Zhongzhi Luan
PRAGMA: A Profiling-Reasoned Multi-Agent Framework for Automatic Kernel Optimization
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Designing high-performance kernels requires expert-level tuning and a deep understanding of hardware characteristics. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled automated kernel generation, yet most existing systems rely solely on correctness or execution time feedback, lacking the ability to reason about low-level performance bottlenecks. In this paper, we introduce PRAGMA, a profile-guided AI kernel generation framework that integrates execution feedback and fine-grained hardware profiling into the reasoning loop. PRAGMA enables LLMs to identify performance bottlenecks, preserve historical best versions, and iteratively refine code quality. We evaluate PRAGMA on KernelBench, covering GPU and CPU backends. Results show that PRAGMA consistently outperforms baseline AIKG without profiling enabled and achieves 2.81$\times$ and 2.30$\times$ averaged speedups against Torch on CPU and GPU platforms, respectively.
Strategic priorities for transformative progress in advancing biology with proteomics and artificial intelligence
Feb 21, 2025

Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming scientific research, including proteomics. Advances in mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics data quality, diversity, and scale, combined with groundbreaking AI techniques, are unlocking new challenges and opportunities in biological discovery. Here, we highlight key areas where AI is driving innovation, from data analysis to new biological insights. These include developing an AI-friendly ecosystem for proteomics data generation, sharing, and analysis; improving peptide and protein identification and quantification; characterizing protein-protein interactions and protein complexes; advancing spatial and perturbation proteomics; integrating multi-omics data; and ultimately enabling AI-empowered virtual cells.
Beyond Window-Based Detection: A Graph-Centric Framework for Discrete Log Anomaly Detection
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Detecting anomalies in discrete event logs is critical for ensuring system reliability, security, and efficiency. Traditional window-based methods for log anomaly detection often suffer from context bias and fuzzy localization, which hinder their ability to precisely and efficiently identify anomalies. To address these challenges, we propose a graph-centric framework, TempoLog, which leverages multi-scale temporal graph networks for discrete log anomaly detection. Unlike conventional methods, TempoLog constructs continuous-time dynamic graphs directly from event logs, eliminating the need for fixed-size window grouping. By representing log templates as nodes and their temporal relationships as edges, the framework dynamically captures both local and global dependencies across multiple temporal scales. Additionally, a semantic-aware model enhances detection by incorporating rich contextual information. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in event-level anomaly detection, significantly outperforming existing approaches in both accuracy and efficiency.
Quantum Machine Learning in Log-based Anomaly Detection: Challenges and Opportunities
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Log-based anomaly detection (LogAD) is the main component of Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps), which can detect anomalous that occur during the system on-the-fly. Existing methods commonly extract log sequence features using classical machine learning techniques to identify whether a new sequence is an anomaly or not. However, these classical approaches often require trade-offs between efficiency and accuracy. The advent of quantum machine learning (QML) offers a promising alternative. By transforming parts of classical machine learning computations into parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs), QML can significantly reduce the number of trainable parameters while maintaining accuracy comparable to classical counterparts. In this work, we introduce a unified framework, \ourframework{}, for evaluating QML models in the context of LogAD. This framework incorporates diverse log data, integrated QML models, and comprehensive evaluation metrics. State-of-the-art methods such as DeepLog, LogAnomaly, and LogRobust, along with their quantum-transformed counterparts, are included in our framework.Beyond standard metrics like F1 score, precision, and recall, our evaluation extends to factors critical to QML performance, such as specificity, the number of circuits, circuit design, and quantum state encoding. Using \ourframework{}, we conduct extensive experiments to assess the performance of these models and their quantum counterparts, uncovering valuable insights and paving the way for future research in QML model selection and design for LogAD.
On Domain-Specific Post-Training for Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 29, 2024

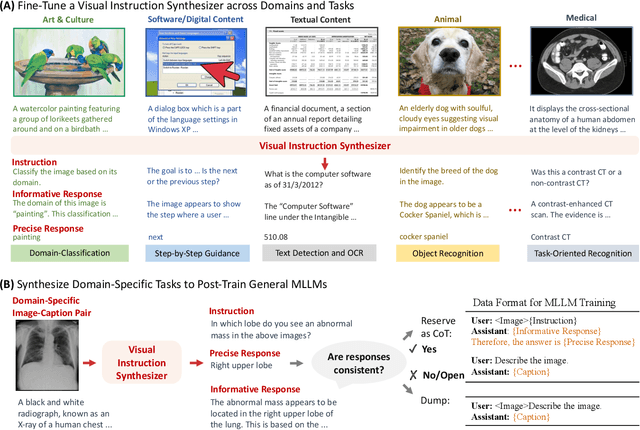

Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the rapid development of general multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, adapting general MLLMs to specific domains, such as scientific fields and industrial applications, remains less explored. This paper systematically investigates domain adaptation of MLLMs through post-training, focusing on data synthesis, training pipelines, and task evaluation. (1) Data Synthesis: Using open-source models, we develop a visual instruction synthesizer that effectively generates diverse visual instruction tasks from domain-specific image-caption pairs. Our synthetic tasks surpass those generated by manual rules, GPT-4, and GPT-4V in enhancing the domain-specific performance of MLLMs. (2) Training Pipeline: While the two-stage training--initially on image-caption pairs followed by visual instruction tasks--is commonly adopted for developing general MLLMs, we apply a single-stage training pipeline to enhance task diversity for domain-specific post-training. (3) Task Evaluation: We conduct experiments in two domains, biomedicine and food, by post-training MLLMs of different sources and scales (e.g., Qwen2-VL-2B, LLaVA-v1.6-8B, Llama-3.2-11B), and then evaluating MLLM performance on various domain-specific tasks. To support further research in MLLM domain adaptation, we will open-source our implementations.
LogGPT: Exploring ChatGPT for Log-Based Anomaly Detection
Sep 03, 2023



Abstract:The increasing volume of log data produced by software-intensive systems makes it impractical to analyze them manually. Many deep learning-based methods have been proposed for log-based anomaly detection. These methods face several challenges such as high-dimensional and noisy log data, class imbalance, generalization, and model interpretability. Recently, ChatGPT has shown promising results in various domains. However, there is still a lack of study on the application of ChatGPT for log-based anomaly detection. In this work, we proposed LogGPT, a log-based anomaly detection framework based on ChatGPT. By leveraging the ChatGPT's language interpretation capabilities, LogGPT aims to explore the transferability of knowledge from large-scale corpora to log-based anomaly detection. We conduct experiments to evaluate the performance of LogGPT and compare it with three deep learning-based methods on BGL and Spirit datasets. LogGPT shows promising results and has good interpretability. This study provides preliminary insights into prompt-based models, such as ChatGPT, for the log-based anomaly detection task.
Scaling Sentence Embeddings with Large Language Models
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently garnered significant interest. With in-context learning, LLMs achieve impressive results in various natural language tasks. However, the application of LLMs to sentence embeddings remains an area of ongoing research. In this work, we propose an in-context learning-based method aimed at improving sentence embeddings performance. Our approach involves adapting the previous prompt-based representation method for autoregressive models, constructing a demonstration set that enables LLMs to perform in-context learning, and scaling up the LLMs to different model sizes. Through extensive experiments, in-context learning enables LLMs to generate high-quality sentence embeddings without any fine-tuning. It helps LLMs achieve performance comparable to current contrastive learning methods. By scaling model size, we find scaling to more than tens of billion parameters harms the performance on semantic textual similarity (STS) tasks. However, the largest model outperforms other counterparts and achieves the new state-of-the-art result on transfer tasks. We also fine-tune LLMs with current contrastive learning approach, and the 2.7B OPT model, incorporating our prompt-based method, surpasses the performance of 4.8B ST5, achieving the new state-of-the-art results on STS tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/kongds/scaling_sentemb.
FamilySeer: Towards Optimized Tensor Codes by Exploiting Computation Subgraph Similarity
Jan 01, 2022
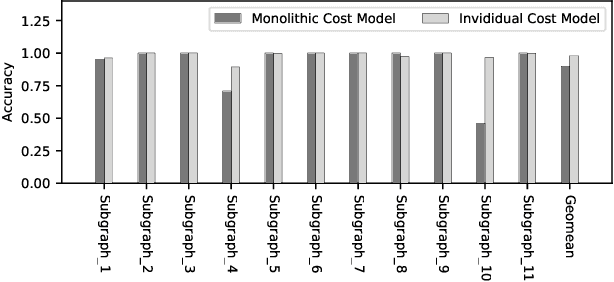
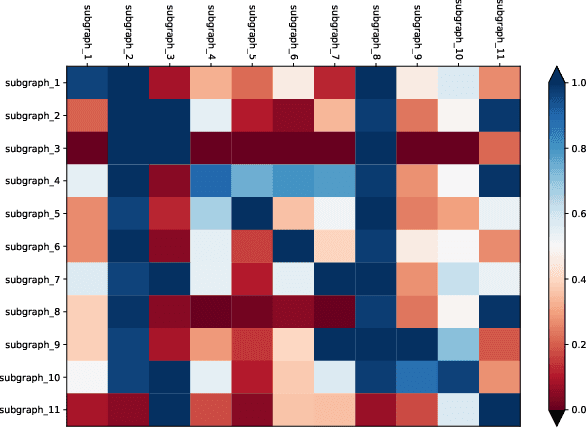

Abstract:Deploying various deep learning (DL) models efficiently has boosted the research on DL compilers. The difficulty of generating optimized tensor codes drives DL compiler to ask for the auto-tuning approaches, and the increasing demands require increasing auto-tuning efficiency and quality. Currently, the DL compilers partition the input DL models into several subgraphs and leverage the auto-tuning to find the optimal tensor codes of these subgraphs. However, existing auto-tuning approaches usually regard subgraphs as individual ones and overlook the similarities across them, and thus fail to exploit better tensor codes under limited time budgets. We propose FamilySeer, an auto-tuning framework for DL compilers that can generate better tensor codes even with limited time budgets. FamilySeer exploits the similarities and differences among subgraphs can organize them into subgraph families, where the tuning of one subgraph can also improve other subgraphs within the same family. The cost model of each family gets more purified training samples generated by the family and becomes more accurate so that the costly measurements on real hardware can be replaced with the lightweight estimation through cost model. Our experiments show that FamilySeer can generate model codes with the same code performance more efficiently than state-of-the-art auto-tuning frameworks.
The Deep Learning Compiler: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 27, 2020



Abstract:The difficulty of deploying various deep learning (DL) models on diverse DL hardware has boosted the research and development of DL compilers in the community. Several DL compilers have been proposed from both industry and academia such as Tensorflow XLA and TVM. Similarly, the DL compilers take the DL models described in different DL frameworks as input, and then generate optimized codes for diverse DL hardware as output. However, none of the existing survey has analyzed the unique design of the DL compilers comprehensively. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive survey of existing DL compilers by dissecting the commonly adopted design in details, with emphasis on the DL oriented multi-level IRs, and frontend/backend optimizations. Specifically, we provide a comprehensive comparison among existing DL compilers from various aspects. In addition, we present detailed analysis of the multi-level IR design and compiler optimization techniques. Finally, several insights are highlighted as the potential research directions of DL compiler. This is the first survey paper focusing on the unique design of DL compiler, which we hope can pave the road for future research towards the DL compiler.
Privacy for Rescue: A New Testimony Why Privacy is Vulnerable In Deep Models
Dec 31, 2019



Abstract:The huge computation demand of deep learning models and limited computation resources on the edge devices calls for the cooperation between edge device and cloud service by splitting the deep models into two halves. However, transferring the intermediates results from the partial models between edge device and cloud service makes the user privacy vulnerable since the attacker can intercept the intermediate results and extract privacy information from them. Existing research works rely on metrics that are either impractical or insufficient to measure the effectiveness of privacy protection methods in the above scenario, especially from the aspect of a single user. In this paper, we first present a formal definition of the privacy protection problem in the edge-cloud system running DNN models. Then, we analyze the-state-of-the-art methods and point out the drawbacks of their methods, especially the evaluation metrics such as the Mutual Information (MI). In addition, we perform several experiments to demonstrate that although existing methods perform well under MI, they are not effective enough to protect the privacy of a single user. To address the drawbacks of the evaluation metrics, we propose two new metrics that are more accurate to measure the effectiveness of privacy protection methods. Finally, we highlight several potential research directions to encourage future efforts addressing the privacy protection problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge