Honglong Chen
Unbiased Semantic Decoding with Vision Foundation Models for Few-shot Segmentation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Few-shot segmentation has garnered significant attention. Many recent approaches attempt to introduce the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to handle this task. With the strong generalization ability and rich object-specific extraction ability of the SAM model, such a solution shows great potential in few-shot segmentation. However, the decoding process of SAM highly relies on accurate and explicit prompts, making previous approaches mainly focus on extracting prompts from the support set, which is insufficient to activate the generalization ability of SAM, and this design is easy to result in a biased decoding process when adapting to the unknown classes. In this work, we propose an Unbiased Semantic Decoding (USD) strategy integrated with SAM, which extracts target information from both the support and query set simultaneously to perform consistent predictions guided by the semantics of the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model. Specifically, to enhance the unbiased semantic discrimination of SAM, we design two feature enhancement strategies that leverage the semantic alignment capability of CLIP to enrich the original SAM features, mainly including a global supplement at the image level to provide a generalize category indicate with support image and a local guidance at the pixel level to provide a useful target location with query image. Besides, to generate target-focused prompt embeddings, a learnable visual-text target prompt generator is proposed by interacting target text embeddings and clip visual features. Without requiring re-training of the vision foundation models, the features with semantic discrimination draw attention to the target region through the guidance of prompt with rich target information.
Sigil: Server-Enforced Watermarking in U-Shaped Split Federated Learning via Gradient Injection
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:In decentralized machine learning paradigms such as Split Federated Learning (SFL) and its variant U-shaped SFL, the server's capabilities are severely restricted. Although this enhances client-side privacy, it also leaves the server highly vulnerable to model theft by malicious clients. Ensuring intellectual property protection for such capability-limited servers presents a dual challenge: watermarking schemes that depend on client cooperation are unreliable in adversarial settings, whereas traditional server-side watermarking schemes are technically infeasible because the server lacks access to critical elements such as model parameters or labels. To address this challenge, this paper proposes Sigil, a mandatory watermarking framework designed specifically for capability-limited servers. Sigil defines the watermark as a statistical constraint on the server-visible activation space and embeds the watermark into the client model via gradient injection, without requiring any knowledge of the data. Besides, we design an adaptive gradient clipping mechanism to ensure that our watermarking process remains both mandatory and stealthy, effectively countering existing gradient anomaly detection methods and a specifically designed adaptive subspace removal attack. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets and models demonstrate Sigil's fidelity, robustness, and stealthiness.
Robust Client-Server Watermarking for Split Federated Learning
Nov 17, 2025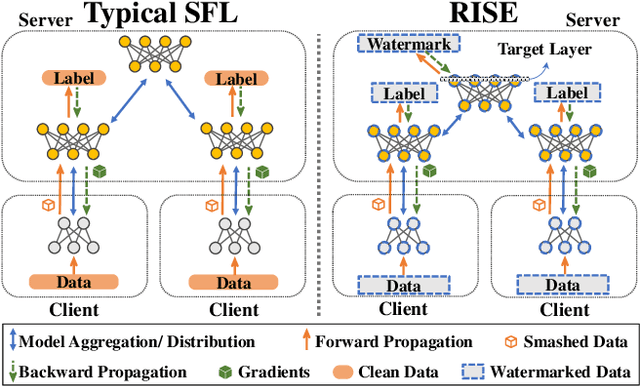
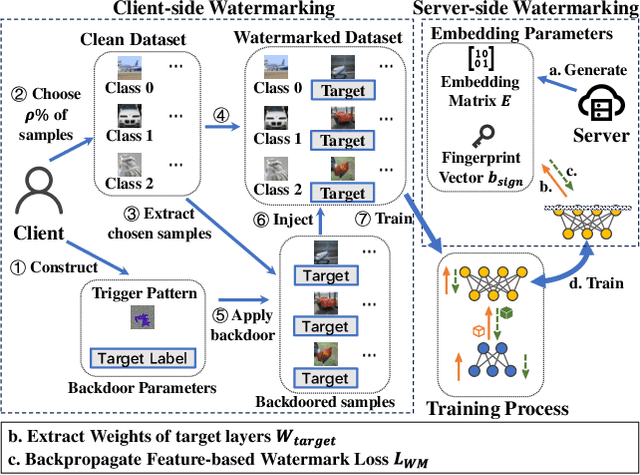
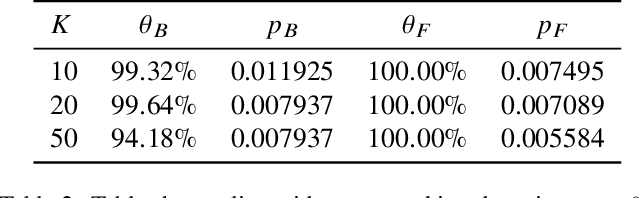
Abstract:Split Federated Learning (SFL) is renowned for its privacy-preserving nature and low computational overhead among decentralized machine learning paradigms. In this framework, clients employ lightweight models to process private data locally and transmit intermediate outputs to a powerful server for further computation. However, SFL is a double-edged sword: while it enables edge computing and enhances privacy, it also introduces intellectual property ambiguity as both clients and the server jointly contribute to training. Existing watermarking techniques fail to protect both sides since no single participant possesses the complete model. To address this, we propose RISE, a Robust model Intellectual property protection scheme using client-Server watermark Embedding for SFL. Specifically, RISE adopts an asymmetric client-server watermarking design: the server embeds feature-based watermarks through a loss regularization term, while clients embed backdoor-based watermarks by injecting predefined trigger samples into private datasets. This co-embedding strategy enables both clients and the server to verify model ownership. Experimental results on standard datasets and multiple network architectures show that RISE achieves over $95\%$ watermark detection rate ($p-value \lt 0.03$) across most settings. It exhibits no mutual interference between client- and server-side watermarks and remains robust against common removal attacks.
FFCBA: Feature-based Full-target Clean-label Backdoor Attacks
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Backdoor attacks pose a significant threat to deep neural networks, as backdoored models would misclassify poisoned samples with specific triggers into target classes while maintaining normal performance on clean samples. Among these, multi-target backdoor attacks can simultaneously target multiple classes. However, existing multi-target backdoor attacks all follow the dirty-label paradigm, where poisoned samples are mislabeled, and most of them require an extremely high poisoning rate. This makes them easily detectable by manual inspection. In contrast, clean-label attacks are more stealthy, as they avoid modifying the labels of poisoned samples. However, they generally struggle to achieve stable and satisfactory attack performance and often fail to scale effectively to multi-target attacks. To address this issue, we propose the Feature-based Full-target Clean-label Backdoor Attacks (FFCBA) which consists of two paradigms: Feature-Spanning Backdoor Attacks (FSBA) and Feature-Migrating Backdoor Attacks (FMBA). FSBA leverages class-conditional autoencoders to generate noise triggers that align perturbed in-class samples with the original category's features, ensuring the effectiveness, intra-class consistency, inter-class specificity and natural-feature correlation of triggers. While FSBA supports swift and efficient attacks, its cross-model attack capability is relatively weak. FMBA employs a two-stage class-conditional autoencoder training process that alternates between using out-of-class samples and in-class samples. This allows FMBA to generate triggers with strong target-class features, making it highly effective for cross-model attacks. We conduct experiments on multiple datasets and models, the results show that FFCBA achieves outstanding attack performance and maintains desirable robustness against the state-of-the-art backdoor defenses.
SFIBA: Spatial-based Full-target Invisible Backdoor Attacks
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Multi-target backdoor attacks pose significant security threats to deep neural networks, as they can preset multiple target classes through a single backdoor injection. This allows attackers to control the model to misclassify poisoned samples with triggers into any desired target class during inference, exhibiting superior attack performance compared with conventional backdoor attacks. However, existing multi-target backdoor attacks fail to guarantee trigger specificity and stealthiness in black-box settings, resulting in two main issues. First, they are unable to simultaneously target all classes when only training data can be manipulated, limiting their effectiveness in realistic attack scenarios. Second, the triggers often lack visual imperceptibility, making poisoned samples easy to detect. To address these problems, we propose a Spatial-based Full-target Invisible Backdoor Attack, called SFIBA. It restricts triggers for different classes to specific local spatial regions and morphologies in the pixel space to ensure specificity, while employing a frequency-domain-based trigger injection method to guarantee stealthiness. Specifically, for injection of each trigger, we first apply fast fourier transform to obtain the amplitude spectrum of clean samples in local spatial regions. Then, we employ discrete wavelet transform to extract the features from the amplitude spectrum and use singular value decomposition to integrate the trigger. Subsequently, we selectively filter parts of the trigger in pixel space to implement trigger morphology constraints and adjust injection coefficients based on visual effects. We conduct experiments on multiple datasets and models. The results demonstrate that SFIBA can achieve excellent attack performance and stealthiness, while preserving the model's performance on benign samples, and can also bypass existing backdoor defenses.
Rethinking Prior Information Generation with CLIP for Few-Shot Segmentation
May 14, 2024Abstract:Few-shot segmentation remains challenging due to the limitations of its labeling information for unseen classes. Most previous approaches rely on extracting high-level feature maps from the frozen visual encoder to compute the pixel-wise similarity as a key prior guidance for the decoder. However, such a prior representation suffers from coarse granularity and poor generalization to new classes since these high-level feature maps have obvious category bias. In this work, we propose to replace the visual prior representation with the visual-text alignment capacity to capture more reliable guidance and enhance the model generalization. Specifically, we design two kinds of training-free prior information generation strategy that attempts to utilize the semantic alignment capability of the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training model (CLIP) to locate the target class. Besides, to acquire more accurate prior guidance, we build a high-order relationship of attention maps and utilize it to refine the initial prior information. Experiments on both the PASCAL-5{i} and COCO-20{i} datasets show that our method obtains a clearly substantial improvement and reaches the new state-of-the-art performance.
Balancing Privacy Protection and Interpretability in Federated Learning
Feb 16, 2023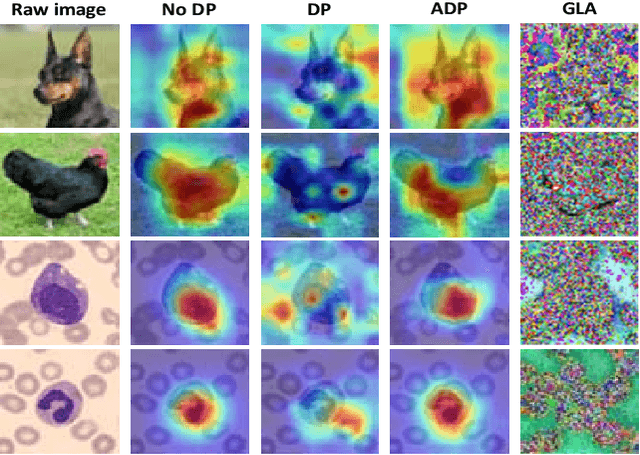
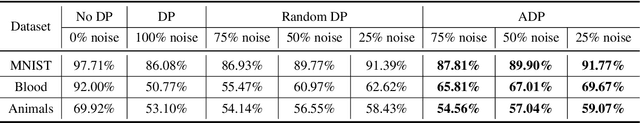
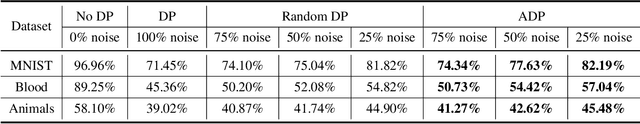
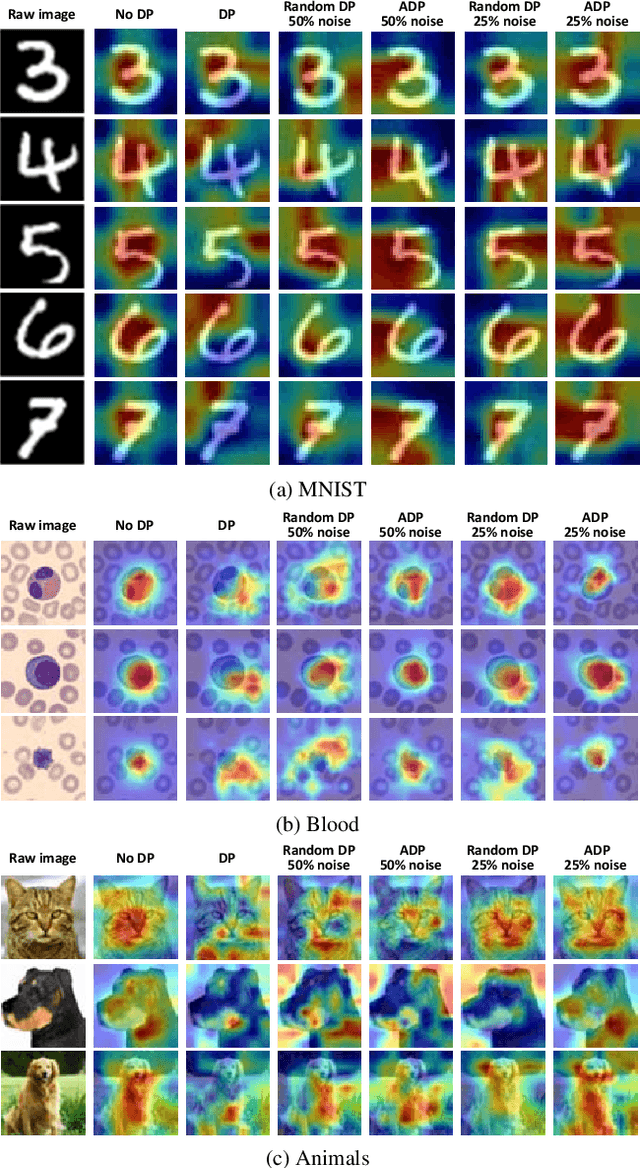
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) aims to collaboratively train the global model in a distributed manner by sharing the model parameters from local clients to a central server, thereby potentially protecting users' private information. Nevertheless, recent studies have illustrated that FL still suffers from information leakage as adversaries try to recover the training data by analyzing shared parameters from local clients. To deal with this issue, differential privacy (DP) is adopted to add noise to the gradients of local models before aggregation. It, however, results in the poor performance of gradient-based interpretability methods, since some weights capturing the salient region in feature map will be perturbed. To overcome this problem, we propose a simple yet effective adaptive differential privacy (ADP) mechanism that selectively adds noisy perturbations to the gradients of client models in FL. We also theoretically analyze the impact of gradient perturbation on the model interpretability. Finally, extensive experiments on both IID and Non-IID data demonstrate that the proposed ADP can achieve a good trade-off between privacy and interpretability in FL.
Adversarial RAW: Image-Scaling Attack Against Imaging Pipeline
Jun 02, 2022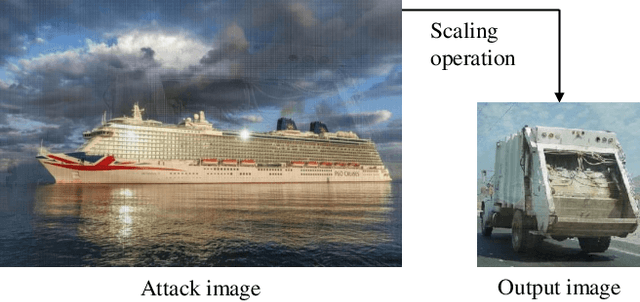
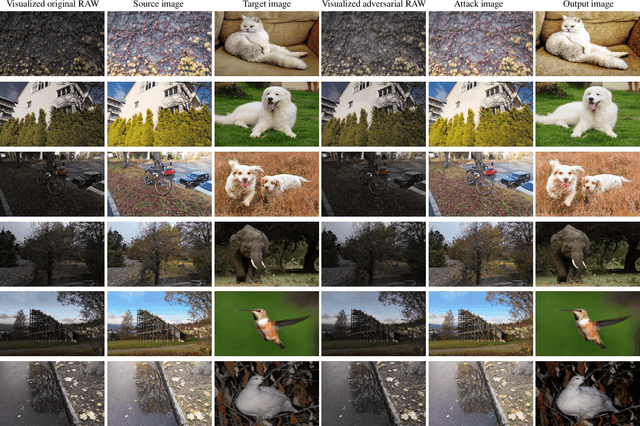

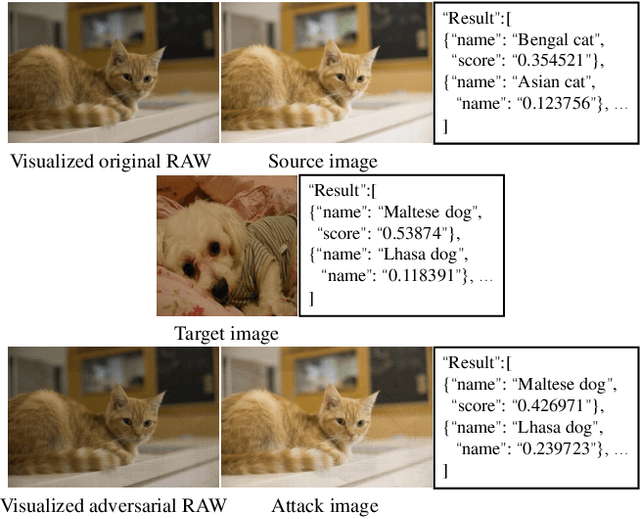

Abstract:Deep learning technologies have become the backbone for the development of computer vision. With further explorations, deep neural networks have been found vulnerable to well-designed adversarial attacks. Most of the vision devices are equipped with image signal processing (ISP) pipeline to implement RAW-to-RGB transformations and embedded into data preprocessing module for efficient image processing. Actually, ISP pipeline can introduce adversarial behaviors to post-capture images while data preprocessing may destroy attack patterns. However, none of the existing adversarial attacks takes into account the impacts of both ISP pipeline and data preprocessing. In this paper, we develop an image-scaling attack targeting on ISP pipeline, where the crafted adversarial RAW can be transformed into attack image that presents entirely different appearance once being scaled to a specific-size image. We first consider the gradient-available ISP pipeline, i.e., the gradient information can be directly used in the generation process of adversarial RAW to launch the attack. To make the adversarial attack more applicable, we further consider the gradient-unavailable ISP pipeline, in which a proxy model that well learns the RAW-to-RGB transformations is proposed as the gradient oracles. Extensive experiments show that the proposed adversarial attacks can craft adversarial RAW data against the target ISP pipelines with high attack rates.
VRConvMF: Visual Recurrent Convolutional Matrix Factorization for Movie Recommendation
Feb 16, 2022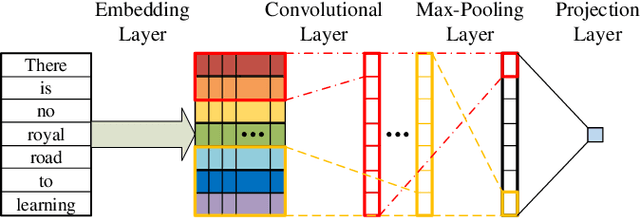
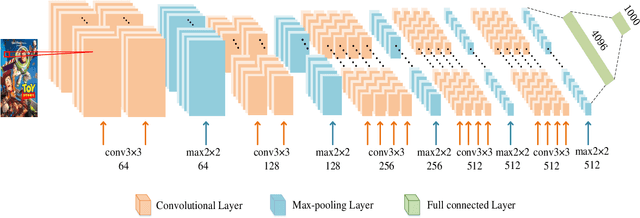
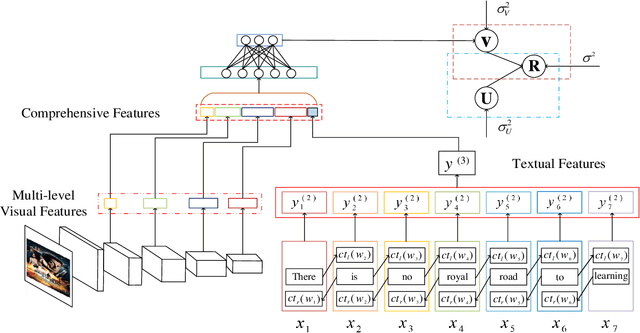
Abstract:Sparsity of user-to-item rating data becomes one of challenging issues in the recommender systems, which severely deteriorates the recommendation performance. Fortunately, context-aware recommender systems can alleviate the sparsity problem by making use of some auxiliary information, such as the information of both the users and items. In particular, the visual information of items, such as the movie poster, can be considered as the supplement for item description documents, which helps to obtain more item features. In this paper, we focus on movie recommender system and propose a probabilistic matrix factorization based recommendation scheme called visual recurrent convolutional matrix factorization (VRConvMF), which utilizes the textual and multi-level visual features extracted from the descriptive texts and posters respectively. We implement the proposed VRConvMF and conduct extensive experiments on three commonly used real world datasets to validate its effectiveness. The experimental results illustrate that the proposed VRConvMF outperforms the existing schemes.
Edge Data Based Trailer Inception Probabilistic Matrix Factorization for Context-Aware Movie Recommendation
Feb 16, 2022
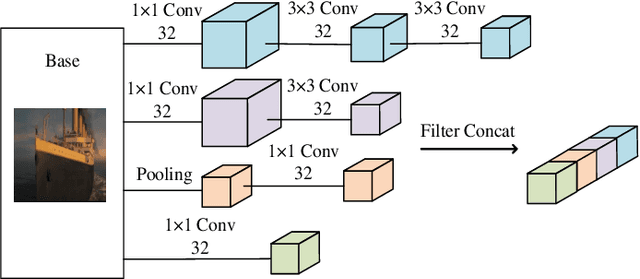
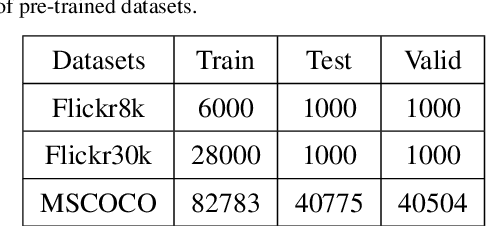
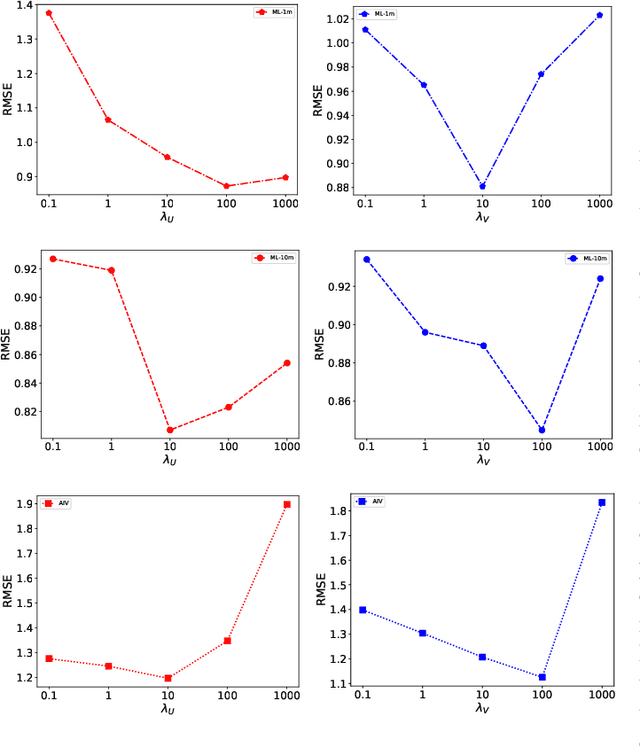
Abstract:The rapid growth of edge data generated by mobile devices and applications deployed at the edge of the network has exacerbated the problem of information overload. As an effective way to alleviate information overload, recommender system can improve the quality of various services by adding application data generated by users on edge devices, such as visual and textual information, on the basis of sparse rating data. The visual information in the movie trailer is a significant part of the movie recommender system. However, due to the complexity of visual information extraction, data sparsity cannot be remarkably alleviated by merely using the rough visual features to improve the rating prediction accuracy. Fortunately, the convolutional neural network can be used to extract the visual features precisely. Therefore, the end-to-end neural image caption (NIC) model can be utilized to obtain the textual information describing the visual features of movie trailers. This paper proposes a trailer inception probabilistic matrix factorization model called Ti-PMF, which combines NIC, recurrent convolutional neural network, and probabilistic matrix factorization models as the rating prediction model. We implement the proposed Ti-PMF model with extensive experiments on three real-world datasets to validate its effectiveness. The experimental results illustrate that the proposed Ti-PMF outperforms the existing ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge