (AO) framework by adopting semidefinite relaxation (SDR) and successive convex approximation (SCA) technique. Numerical results reveal that the proposed MA-assisted ISAC system achieves lower estimation CRB compared to the fixed-position antenna (FPA) counterpart.
Enhancing Robustness and Security in ISAC Network Design: Leveraging Transmissive Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface with RSMA
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel transmissive reconfigurable intelligent surface transceiver-enhanced robust and secure integrated sensing and communication network. A time-division sensing communication mechanism is designed for the scenario, which enables communication and sensing to share wireless resources. To address the interference management problem and hinder eavesdropping, we implement rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), where the common stream is designed as a useful signal and an artificial noise, while taking into account the imperfect channel state information and modeling the channel for the illegal users in a fine-grained manner as well as giving an upper bound on the error. We introduce the secrecy outage probability and construct an optimization problem with secrecy sum-rate as the objective functions to optimize the common stream beamforming matrix, the private stream beamforming matrix and the timeslot duration variable. Due to the coupling of the optimization variables and the infinity of the error set, the proposed problem is a nonconvex optimization problem that cannot be solved directly. In order to address the above challenges, the block coordinate descent-based second-order cone programming algorithm is used to decouple the optimization variables and solving the problem. Specifically, the problem is decoupled into two subproblems concerning the common stream beamforming matrix, the private stream beamforming matrix, and the timeslot duration variable, which are solved by alternating optimization until convergence is reached. To solve the problem, S-procedure, Bernstein's inequality and successive convex approximation are employed to deal with the objective function and non-convex constraints. Numerical simulation results verify the superiority of the proposed scheme in improving the secrecy energy efficiency and the Cram\'{e}r-Rao boundary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge