Avinava Dubey
Google Research
Inference-time Unlearning Using Conformal Prediction
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning is the process of efficiently removing specific information from a trained machine learning model without retraining from scratch. Existing unlearning methods, which often provide provable guarantees, typically involve retraining a subset of model parameters based on a forget set. While these approaches show promise in certain scenarios, their underlying assumptions are often challenged in real-world applications -- particularly when applied to generative models. Furthermore, updating parameters using these unlearning procedures often degrades the general-purpose capabilities the model acquired during pre-training. Motivated by these shortcomings, this paper considers the paradigm of inference time unlearning -- wherein, the generative model is equipped with an (approximately correct) verifier that judges whether the model's response satisfies appropriate unlearning guarantees. This paper introduces a framework that iteratively refines the quality of the generated responses using feedback from the verifier without updating the model parameters. The proposed framework leverages conformal prediction to reduce computational overhead and provide distribution-free unlearning guarantees. This paper's approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, reducing unlearning error by up to 93% across challenging unlearning benchmarks.
EUGens: Efficient, Unified, and General Dense Layers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Efficient neural networks are essential for scaling machine learning models to real-time applications and resource-constrained environments. Fully-connected feedforward layers (FFLs) introduce computation and parameter count bottlenecks within neural network architectures. To address this challenge, in this work, we propose a new class of dense layers that generalize standard fully-connected feedforward layers, \textbf{E}fficient, \textbf{U}nified and \textbf{Gen}eral dense layers (EUGens). EUGens leverage random features to approximate standard FFLs and go beyond them by incorporating a direct dependence on the input norms in their computations. The proposed layers unify existing efficient FFL extensions and improve efficiency by reducing inference complexity from quadratic to linear time. They also lead to \textbf{the first} unbiased algorithms approximating FFLs with arbitrary polynomial activation functions. Furthermore, EuGens reduce the parameter count and computational overhead while preserving the expressive power and adaptability of FFLs. We also present a layer-wise knowledge transfer technique that bypasses backpropagation, enabling efficient adaptation of EUGens to pre-trained models. Empirically, we observe that integrating EUGens into Transformers and MLPs yields substantial improvements in inference speed (up to \textbf{27}\%) and memory efficiency (up to \textbf{30}\%) across a range of tasks, including image classification, language model pre-training, and 3D scene reconstruction. Overall, our results highlight the potential of EUGens for the scalable deployment of large-scale neural networks in real-world scenarios.
Computationally-efficient Graph Modeling with Refined Graph Random Features
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:We propose refined GRFs (GRFs++), a new class of Graph Random Features (GRFs) for efficient and accurate computations involving kernels defined on the nodes of a graph. GRFs++ resolve some of the long-standing limitations of regular GRFs, including difficulty modeling relationships between more distant nodes. They reduce dependence on sampling long graph random walks via a novel walk-stitching technique, concatenating several shorter walks without breaking unbiasedness. By applying these techniques, GRFs++ inherit the approximation quality provided by longer walks but with greater efficiency, trading sequential, inefficient sampling of a long walk for parallel computation of short walks and matrix-matrix multiplication. Furthermore, GRFs++ extend the simplistic GRFs walk termination mechanism (Bernoulli schemes with fixed halting probabilities) to a broader class of strategies, applying general distributions on the walks' lengths. This improves the approximation accuracy of graph kernels, without incurring extra computational cost. We provide empirical evaluations to showcase all our claims and complement our results with theoretical analysis.
Fundamental Limits of Perfect Concept Erasure
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Concept erasure is the task of erasing information about a concept (e.g., gender or race) from a representation set while retaining the maximum possible utility -- information from original representations. Concept erasure is useful in several applications, such as removing sensitive concepts to achieve fairness and interpreting the impact of specific concepts on a model's performance. Previous concept erasure techniques have prioritized robustly erasing concepts over retaining the utility of the resultant representations. However, there seems to be an inherent tradeoff between erasure and retaining utility, making it unclear how to achieve perfect concept erasure while maintaining high utility. In this paper, we offer a fresh perspective toward solving this problem by quantifying the fundamental limits of concept erasure through an information-theoretic lens. Using these results, we investigate constraints on the data distribution and the erasure functions required to achieve the limits of perfect concept erasure. Empirically, we show that the derived erasure functions achieve the optimal theoretical bounds. Additionally, we show that our approach outperforms existing methods on a range of synthetic and real-world datasets using GPT-4 representations.
Learning the RoPEs: Better 2D and 3D Position Encodings with STRING
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We introduce STRING: Separable Translationally Invariant Position Encodings. STRING extends Rotary Position Encodings, a recently proposed and widely used algorithm in large language models, via a unifying theoretical framework. Importantly, STRING still provides exact translation invariance, including token coordinates of arbitrary dimensionality, whilst maintaining a low computational footprint. These properties are especially important in robotics, where efficient 3D token representation is key. We integrate STRING into Vision Transformers with RGB(-D) inputs (color plus optional depth), showing substantial gains, e.g. in open-vocabulary object detection and for robotics controllers. We complement our experiments with a rigorous mathematical analysis, proving the universality of our methods.
Optimal Time Complexity Algorithms for Computing General Random Walk Graph Kernels on Sparse Graphs
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:We present the first linear time complexity randomized algorithms for unbiased approximation of the celebrated family of general random walk kernels (RWKs) for sparse graphs. This includes both labelled and unlabelled instances. The previous fastest methods for general RWKs were of cubic time complexity and not applicable to labelled graphs. Our method samples dependent random walks to compute novel graph embeddings in $\mathbb{R}^d$ whose dot product is equal to the true RWK in expectation. It does so without instantiating the direct product graph in memory, meaning we can scale to massive datasets that cannot be stored on a single machine. We derive exponential concentration bounds to prove that our estimator is sharp, and show that the ability to approximate general RWKs (rather than just special cases) unlocks efficient implicit graph kernel learning. Our method is up to $\mathbf{27\times}$ faster than its counterparts for efficient computation on large graphs and scales to graphs $\mathbf{128 \times}$ bigger than largest examples amenable to brute-force computation.
Magnituder Layers for Implicit Neural Representations in 3D
Oct 13, 2024



Abstract:Improving the efficiency and performance of implicit neural representations in 3D, particularly Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Signed Distance Fields (SDF) is crucial for enabling their use in real-time applications. These models, while capable of generating photo-realistic novel views and detailed 3D reconstructions, often suffer from high computational costs and slow inference times. To address this, we introduce a novel neural network layer called the "magnituder", designed to reduce the number of training parameters in these models without sacrificing their expressive power. By integrating magnituders into standard feed-forward layer stacks, we achieve improved inference speed and adaptability. Furthermore, our approach enables a zero-shot performance boost in trained implicit neural representation models through layer-wise knowledge transfer without backpropagation, leading to more efficient scene reconstruction in dynamic environments.
Conditioned Language Policy: A General Framework for Steerable Multi-Objective Finetuning
Jul 22, 2024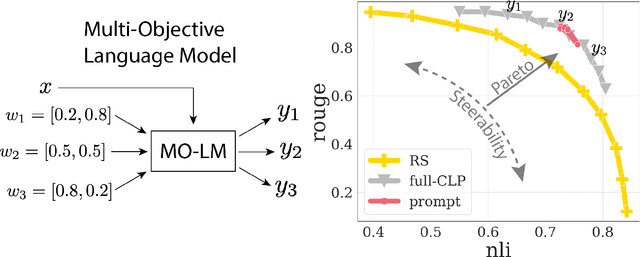
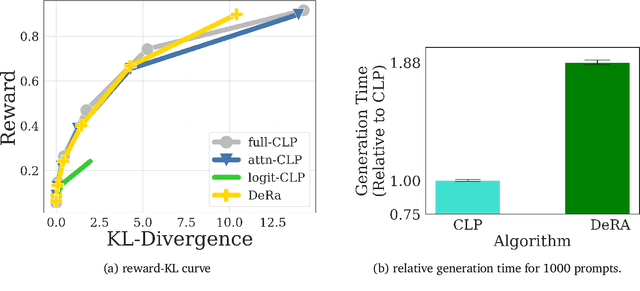
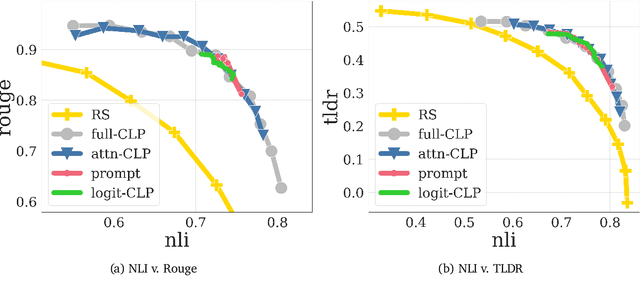
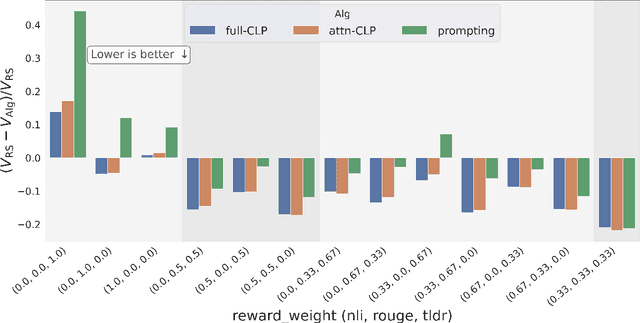
Abstract:Reward-based finetuning is crucial for aligning language policies with intended behaviors (e.g., creativity and safety). A key challenge here is to develop steerable language models that trade-off multiple (conflicting) objectives in a flexible and efficient manner. This paper presents Conditioned Language Policy (CLP), a general framework for finetuning language models on multiple objectives. Building on techniques from multi-task training and parameter-efficient finetuning, CLP can learn steerable models that effectively trade-off conflicting objectives at inference time. Notably, this does not require training or maintaining multiple models to achieve different trade-offs between the objectives. Through an extensive set of experiments and ablations, we show that the CLP framework learns steerable models that outperform and Pareto-dominate the current state-of-the-art approaches for multi-objective finetuning.
Structured Unrestricted-Rank Matrices for Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Recent efforts to scale Transformer models have demonstrated rapid progress across a wide range of tasks (Wei et al., 2022). However, fine-tuning these models for downstream tasks is expensive due to their large parameter counts. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approaches have emerged as a viable alternative by allowing us to fine-tune models by updating only a small number of parameters. In this work, we propose a general framework for parameter efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), based on structured unrestricted-rank matrices (SURM) which can serve as a drop-in replacement for popular approaches such as Adapters and LoRA. Unlike other methods like LoRA, SURMs provides more flexibility in finding the right balance between compactness and expressiveness. This is achieved by using low displacement rank matrices (LDRMs), which hasn't been used in this context before. SURMs remain competitive with baselines, often providing significant quality improvements while using a smaller parameter budget. SURMs achieve 5-7% accuracy gains on various image classification tasks while replacing low-rank matrices in LoRA. It also results in up to 12x reduction of the number of parameters in adapters (with virtually no loss in quality) on the GLUE benchmark.
Towards Scalable Exact Machine Unlearning Using Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Machine unlearning is the process of efficiently removing the influence of a training data instance from a trained machine learning model without retraining it from scratch. A popular subclass of unlearning approaches is exact machine unlearning, which focuses on techniques that explicitly guarantee the removal of the influence of a data instance from a model. Exact unlearning approaches use a machine learning model in which individual components are trained on disjoint subsets of the data. During deletion, exact unlearning approaches only retrain the affected components rather than the entire model. While existing approaches reduce retraining costs, it can still be expensive for an organization to retrain a model component as it requires halting a system in production, which leads to service failure and adversely impacts customers. To address these challenges, we introduce an exact unlearning framework -- Sequence-aware Sharded Sliced Training (S3T), designed to enhance the deletion capabilities of an exact unlearning system while minimizing the impact on model's performance. At the core of S3T, we utilize a lightweight parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach that enables parameter isolation by sequentially training layers with disjoint data slices. This enables efficient unlearning by simply deactivating the layers affected by data deletion. Furthermore, to reduce the retraining cost and improve model performance, we train the model on multiple data sequences, which allows S3T to handle an increased number of deletion requests. Both theoretically and empirically, we demonstrate that S3T attains superior deletion capabilities and enhanced performance compared to baselines across a wide range of settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge