Snigdha Chaturvedi
EUGens: Efficient, Unified, and General Dense Layers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Efficient neural networks are essential for scaling machine learning models to real-time applications and resource-constrained environments. Fully-connected feedforward layers (FFLs) introduce computation and parameter count bottlenecks within neural network architectures. To address this challenge, in this work, we propose a new class of dense layers that generalize standard fully-connected feedforward layers, \textbf{E}fficient, \textbf{U}nified and \textbf{Gen}eral dense layers (EUGens). EUGens leverage random features to approximate standard FFLs and go beyond them by incorporating a direct dependence on the input norms in their computations. The proposed layers unify existing efficient FFL extensions and improve efficiency by reducing inference complexity from quadratic to linear time. They also lead to \textbf{the first} unbiased algorithms approximating FFLs with arbitrary polynomial activation functions. Furthermore, EuGens reduce the parameter count and computational overhead while preserving the expressive power and adaptability of FFLs. We also present a layer-wise knowledge transfer technique that bypasses backpropagation, enabling efficient adaptation of EUGens to pre-trained models. Empirically, we observe that integrating EUGens into Transformers and MLPs yields substantial improvements in inference speed (up to \textbf{27}\%) and memory efficiency (up to \textbf{30}\%) across a range of tasks, including image classification, language model pre-training, and 3D scene reconstruction. Overall, our results highlight the potential of EUGens for the scalable deployment of large-scale neural networks in real-world scenarios.
Socratic Students: Teaching Language Models to Learn by Asking Questions
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at static interactions, where they answer user queries by retrieving knowledge encoded in their parameters. However, in many real-world settings, such as educational tutoring or medical assistance, relevant information is not directly available and must be actively acquired through dynamic interactions. An interactive agent would recognize its own uncertainty, ask targeted questions, and retain new knowledge efficiently. Prior work has primarily explored effective ways for a teacher to instruct the student, where the teacher identifies student gaps and provides guidance. In this work, we shift the focus to the student and investigate effective strategies to actively query the teacher in seeking useful information. Across math and coding benchmarks, where baseline student models begin with near-zero performance, we show that student-led approaches consistently yield absolute Pass@k improvements of at least 0.5 over static baselines. To improve question quality, we train students using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with guidance from either self or stronger students. We find that this guided training enables smaller models to learn how to ask better questions, further enhancing learning efficiency.
Classifying Unreliable Narrators with Large Language Models
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Often when we interact with a first-person account of events, we consider whether or not the narrator, the primary speaker of the text, is reliable. In this paper, we propose using computational methods to identify unreliable narrators, i.e. those who unintentionally misrepresent information. Borrowing literary theory from narratology to define different types of unreliable narrators based on a variety of textual phenomena, we present TUNa, a human-annotated dataset of narratives from multiple domains, including blog posts, subreddit posts, hotel reviews, and works of literature. We define classification tasks for intra-narrational, inter-narrational, and inter-textual unreliabilities and analyze the performance of popular open-weight and proprietary LLMs for each. We propose learning from literature to perform unreliable narrator classification on real-world text data. To this end, we experiment with few-shot, fine-tuning, and curriculum learning settings. Our results show that this task is very challenging, and there is potential for using LLMs to identify unreliable narrators. We release our expert-annotated dataset and code and invite future research in this area.
Improving Fairness of Large Language Models in Multi-document Summarization
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Fairness in multi-document summarization (MDS) is crucial for providing comprehensive views across documents with diverse social attribute values, which can significantly impact decision-making. For example, a summarization system that tends to overrepresent negative reviews of products can mislead customers into disregarding good products. Previous works measure fairness in MDS at two levels: summary-level and corpus-level. While summary-level fairness focuses on individual summaries, corpus-level fairness focuses on a corpus of summaries. Recent methods primarily focus on summary-level fairness. We propose FairPO, a preference tuning method that focuses on both summary-level and corpus-level fairness in MDS. To improve summary-level fairness, we propose to generate preference pairs by perturbing document sets. To improve corpus-level fairness, we propose fairness-aware preference tuning by dynamically adjusting the weights of preference pairs. Our experiments show that FairPO outperforms strong baselines while maintaining the critical qualities of summaries. The code is available at https://github.com/leehaoyuan/coverage_fairnes.
MarginSel : Max-Margin Demonstration Selection for LLMs
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at few-shot learning via in-context learning (ICL). However, the effectiveness of ICL is often sensitive to the selection and ordering of demonstration examples. To address this, we present MarginSel: Max-Margin Demonstration Selection for LLMs, a two-step method that selects hard demonstration examples for the ICL prompt, adapting to each test instance. Our approach achieves 2-7% absolute improvement in F1-score across classification tasks, compared to a random selection of examples. We also provide theoretical insights and empirical evidence showing that MarginSel induces max-margin behavior in LLMs by effectively increasing the margin for hard examples, analogous to support vectors, thereby shifting the decision boundary in a beneficial direction.
Fundamental Limits of Perfect Concept Erasure
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Concept erasure is the task of erasing information about a concept (e.g., gender or race) from a representation set while retaining the maximum possible utility -- information from original representations. Concept erasure is useful in several applications, such as removing sensitive concepts to achieve fairness and interpreting the impact of specific concepts on a model's performance. Previous concept erasure techniques have prioritized robustly erasing concepts over retaining the utility of the resultant representations. However, there seems to be an inherent tradeoff between erasure and retaining utility, making it unclear how to achieve perfect concept erasure while maintaining high utility. In this paper, we offer a fresh perspective toward solving this problem by quantifying the fundamental limits of concept erasure through an information-theoretic lens. Using these results, we investigate constraints on the data distribution and the erasure functions required to achieve the limits of perfect concept erasure. Empirically, we show that the derived erasure functions achieve the optimal theoretical bounds. Additionally, we show that our approach outperforms existing methods on a range of synthetic and real-world datasets using GPT-4 representations.
Coverage-based Fairness in Multi-document Summarization
Dec 11, 2024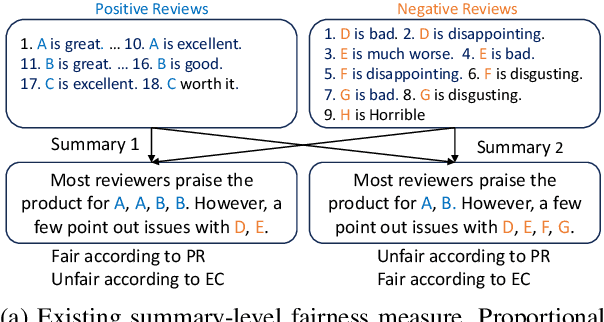

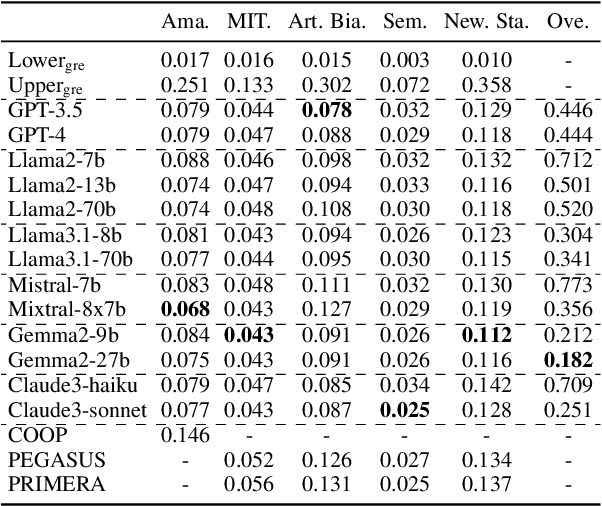

Abstract:Fairness in multi-document summarization (MDS) measures whether a system can generate a summary fairly representing information from documents with different social attribute values. Fairness in MDS is crucial since a fair summary can offer readers a comprehensive view. Previous works focus on quantifying summary-level fairness using Proportional Representation, a fairness measure based on Statistical Parity. However, Proportional Representation does not consider redundancy in input documents and overlooks corpus-level unfairness. In this work, we propose a new summary-level fairness measure, Equal Coverage, which is based on coverage of documents with different social attribute values and considers the redundancy within documents. To detect the corpus-level unfairness, we propose a new corpus-level measure, Coverage Parity. Our human evaluations show that our measures align more with our definition of fairness. Using our measures, we evaluate the fairness of thirteen different LLMs. We find that Claude3-sonnet is the fairest among all evaluated LLMs. We also find that almost all LLMs overrepresent different social attribute values.
SocialGaze: Improving the Integration of Human Social Norms in Large Language Models
Oct 11, 2024
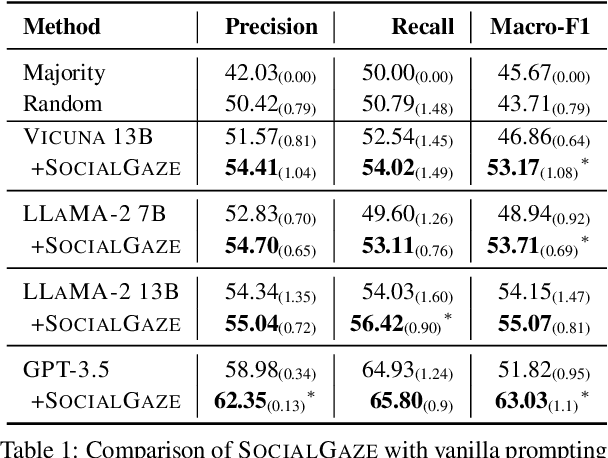
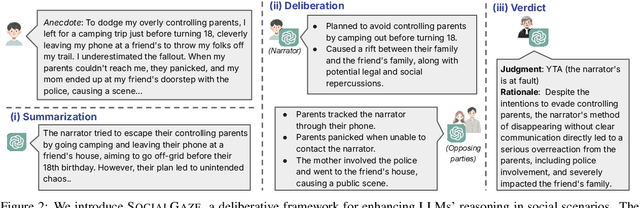
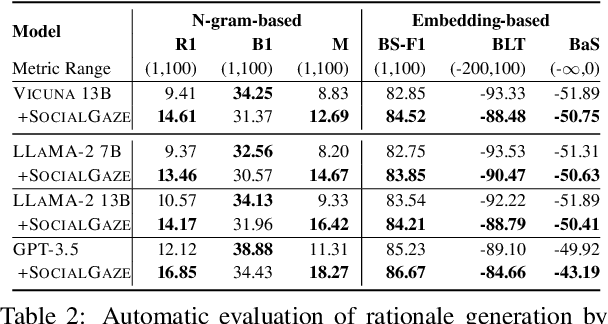
Abstract:While much research has explored enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in the last few years, there is a gap in understanding the alignment of these models with social values and norms. We introduce the task of judging social acceptance. Social acceptance requires models to judge and rationalize the acceptability of people's actions in social situations. For example, is it socially acceptable for a neighbor to ask others in the community to keep their pets indoors at night? We find that LLMs' understanding of social acceptance is often misaligned with human consensus. To alleviate this, we introduce SocialGaze, a multi-step prompting framework, in which a language model verbalizes a social situation from multiple perspectives before forming a judgment. Our experiments demonstrate that the SocialGaze approach improves the alignment with human judgments by up to 11 F1 points with the GPT-3.5 model. We also identify biases and correlations in LLMs in assigning blame that is related to features such as the gender (males are significantly more likely to be judged unfairly) and age (LLMs are more aligned with humans for older narrators).
Structured Unrestricted-Rank Matrices for Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Recent efforts to scale Transformer models have demonstrated rapid progress across a wide range of tasks (Wei et al., 2022). However, fine-tuning these models for downstream tasks is expensive due to their large parameter counts. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approaches have emerged as a viable alternative by allowing us to fine-tune models by updating only a small number of parameters. In this work, we propose a general framework for parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), based on structured unrestricted-rank matrices (SURM) which can serve as a drop-in replacement for popular approaches such as Adapters and LoRA. Unlike other methods like LoRA, SURMs provides more flexibility in finding the right balance between compactness and expressiveness. This is achieved by using low displacement rank matrices (LDRMs), which hasn't been used in this context before. SURMs remain competitive with baselines, often providing significant quality improvements while using a smaller parameter budget. SURMs achieve 5-7% accuracy gains on various image classification tasks while replacing low-rank matrices in LoRA. It also results in up to 12x reduction of the number of parameters in adapters (with virtually no loss in quality) on the GLUE benchmark.
Towards Scalable Exact Machine Unlearning Using Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Machine unlearning is the process of efficiently removing the influence of a training data instance from a trained machine learning model without retraining it from scratch. A popular subclass of unlearning approaches is exact machine unlearning, which focuses on techniques that explicitly guarantee the removal of the influence of a data instance from a model. Exact unlearning approaches use a machine learning model in which individual components are trained on disjoint subsets of the data. During deletion, exact unlearning approaches only retrain the affected components rather than the entire model. While existing approaches reduce retraining costs, it can still be expensive for an organization to retrain a model component as it requires halting a system in production, which leads to service failure and adversely impacts customers. To address these challenges, we introduce an exact unlearning framework -- Sequence-aware Sharded Sliced Training (S3T), designed to enhance the deletion capabilities of an exact unlearning system while minimizing the impact on model's performance. At the core of S3T, we utilize a lightweight parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach that enables parameter isolation by sequentially training layers with disjoint data slices. This enables efficient unlearning by simply deactivating the layers affected by data deletion. Furthermore, to reduce the retraining cost and improve model performance, we train the model on multiple data sequences, which allows S3T to handle an increased number of deletion requests. Both theoretically and empirically, we demonstrate that S3T attains superior deletion capabilities and enhanced performance compared to baselines across a wide range of settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge