Yufei Wei
BEV-ODOM2: Enhanced BEV-based Monocular Visual Odometry with PV-BEV Fusion and Dense Flow Supervision for Ground Robots
Sep 18, 2025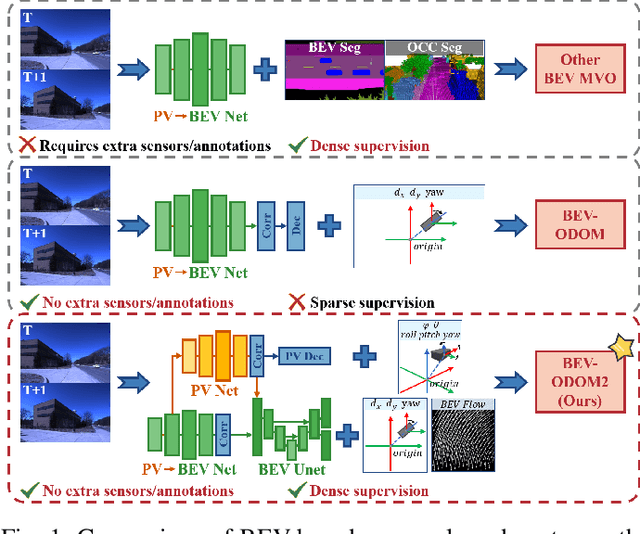
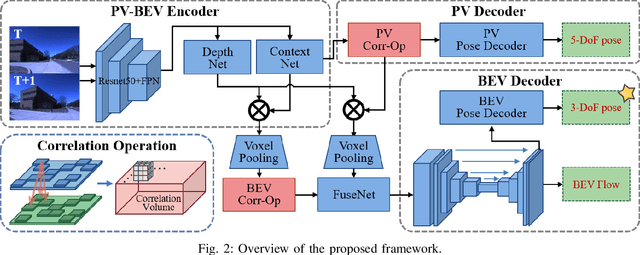
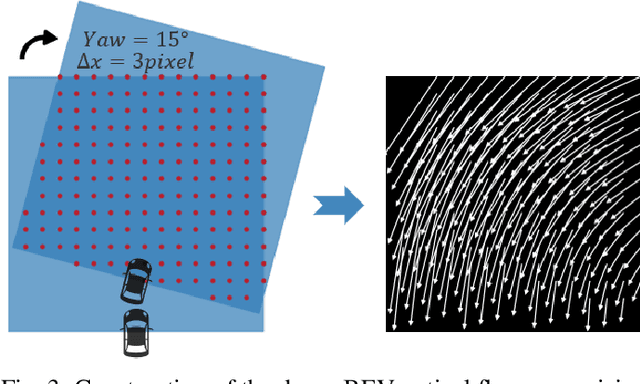
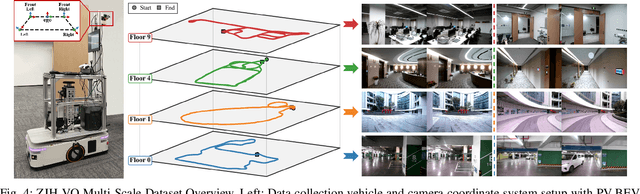
Abstract:Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) representation offers a metric-scaled planar workspace, facilitating the simplification of 6-DoF ego-motion to a more robust 3-DoF model for monocular visual odometry (MVO) in intelligent transportation systems. However, existing BEV methods suffer from sparse supervision signals and information loss during perspective-to-BEV projection. We present BEV-ODOM2, an enhanced framework addressing both limitations without additional annotations. Our approach introduces: (1) dense BEV optical flow supervision constructed from 3-DoF pose ground truth for pixel-level guidance; (2) PV-BEV fusion that computes correlation volumes before projection to preserve 6-DoF motion cues while maintaining scale consistency. The framework employs three supervision levels derived solely from pose data: dense BEV flow, 5-DoF for the PV branch, and final 3-DoF output. Enhanced rotation sampling further balances diverse motion patterns in training. Extensive evaluation on KITTI, NCLT, Oxford, and our newly collected ZJH-VO multi-scale dataset demonstrates state-of-the-art performance, achieving 40 improvement in RTE compared to previous BEV methods. The ZJH-VO dataset, covering diverse ground vehicle scenarios from underground parking to outdoor plazas, is publicly available to facilitate future research.
BEV-DWPVO: BEV-based Differentiable Weighted Procrustes for Low Scale-drift Monocular Visual Odometry on Ground
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Monocular Visual Odometry (MVO) provides a cost-effective, real-time positioning solution for autonomous vehicles. However, MVO systems face the common issue of lacking inherent scale information from monocular cameras. Traditional methods have good interpretability but can only obtain relative scale and suffer from severe scale drift in long-distance tasks. Learning-based methods under perspective view leverage large amounts of training data to acquire prior knowledge and estimate absolute scale by predicting depth values. However, their generalization ability is limited due to the need to accurately estimate the depth of each point. In contrast, we propose a novel MVO system called BEV-DWPVO. Our approach leverages the common assumption of a ground plane, using Bird's-Eye View (BEV) feature maps to represent the environment in a grid-based structure with a unified scale. This enables us to reduce the complexity of pose estimation from 6 Degrees of Freedom (DoF) to 3-DoF. Keypoints are extracted and matched within the BEV space, followed by pose estimation through a differentiable weighted Procrustes solver. The entire system is fully differentiable, supporting end-to-end training with only pose supervision and no auxiliary tasks. We validate BEV-DWPVO on the challenging long-sequence datasets NCLT, Oxford, and KITTI, achieving superior results over existing MVO methods on most evaluation metrics.
OccGS: Zero-shot 3D Occupancy Reconstruction with Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussian Splatting
Feb 07, 2025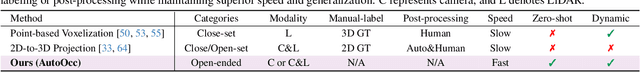
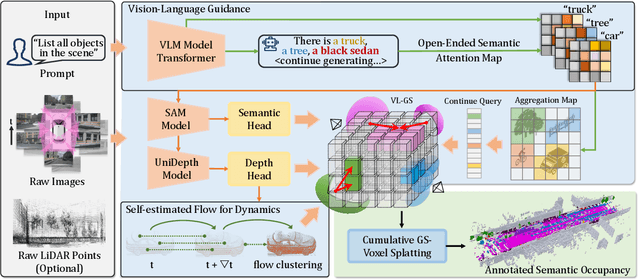
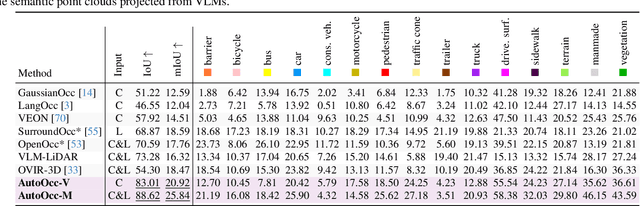
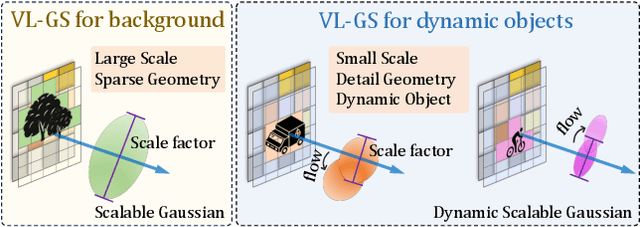
Abstract:Obtaining semantic 3D occupancy from raw sensor data without manual annotations remains an essential yet challenging task. While prior works have approached this as a perception prediction problem, we formulate it as scene-aware 3D occupancy reconstruction with geometry and semantics. In this work, we propose OccGS, a novel 3D Occupancy reconstruction framework utilizing Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussian Splatting in a zero-shot manner. Leveraging semantics extracted from vision-language models and geometry guided by LiDAR points, OccGS constructs Semantic and Geometric-Aware Gaussians from raw multisensor data. We also develop a cumulative Gaussian-to-3D voxel splatting method for reconstructing occupancy from the Gaussians. OccGS performs favorably against self-supervised methods in occupancy prediction, achieving comparable performance to fully supervised approaches and achieving state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot semantic 3D occupancy estimation.
Multi-cam Multi-map Visual Inertial Localization: System, Validation and Dataset
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Map-based localization is crucial for the autonomous movement of robots as it provides real-time positional feedback. However, existing VINS and SLAM systems cannot be directly integrated into the robot's control loop. Although VINS offers high-frequency position estimates, it suffers from drift in long-term operation. And the drift-free trajectory output by SLAM is post-processed with loop correction, which is non-causal. In practical control, it is impossible to update the current pose with future information. Furthermore, existing SLAM evaluation systems measure accuracy after aligning the entire trajectory, which overlooks the transformation error between the odometry start frame and the ground truth frame. To address these issues, we propose a multi-cam multi-map visual inertial localization system, which provides real-time, causal and drift-free position feedback to the robot control loop. Additionally, we analyze the error composition of map-based localization systems and propose a set of evaluation metric suitable for measuring causal localization performance. To validate our system, we design a multi-camera IMU hardware setup and collect a long-term challenging campus dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the higher real-time localization accuracy of the proposed system. To foster community development, both the system and the dataset have been made open source https://github.com/zoeylove/Multi-cam-Multi-map-VILO/tree/main.
BEV-ODOM: Reducing Scale Drift in Monocular Visual Odometry with BEV Representation
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Monocular visual odometry (MVO) is vital in autonomous navigation and robotics, providing a cost-effective and flexible motion tracking solution, but the inherent scale ambiguity in monocular setups often leads to cumulative errors over time. In this paper, we present BEV-ODOM, a novel MVO framework leveraging the Bird's Eye View (BEV) Representation to address scale drift. Unlike existing approaches, BEV-ODOM integrates a depth-based perspective-view (PV) to BEV encoder, a correlation feature extraction neck, and a CNN-MLP-based decoder, enabling it to estimate motion across three degrees of freedom without the need for depth supervision or complex optimization techniques. Our framework reduces scale drift in long-term sequences and achieves accurate motion estimation across various datasets, including NCLT, Oxford, and KITTI. The results indicate that BEV-ODOM outperforms current MVO methods, demonstrating reduced scale drift and higher accuracy.
TEOcc: Radar-camera Multi-modal Occupancy Prediction via Temporal Enhancement
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:As a novel 3D scene representation, semantic occupancy has gained much attention in autonomous driving. However, existing occupancy prediction methods mainly focus on designing better occupancy representations, such as tri-perspective view or neural radiance fields, while ignoring the advantages of using long-temporal information. In this paper, we propose a radar-camera multi-modal temporal enhanced occupancy prediction network, dubbed TEOcc. Our method is inspired by the success of utilizing temporal information in 3D object detection. Specifically, we introduce a temporal enhancement branch to learn temporal occupancy prediction. In this branch, we randomly discard the t-k input frame of the multi-view camera and predict its 3D occupancy by long-term and short-term temporal decoders separately with the information from other adjacent frames and multi-modal inputs. Besides, to reduce computational costs and incorporate multi-modal inputs, we specially designed 3D convolutional layers for long-term and short-term temporal decoders. Furthermore, since the lightweight occupancy prediction head is a dense classification head, we propose to use a shared occupancy prediction head for the temporal enhancement and main branches. It is worth noting that the temporal enhancement branch is only performed during training and is discarded during inference. Experiment results demonstrate that TEOcc achieves state-of-the-art occupancy prediction on nuScenes benchmarks. In addition, the proposed temporal enhancement branch is a plug-and-play module that can be easily integrated into existing occupancy prediction methods to improve the performance of occupancy prediction. The code and models will be released at https://github.com/VDIGPKU/TEOcc.
2nd Place Solution for IJCAI-PRICAI 2020 3D AI Challenge: 3D Object Reconstruction from A Single Image
May 28, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we present our solution for the {\it IJCAI--PRICAI--20 3D AI Challenge: 3D Object Reconstruction from A Single Image}. We develop a variant of AtlasNet that consumes single 2D images and generates 3D point clouds through 2D to 3D mapping. To push the performance to the limit and present guidance on crucial implementation choices, we conduct extensive experiments to analyze the influence of decoder design and different settings on the normalization, projection, and sampling methods. Our method achieves 2nd place in the final track with a score of $70.88$, a chamfer distance of $36.87$, and a mean f-score of $59.18$. The source code of our method will be available at https://github.com/em-data/Enhanced_AtlasNet_3DReconstruction.
* 5 pages, 2 figures, 5 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge