Zhu Wang
Graph-based Agent Memory: Taxonomy, Techniques, and Applications
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Memory emerges as the core module in the Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents for long-horizon complex tasks (e.g., multi-turn dialogue, game playing, scientific discovery), where memory can enable knowledge accumulation, iterative reasoning and self-evolution. Among diverse paradigms, graph stands out as a powerful structure for agent memory due to the intrinsic capabilities to model relational dependencies, organize hierarchical information, and support efficient retrieval. This survey presents a comprehensive review of agent memory from the graph-based perspective. First, we introduce a taxonomy of agent memory, including short-term vs. long-term memory, knowledge vs. experience memory, non-structural vs. structural memory, with an implementation view of graph-based memory. Second, according to the life cycle of agent memory, we systematically analyze the key techniques in graph-based agent memory, covering memory extraction for transforming the data into the contents, storage for organizing the data efficiently, retrieval for retrieving the relevant contents from memory to support reasoning, and evolution for updating the contents in the memory. Third, we summarize the open-sourced libraries and benchmarks that support the development and evaluation of self-evolving agent memory. We also explore diverse application scenarios. Finally, we identify critical challenges and future research directions. This survey aims to offer actionable insights to advance the development of more efficient and reliable graph-based agent memory systems. All the related resources, including research papers, open-source data, and projects, are collected for the community in https://github.com/DEEP-PolyU/Awesome-GraphMemory.
Multiview Self-Representation Learning across Heterogeneous Views
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Features of the same sample generated by different pretrained models often exhibit inherently distinct feature distributions because of discrepancies in the model pretraining objectives or architectures. Learning invariant representations from large-scale unlabeled visual data with various pretrained models in a fully unsupervised transfer manner remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose a multiview self-representation learning (MSRL) method in which invariant representations are learned by exploiting the self-representation property of features across heterogeneous views. The features are derived from large-scale unlabeled visual data through transfer learning with various pretrained models and are referred to as heterogeneous multiview data. An individual linear model is stacked on top of its corresponding frozen pretrained backbone. We introduce an information-passing mechanism that relies on self-representation learning to support feature aggregation over the outputs of the linear model. Moreover, an assignment probability distribution consistency scheme is presented to guide multiview self-representation learning by exploiting complementary information across different views. Consequently, representation invariance across different linear models is enforced through this scheme. In addition, we provide a theoretical analysis of the information-passing mechanism, the assignment probability distribution consistency and the incremental views. Extensive experiments with multiple benchmark visual datasets demonstrate that the proposed MSRL method consistently outperforms several state-of-the-art approaches.
Targeted Unlearning Using Perturbed Sign Gradient Methods With Applications On Medical Images
May 28, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning aims to remove the influence of specific training samples from a trained model without full retraining. While prior work has largely focused on privacy-motivated settings, we recast unlearning as a general-purpose tool for post-deployment model revision. Specifically, we focus on utilizing unlearning in clinical contexts where data shifts, device deprecation, and policy changes are common. To this end, we propose a bilevel optimization formulation of boundary-based unlearning that can be solved using iterative algorithms. We provide convergence guarantees when first-order algorithms are used to unlearn. Our method introduces tunable loss design for controlling the forgetting-retention tradeoff and supports novel model composition strategies that merge the strengths of distinct unlearning runs. Across benchmark and real-world clinical imaging datasets, our approach outperforms baselines on both forgetting and retention metrics, including scenarios involving imaging devices and anatomical outliers. This work establishes machine unlearning as a modular, practical alternative to retraining for real-world model maintenance in clinical applications.
Benchmarking Large Language Models via Random Variables
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:With the continuous advancement of large language models (LLMs) in mathematical reasoning, evaluating their performance in this domain has become a prominent research focus. Recent studies have raised concerns about the reliability of current mathematical benchmarks, highlighting issues such as simplistic design and potential data leakage. Therefore, creating a reliable benchmark that effectively evaluates the genuine capabilities of LLMs in mathematical reasoning remains a significant challenge. To address this, we propose RV-Bench, a framework for Benchmarking LLMs via Random Variables in mathematical reasoning. Specifically, the background content of a random variable question (RV question) mirrors the original problem in existing standard benchmarks, but the variable combinations are randomized into different values. LLMs must fully understand the problem-solving process for the original problem to correctly answer RV questions with various combinations of variable values. As a result, the LLM's genuine capability in mathematical reasoning is reflected by its accuracy on RV-Bench. Extensive experiments are conducted with 29 representative LLMs across 900+ RV questions. A leaderboard for RV-Bench ranks the genuine capability of these LLMs. Further analysis of accuracy dropping indicates that current LLMs still struggle with complex mathematical reasoning problems.
Self-Supervised Conditional Distribution Learning on Graphs
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Graph contrastive learning (GCL) has shown promising performance in semisupervised graph classification. However, existing studies still encounter significant challenges in GCL. First, successive layers in graph neural network (GNN) tend to produce more similar node embeddings, while GCL aims to increase the dissimilarity between negative pairs of node embeddings. This inevitably results in a conflict between the message-passing mechanism of GNNs and the contrastive learning of negative pairs via intraviews. Second, leveraging the diversity and quantity of data provided by graph-structured data augmentations while preserving intrinsic semantic information is challenging. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised conditional distribution learning (SSCDL) method designed to learn graph representations from graph-structured data for semisupervised graph classification. Specifically, we present an end-to-end graph representation learning model to align the conditional distributions of weakly and strongly augmented features over the original features. This alignment effectively reduces the risk of disrupting intrinsic semantic information through graph-structured data augmentation. To avoid conflict between the message-passing mechanism and contrastive learning of negative pairs, positive pairs of node representations are retained for measuring the similarity between the original features and the corresponding weakly augmented features. Extensive experiments with several benchmark graph datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed SSCDL method.
SOAR: Simultaneous Exploration and Photographing with Heterogeneous UAVs for Fast Autonomous Reconstruction
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have gained significant popularity in scene reconstruction. This paper presents SOAR, a LiDAR-Visual heterogeneous multi-UAV system specifically designed for fast autonomous reconstruction of complex environments. Our system comprises a LiDAR-equipped explorer with a large field-of-view (FoV), alongside photographers equipped with cameras. To ensure rapid acquisition of the scene's surface geometry, we employ a surface frontier-based exploration strategy for the explorer. As the surface is progressively explored, we identify the uncovered areas and generate viewpoints incrementally. These viewpoints are then assigned to photographers through solving a Consistent Multiple Depot Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem (Consistent-MDMTSP), which optimizes scanning efficiency while ensuring task consistency. Finally, photographers utilize the assigned viewpoints to determine optimal coverage paths for acquiring images. We present extensive benchmarks in the realistic simulator, which validates the performance of SOAR compared with classical and state-of-the-art methods. For more details, please see our project page at https://sysu-star.github.io/SOAR}{sysu-star.github.io/SOAR.
Graph Anomaly Detection with Noisy Labels by Reinforcement Learning
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD) has been widely applied in many areas, e.g., fraud detection in finance and robot accounts in social networks. Existing methods are dedicated to identifying the outlier nodes that deviate from normal ones. While they heavily rely on high-quality annotation, which is hard to obtain in real-world scenarios, this could lead to severely degraded performance based on noisy labels. Thus, we are motivated to cut the edges of suspicious nodes to alleviate the impact of noise. However, it remains difficult to precisely identify the nodes with noisy labels. Moreover, it is hard to quantitatively evaluate the regret of cutting the edges, which may have either positive or negative influences. To this end, we propose a novel framework REGAD, i.e., REinforced Graph Anomaly Detector. Specifically, we aim to maximize the performance improvement (AUC) of a base detector by cutting noisy edges approximated through the nodes with high-confidence labels. (i) We design a tailored action and search space to train a policy network to carefully prune edges step by step, where only a few suspicious edges are prioritized in each step. (ii) We design a policy-in-the-loop mechanism to iteratively optimize the policy based on the feedback from base detector. The overall performance is evaluated by the cumulative rewards. Extensive experiments are conducted on three datasets under different anomaly ratios. The results indicate the superior performance of our proposed REGAD.
A Comprehensive Survey on AI-based Methods for Patents
Apr 02, 2024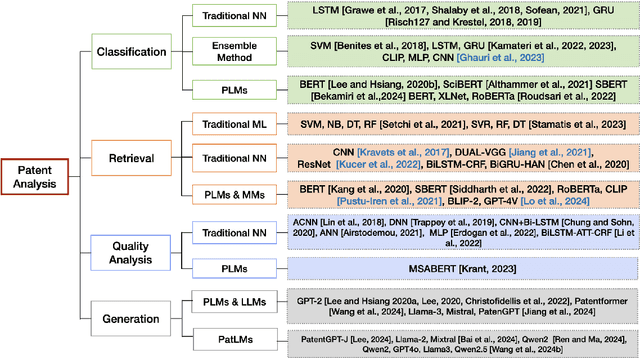
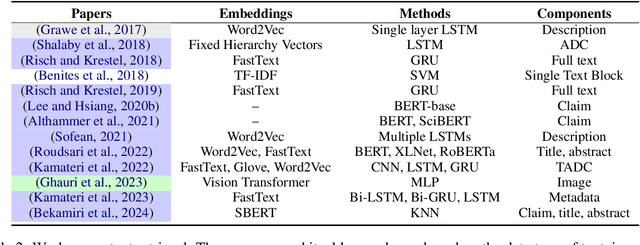
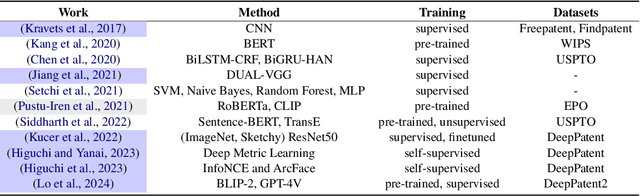
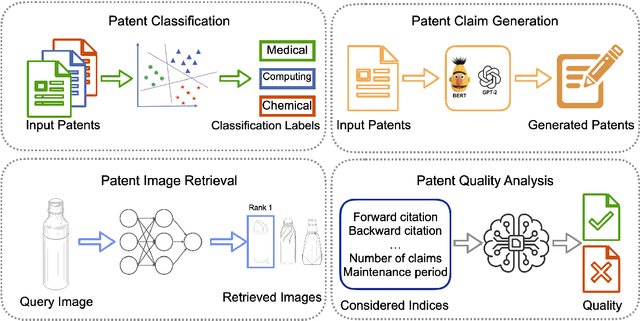
Abstract:Recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning have demonstrated transformative capabilities across diverse domains. This progress extends to the field of patent analysis and innovation, where AI-based tools present opportunities to streamline and enhance important tasks in the patent cycle such as classification, retrieval, and valuation prediction. This not only accelerates the efficiency of patent researchers and applicants but also opens new avenues for technological innovation and discovery. Our survey provides a comprehensive summary of recent AI tools in patent analysis from more than 40 papers from 26 venues between 2017 and 2023. Unlike existing surveys, we include methods that work for patent image and text data. Furthermore, we introduce a novel taxonomy for the categorization based on the tasks in the patent life cycle as well as the specifics of the AI methods. This survey aims to serve as a resource for researchers, practitioners, and patent offices in the domain of AI-powered patent analysis.
Contextualized Structural Self-supervised Learning for Ontology Matching
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Ontology matching (OM) entails the identification of semantic relationships between concepts within two or more knowledge graphs (KGs) and serves as a critical step in integrating KGs from various sources. Recent advancements in deep OM models have harnessed the power of transformer-based language models and the advantages of knowledge graph embedding. Nevertheless, these OM models still face persistent challenges, such as a lack of reference alignments, runtime latency, and unexplored different graph structures within an end-to-end framework. In this study, we introduce a novel self-supervised learning OM framework with input ontologies, called LaKERMap. This framework capitalizes on the contextual and structural information of concepts by integrating implicit knowledge into transformers. Specifically, we aim to capture multiple structural contexts, encompassing both local and global interactions, by employing distinct training objectives. To assess our methods, we utilize the Bio-ML datasets and tasks. The findings from our innovative approach reveal that LaKERMap surpasses state-of-the-art systems in terms of alignment quality and inference time. Our models and codes are available here: https://github.com/ellenzhuwang/lakermap.
Accelerated Neural Network Training with Rooted Logistic Objectives
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Many neural networks deployed in the real world scenarios are trained using cross entropy based loss functions. From the optimization perspective, it is known that the behavior of first order methods such as gradient descent crucially depend on the separability of datasets. In fact, even in the most simplest case of binary classification, the rate of convergence depends on two factors: (1) condition number of data matrix, and (2) separability of the dataset. With no further pre-processing techniques such as over-parametrization, data augmentation etc., separability is an intrinsic quantity of the data distribution under consideration. We focus on the landscape design of the logistic function and derive a novel sequence of {\em strictly} convex functions that are at least as strict as logistic loss. The minimizers of these functions coincide with those of the minimum norm solution wherever possible. The strict convexity of the derived function can be extended to finetune state-of-the-art models and applications. In empirical experimental analysis, we apply our proposed rooted logistic objective to multiple deep models, e.g., fully-connected neural networks and transformers, on various of classification benchmarks. Our results illustrate that training with rooted loss function is converged faster and gains performance improvements. Furthermore, we illustrate applications of our novel rooted loss function in generative modeling based downstream applications, such as finetuning StyleGAN model with the rooted loss. The code implementing our losses and models can be found here for open source software development purposes: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/rooted_loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge