Dongdong Zhao
Known Meets Unknown: Mitigating Overconfidence in Open Set Recognition
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Open Set Recognition (OSR) requires models not only to accurately classify known classes but also to effectively reject unknown samples. However, when unknown samples are semantically similar to known classes, inter-class overlap in the feature space often causes models to assign unjustifiably high confidence to them, leading to misclassification as known classes -- a phenomenon known as overconfidence. This overconfidence undermines OSR by blurring the decision boundary between known and unknown classes. To address this issue, we propose a framework that explicitly mitigates overconfidence caused by inter-class overlap. The framework consists of two components: a perturbation-based uncertainty estimation module, which applies controllable parameter perturbations to generate diverse predictions and quantify predictive uncertainty, and an unknown detection module with distinct learning-based classifiers, implemented as a two-stage procedure, which leverages the estimated uncertainty to improve discrimination between known and unknown classes, thereby enhancing OSR performance. Experimental results on three public datasets show that the proposed framework achieves superior performance over existing OSR methods.
Model Inversion Attack Against Deep Hashing
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Deep hashing improves retrieval efficiency through compact binary codes, yet it introduces severe and often overlooked privacy risks. The ability to reconstruct original training data from hash codes could lead to serious threats such as biometric forgery and privacy breaches. However, model inversion attacks specifically targeting deep hashing models remain unexplored, leaving their security implications unexamined. This research gap stems from the inaccessibility of genuine training hash codes and the highly discrete Hamming space, which prevents existing methods from adapting to deep hashing. To address these challenges, we propose DHMI, the first diffusion-based model inversion framework designed for deep hashing. DHMI first clusters an auxiliary dataset to derive semantic hash centers as surrogate anchors. It then introduces a surrogate-guided denoising optimization method that leverages a novel attack metric (fusing classification consistency and hash proximity) to dynamically select candidate samples. A cluster of surrogate models guides the refinement of these candidates, ensuring the generation of high-fidelity and semantically consistent images. Experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that DHMI successfully reconstructs high-resolution, high-quality images even under the most challenging black-box setting, where no training hash codes are available. Our method outperforms the existing state-of-the-art model inversion attacks in black-box scenarios, confirming both its practical efficacy and the critical privacy risks inherent in deep hashing systems.
BackWeak: Backdooring Knowledge Distillation Simply with Weak Triggers and Fine-tuning
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) is essential for compressing large models, yet relying on pre-trained "teacher" models downloaded from third-party repositories introduces serious security risks -- most notably backdoor attacks. Existing KD backdoor methods are typically complex and computationally intensive: they employ surrogate student models and simulated distillation to guarantee transferability, and they construct triggers in a way similar to universal adversarial perturbations (UAPs), which being not stealthy in magnitude, inherently exhibit strong adversarial behavior. This work questions whether such complexity is necessary and constructs stealthy "weak" triggers -- imperceptible perturbations that have negligible adversarial effect. We propose BackWeak, a simple, surrogate-free attack paradigm. BackWeak shows that a powerful backdoor can be implanted by simply fine-tuning a benign teacher with a weak trigger using a very small learning rate. We demonstrate that this delicate fine-tuning is sufficient to embed a backdoor that reliably transfers to diverse student architectures during a victim's standard distillation process, yielding high attack success rates. Extensive empirical evaluations on multiple datasets, model architectures, and KD methods show that BackWeak is efficient, simpler, and often more stealthy than previous elaborate approaches. This work calls on researchers studying KD backdoor attacks to pay particular attention to the trigger's stealthiness and its potential adversarial characteristics.
High-Precision Transformer-Based Visual Servoing for Humanoid Robots in Aligning Tiny Objects
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:High-precision tiny object alignment remains a common and critical challenge for humanoid robots in real-world. To address this problem, this paper proposes a vision-based framework for precisely estimating and controlling the relative position between a handheld tool and a target object for humanoid robots, e.g., a screwdriver tip and a screw head slot. By fusing images from the head and torso cameras on a robot with its head joint angles, the proposed Transformer-based visual servoing method can correct the handheld tool's positional errors effectively, especially at a close distance. Experiments on M4-M8 screws demonstrate an average convergence error of 0.8-1.3 mm and a success rate of 93\%-100\%. Through comparative analysis, the results validate that this capability of high-precision tiny object alignment is enabled by the Distance Estimation Transformer architecture and the Multi-Perception-Head mechanism proposed in this paper.
Motion-aware Memory Network for Fast Video Salient Object Detection
Aug 01, 2022

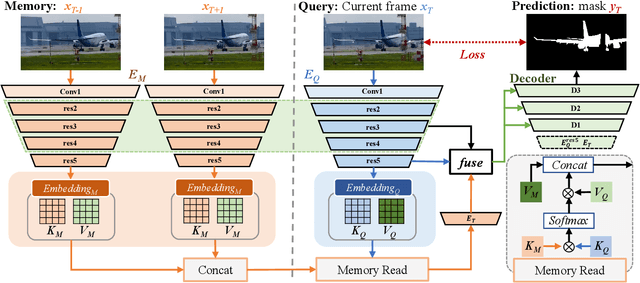
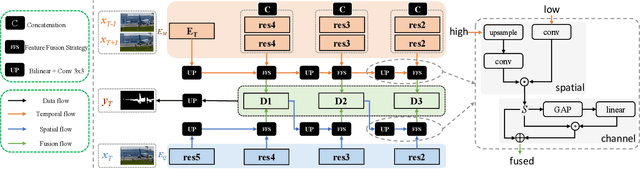
Abstract:Previous methods based on 3DCNN, convLSTM, or optical flow have achieved great success in video salient object detection (VSOD). However, they still suffer from high computational costs or poor quality of the generated saliency maps. To solve these problems, we design a space-time memory (STM)-based network, which extracts useful temporal information of the current frame from adjacent frames as the temporal branch of VSOD. Furthermore, previous methods only considered single-frame prediction without temporal association. As a result, the model may not focus on the temporal information sufficiently. Thus, we initially introduce object motion prediction between inter-frame into VSOD. Our model follows standard encoder--decoder architecture. In the encoding stage, we generate high-level temporal features by using high-level features from the current and its adjacent frames. This approach is more efficient than the optical flow-based methods. In the decoding stage, we propose an effective fusion strategy for spatial and temporal branches. The semantic information of the high-level features is used to fuse the object details in the low-level features, and then the spatiotemporal features are obtained step by step to reconstruct the saliency maps. Moreover, inspired by the boundary supervision commonly used in image salient object detection (ISOD), we design a motion-aware loss for predicting object boundary motion and simultaneously perform multitask learning for VSOD and object motion prediction, which can further facilitate the model to extract spatiotemporal features accurately and maintain the object integrity. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrated the effectiveness of our method and can achieve state-of-the-art metrics on some datasets. The proposed model does not require optical flow or other preprocessing, and can reach a speed of nearly 100 FPS during inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge