Letian Shi
Text2Loc++: Generalizing 3D Point Cloud Localization from Natural Language
Nov 19, 2025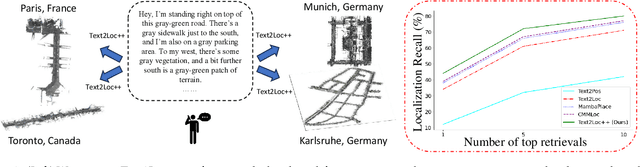
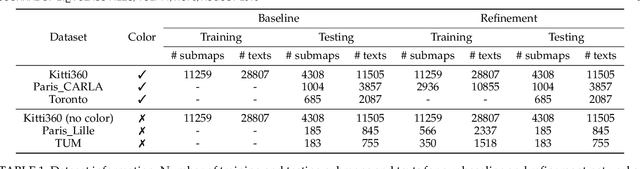
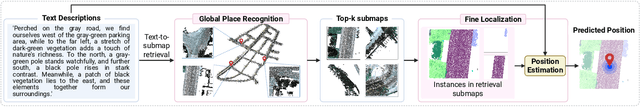
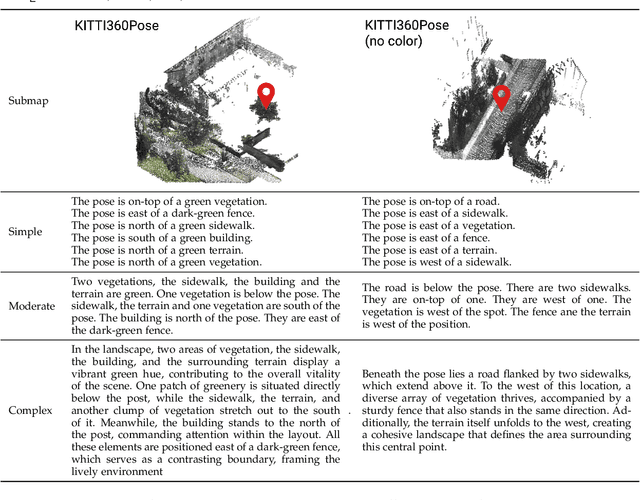
Abstract:We tackle the problem of localizing 3D point cloud submaps using complex and diverse natural language descriptions, and present Text2Loc++, a novel neural network designed for effective cross-modal alignment between language and point clouds in a coarse-to-fine localization pipeline. To support benchmarking, we introduce a new city-scale dataset covering both color and non-color point clouds from diverse urban scenes, and organize location descriptions into three levels of linguistic complexity. In the global place recognition stage, Text2Loc++ combines a pretrained language model with a Hierarchical Transformer with Max pooling (HTM) for sentence-level semantics, and employs an attention-based point cloud encoder for spatial understanding. We further propose Masked Instance Training (MIT) to filter out non-aligned objects and improve multimodal robustness. To enhance the embedding space, we introduce Modality-aware Hierarchical Contrastive Learning (MHCL), incorporating cross-modal, submap-, text-, and instance-level losses. In the fine localization stage, we completely remove explicit text-instance matching and design a lightweight yet powerful framework based on Prototype-based Map Cloning (PMC) and a Cascaded Cross-Attention Transformer (CCAT). Extensive experiments on the KITTI360Pose dataset show that Text2Loc++ outperforms existing methods by up to 15%. In addition, the proposed model exhibits robust generalization when evaluated on the new dataset, effectively handling complex linguistic expressions and a wide variety of urban environments. The code and dataset will be made publicly available.
UniLoc: Towards Universal Place Recognition Using Any Single Modality
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:To date, most place recognition methods focus on single-modality retrieval. While they perform well in specific environments, cross-modal methods offer greater flexibility by allowing seamless switching between map and query sources. It also promises to reduce computation requirements by having a unified model, and achieving greater sample efficiency by sharing parameters. In this work, we develop a universal solution to place recognition, UniLoc, that works with any single query modality (natural language, image, or point cloud). UniLoc leverages recent advances in large-scale contrastive learning, and learns by matching hierarchically at two levels: instance-level matching and scene-level matching. Specifically, we propose a novel Self-Attention based Pooling (SAP) module to evaluate the importance of instance descriptors when aggregated into a place-level descriptor. Experiments on the KITTI-360 dataset demonstrate the benefits of cross-modality for place recognition, achieving superior performance in cross-modal settings and competitive results also for uni-modal scenarios. Our project page is publicly available at https://yan-xia.github.io/projects/UniLoc/.
EPD: Long-term Memory Extraction, Context-awared Planning and Multi-iteration Decision @ EgoPlan Challenge ICML 2024
Jul 28, 2024



Abstract:In this technical report, we present our solution for the EgoPlan Challenge in ICML 2024. To address the real-world egocentric task planning problem, we introduce a novel planning framework which comprises three stages: long-term memory Extraction, context-awared Planning, and multi-iteration Decision, named EPD. Given the task goal, task progress, and current observation, the extraction model first extracts task-relevant memory information from the progress video, transforming the complex long video into summarized memory information. The planning model then combines the context of the memory information with fine-grained visual information from the current observation to predict the next action. Finally, through multi-iteration decision-making, the decision model comprehensively understands the task situation and current state to make the most realistic planning decision. On the EgoPlan-Test set, EPD achieves a planning accuracy of 53.85% over 1,584 egocentric task planning questions. We have made all codes available at https://github.com/Kkskkkskr/EPD .
Text2Loc: 3D Point Cloud Localization from Natural Language
Nov 27, 2023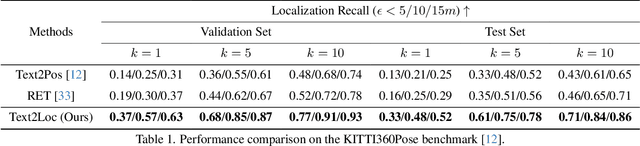
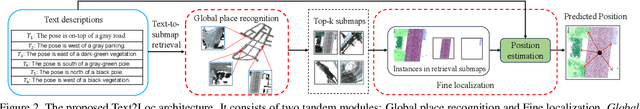
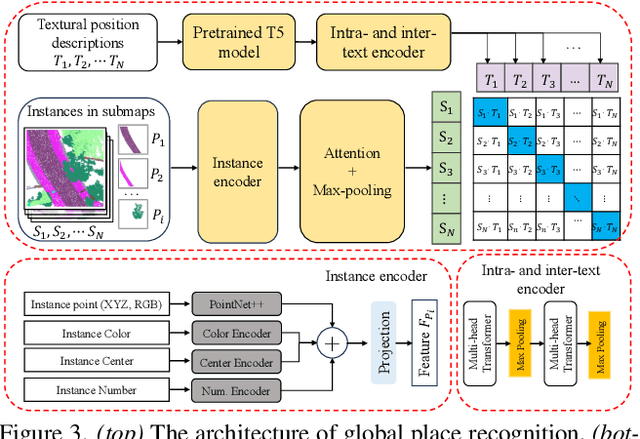
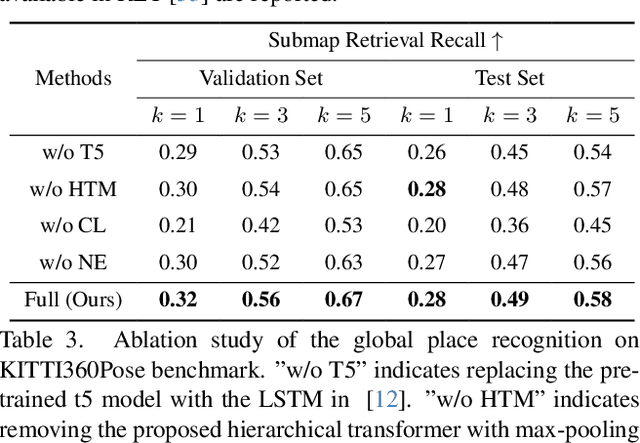
Abstract:We tackle the problem of 3D point cloud localization based on a few natural linguistic descriptions and introduce a novel neural network, Text2Loc, that fully interprets the semantic relationship between points and text. Text2Loc follows a coarse-to-fine localization pipeline: text-submap global place recognition, followed by fine localization. In global place recognition, relational dynamics among each textual hint are captured in a hierarchical transformer with max-pooling (HTM), whereas a balance between positive and negative pairs is maintained using text-submap contrastive learning. Moreover, we propose a novel matching-free fine localization method to further refine the location predictions, which completely removes the need for complicated text-instance matching and is lighter, faster, and more accurate than previous methods. Extensive experiments show that Text2Loc improves the localization accuracy by up to $2\times$ over the state-of-the-art on the KITTI360Pose dataset. We will make the code publicly available.
What Matters to Enhance Traffic Rule Compliance of Imitation Learning for Automated Driving
Sep 14, 2023



Abstract:More research attention has recently been given to end-to-end autonomous driving technologies where the entire driving pipeline is replaced with a single neural network because of its simpler structure and faster inference time. Despite this appealing approach largely reducing the components in driving pipeline, its simplicity also leads to interpretability problems and safety issues arXiv:2003.06404. The trained policy is not always compliant with the traffic rules and it is also hard to discover the reason for the misbehavior because of the lack of intermediate outputs. Meanwhile, Sensors are also critical to autonomous driving's security and feasibility to perceive the surrounding environment under complex driving scenarios. In this paper, we proposed P-CSG, a novel penalty-based imitation learning approach with cross semantics generation sensor fusion technologies to increase the overall performance of End-to-End Autonomous Driving. We conducted an assessment of our model's performance using the Town 05 Long benchmark, achieving an impressive driving score improvement of over 15%. Furthermore, we conducted robustness evaluations against adversarial attacks like FGSM and Dot attacks, revealing a substantial increase in robustness compared to baseline models.More detailed information, such as code-based resources, ablation studies and videos can be found at https://hk-zh.github.io/p-csg-plus.
Penalty-Based Imitation Learning With Cross Semantics Generation Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:With the rapid development of Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision technologies, tasks like object detection or semantic segmentation have achieved even better accuracy than human beings. Based on these solid foundations, autonomous driving is becoming an important research direction, aiming to revolute the future of transportation and mobility. Sensors are critical to autonomous driving's security and feasibility to perceive the surrounding environment. Multi-Sensor fusion has become a current research hot spot because of its potential for multidimensional perception and integration ability. In this paper, we propose a novel feature-level multi-sensor fusion technology for end-to-end autonomous driving navigation with imitation learning. Our paper mainly focuses on fusion technologies for Lidar and RGB information. We also provide a brand-new penalty-based imitation learning method to reinforce the model's compliance with traffic rules and unify the objective of imitation learning and the metric of autonomous driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge