Haoyuan Li
Thinking with Geometry: Active Geometry Integration for Spatial Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in spatial reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) increasingly leverages geometric priors from 3D encoders. However, most existing integration strategies remain passive: geometry is exposed as a global stream and fused in an indiscriminate manner, which often induces semantic-geometry misalignment and redundant signals. We propose GeoThinker, a framework that shifts the paradigm from passive fusion to active perception. Instead of feature mixing, GeoThinker enables the model to selectively retrieve geometric evidence conditioned on its internal reasoning demands. GeoThinker achieves this through Spatial-Grounded Fusion applied at carefully selected VLM layers, where semantic visual priors selectively query and integrate task-relevant geometry via frame-strict cross-attention, further calibrated by Importance Gating that biases per-frame attention toward task-relevant structures. Comprehensive evaluation results show that GeoThinker sets a new state-of-the-art in spatial intelligence, achieving a peak score of 72.6 on the VSI-Bench. Furthermore, GeoThinker demonstrates robust generalization and significantly improved spatial perception across complex downstream scenarios, including embodied referring and autonomous driving. Our results indicate that the ability to actively integrate spatial structures is essential for next-generation spatial intelligence. Code can be found at https://github.com/Li-Hao-yuan/GeoThinker.
Beyond Precision: Training-Inference Mismatch is an Optimization Problem and Simple LR Scheduling Fixes It
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) for training Large Language Models is notoriously unstable. While recent studies attribute this to "training inference mismatch stemming" from inconsistent hybrid engines, standard remedies, such as Importance Sampling, might fail during extended training runs. In this work, we analyze this instability through the lens of optimization, demonstrating that gradient noise and training-inference mismatch escalate in tandem as training progresses. Meanwhile, we find that the mismatch can be effectively suppressed by shrinking the update size. Taken together, we deduce that the mismatch is not merely a static numerical discrepancy, but a dynamic failure coupled with the model's optimization. Based on this insight, we propose a simple yet effective solution: a specialized Learning Rate (LR) scheduler. Instead of pre-defined decay schedule in traditional LR scheduler, our method dynamically triggers LR decay based on response length, which we identify as a reliable early-warning signal for impending instability. Empirical evidence suggests that by reducing the learning rate as gradient noise rises, we can consistently stabilize RL training and keep the training-inference mismatch at a safe level.
Unified Personalized Understanding, Generating and Editing
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Unified large multimodal models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable progress in general-purpose multimodal understanding and generation. However, they still operate under a ``one-size-fits-all'' paradigm and struggle to model user-specific concepts (e.g., generate a photo of \texttt{<maeve>}) in a consistent and controllable manner. Existing personalization methods typically rely on external retrieval, which is inefficient and poorly integrated into unified multimodal pipelines. Recent personalized unified models introduce learnable soft prompts to encode concept information, yet they either couple understanding and generation or depend on complex multi-stage training, leading to cross-task interference and ultimately to fuzzy or misaligned personalized knowledge. We present \textbf{OmniPersona}, an end-to-end personalization framework for unified LMMs that, for the first time, integrates personalized understanding, generation, and image editing within a single architecture. OmniPersona introduces structurally decoupled concept tokens, allocating dedicated subspaces for different tasks to minimize interference, and incorporates an explicit knowledge replay mechanism that propagates personalized attribute knowledge across tasks, enabling consistent personalized behavior. To systematically evaluate unified personalization, we propose \textbf{\texttt{OmniPBench}}, extending the public UnifyBench concept set with personalized editing tasks and cross-task evaluation protocols integrating understanding, generation, and editing. Experimental results demonstrate that OmniPersona delivers competitive and robust performance across diverse personalization tasks. We hope OmniPersona will serve as a strong baseline and spur further research on controllable, unified personalization.
R-Debater: Retrieval-Augmented Debate Generation through Argumentative Memory
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present R-Debater, an agentic framework for generating multi-turn debates built on argumentative memory. Grounded in rhetoric and memory studies, the system views debate as a process of recalling and adapting prior arguments to maintain stance consistency, respond to opponents, and support claims with evidence. Specifically, R-Debater integrates a debate knowledge base for retrieving case-like evidence and prior debate moves with a role-based agent that composes coherent utterances across turns. We evaluate on standardized ORCHID debates, constructing a 1,000-item retrieval corpus and a held-out set of 32 debates across seven domains. Two tasks are evaluated: next-utterance generation, assessed by InspireScore (subjective, logical, and factual), and adversarial multi-turn simulations, judged by Debatrix (argument, source, language, and overall). Compared with strong LLM baselines, R-Debater achieves higher single-turn and multi-turn scores. Human evaluation with 20 experienced debaters further confirms its consistency and evidence use, showing that combining retrieval grounding with structured planning yields more faithful, stance-aligned, and coherent debates across turns.
Helmsman: Autonomous Synthesis of Federated Learning Systems via Multi-Agent Collaboration
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) offers a powerful paradigm for training models on decentralized data, but its promise is often undermined by the immense complexity of designing and deploying robust systems. The need to select, combine, and tune strategies for multifaceted challenges like data heterogeneity and system constraints has become a critical bottleneck, resulting in brittle, bespoke solutions. To address this, we introduce Helmsman, a novel multi-agent system that automates the end-to-end synthesis of federated learning systems from high-level user specifications. It emulates a principled research and development workflow through three collaborative phases: (1) interactive human-in-the-loop planning to formulate a sound research plan, (2) modular code generation by supervised agent teams, and (3) a closed-loop of autonomous evaluation and refinement in a sandboxed simulation environment. To facilitate rigorous evaluation, we also introduce AgentFL-Bench, a new benchmark comprising 16 diverse tasks designed to assess the system-level generation capabilities of agentic systems in FL. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach generates solutions competitive with, and often superior to, established hand-crafted baselines. Our work represents a significant step towards the automated engineering of complex decentralized AI systems.
Matrix-3D: Omnidirectional Explorable 3D World Generation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Explorable 3D world generation from a single image or text prompt forms a cornerstone of spatial intelligence. Recent works utilize video model to achieve wide-scope and generalizable 3D world generation. However, existing approaches often suffer from a limited scope in the generated scenes. In this work, we propose Matrix-3D, a framework that utilize panoramic representation for wide-coverage omnidirectional explorable 3D world generation that combines conditional video generation and panoramic 3D reconstruction. We first train a trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion model that employs scene mesh renders as condition, to enable high-quality and geometrically consistent scene video generation. To lift the panorama scene video to 3D world, we propose two separate methods: (1) a feed-forward large panorama reconstruction model for rapid 3D scene reconstruction and (2) an optimization-based pipeline for accurate and detailed 3D scene reconstruction. To facilitate effective training, we also introduce the Matrix-Pano dataset, the first large-scale synthetic collection comprising 116K high-quality static panoramic video sequences with depth and trajectory annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoramic video generation and 3D world generation. See more in https://matrix-3d.github.io.
Does Your 3D Encoder Really Work? When Pretrain-SFT from 2D VLMs Meets 3D VLMs
Jun 06, 2025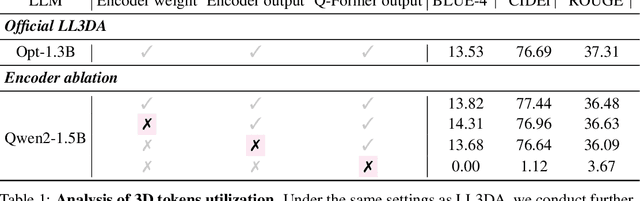
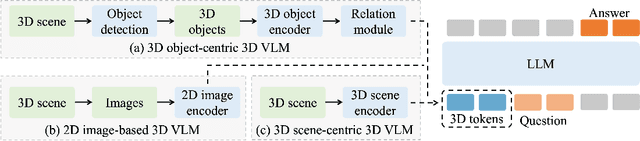

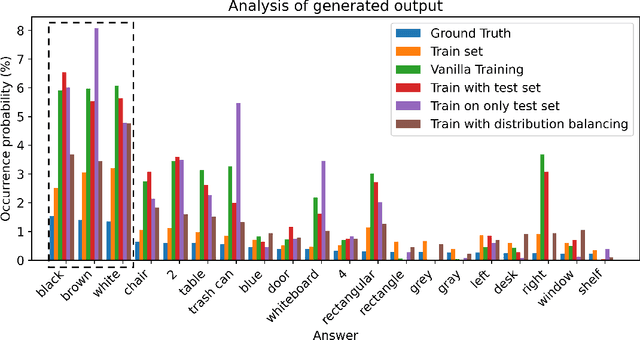
Abstract:Remarkable progress in 2D Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has spurred interest in extending them to 3D settings for tasks like 3D Question Answering, Dense Captioning, and Visual Grounding. Unlike 2D VLMs that typically process images through an image encoder, 3D scenes, with their intricate spatial structures, allow for diverse model architectures. Based on their encoder design, this paper categorizes recent 3D VLMs into 3D object-centric, 2D image-based, and 3D scene-centric approaches. Despite the architectural similarity of 3D scene-centric VLMs to their 2D counterparts, they have exhibited comparatively lower performance compared with the latest 3D object-centric and 2D image-based approaches. To understand this gap, we conduct an in-depth analysis, revealing that 3D scene-centric VLMs show limited reliance on the 3D scene encoder, and the pre-train stage appears less effective than in 2D VLMs. Furthermore, we observe that data scaling benefits are less pronounced on larger datasets. Our investigation suggests that while these models possess cross-modal alignment capabilities, they tend to over-rely on linguistic cues and overfit to frequent answer distributions, thereby diminishing the effective utilization of the 3D encoder. To address these limitations and encourage genuine 3D scene understanding, we introduce a novel 3D Relevance Discrimination QA dataset designed to disrupt shortcut learning and improve 3D understanding. Our findings highlight the need for advanced evaluation and improved strategies for better 3D understanding in 3D VLMs.
Heartcare Suite: Multi-dimensional Understanding of ECG with Raw Multi-lead Signal Modeling
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We present Heartcare Suite, a multimodal comprehensive framework for finegrained electrocardiogram (ECG) understanding. It comprises three key components: (i) Heartcare-220K, a high-quality, structured, and comprehensive multimodal ECG dataset covering essential tasks such as disease diagnosis, waveform morphology analysis, and rhythm interpretation. (ii) Heartcare-Bench, a systematic and multi-dimensional benchmark designed to evaluate diagnostic intelligence and guide the optimization of Medical Multimodal Large Language Models (Med-MLLMs) in ECG scenarios. and (iii) HeartcareGPT with a tailored tokenizer Bidirectional ECG Abstract Tokenization (Beat), which compresses raw multi-lead signals into semantically rich discrete tokens via duallevel vector quantization and query-guided bidirectional diffusion mechanism. Built upon Heartcare-220K, HeartcareGPT achieves strong generalization and SoTA performance across multiple clinically meaningful tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Heartcare Suite is highly effective in advancing ECGspecific multimodal understanding and evaluation. Our project is available at https://github.com/Wznnnnn/Heartcare-Suite .
Fast-Slow Thinking for Large Vision-Language Model Reasoning
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large vision-language models (LVLMs) have revealed an \textit{overthinking} phenomenon, where models generate verbose reasoning across all tasks regardless of questions. To address this issue, we present \textbf{FAST}, a novel \textbf{Fa}st-\textbf{S}low \textbf{T}hinking framework that dynamically adapts reasoning depth based on question characteristics. Through empirical analysis, we establish the feasibility of fast-slow thinking in LVLMs by investigating how response length and data distribution affect performance. We develop FAST-GRPO with three components: model-based metrics for question characterization, an adaptive thinking reward mechanism, and difficulty-aware KL regularization. Experiments across seven reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that FAST achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with over 10\% relative improvement compared to the base model, while reducing token usage by 32.7-67.3\% compared to previous slow-thinking approaches, effectively balancing reasoning length and accuracy.
CMMCoT: Enhancing Complex Multi-Image Comprehension via Multi-Modal Chain-of-Thought and Memory Augmentation
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:While previous multimodal slow-thinking methods have demonstrated remarkable success in single-image understanding scenarios, their effectiveness becomes fundamentally constrained when extended to more complex multi-image comprehension tasks. This limitation stems from their predominant reliance on text-based intermediate reasoning processes. While for human, when engaging in sophisticated multi-image analysis, they typically perform two complementary cognitive operations: (1) continuous cross-image visual comparison through region-of-interest matching, and (2) dynamic memorization of critical visual concepts throughout the reasoning chain. Motivated by these observations, we propose the Complex Multi-Modal Chain-of-Thought (CMMCoT) framework, a multi-step reasoning framework that mimics human-like "slow thinking" for multi-image understanding. Our approach incorporates two key innovations: 1. The construction of interleaved multimodal multi-step reasoning chains, which utilize critical visual region tokens, extracted from intermediate reasoning steps, as supervisory signals. This mechanism not only facilitates comprehensive cross-modal understanding but also enhances model interpretability. 2. The introduction of a test-time memory augmentation module that expands the model reasoning capacity during inference while preserving parameter efficiency. Furthermore, to facilitate research in this direction, we have curated a novel multi-image slow-thinking dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge