Alekh Agarwal
Cost-Optimal Active AI Model Evaluation
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The development lifecycle of generative AI systems requires continual evaluation, data acquisition, and annotation, which is costly in both resources and time. In practice, rapid iteration often makes it necessary to rely on synthetic annotation data because of the low cost, despite the potential for substantial bias. In this paper, we develop novel, cost-aware methods for actively balancing the use of a cheap, but often inaccurate, weak rater -- such as a model-based autorater that is designed to automatically assess the quality of generated content -- with a more expensive, but also more accurate, strong rater alternative such as a human. More specifically, the goal of our approach is to produce a low variance, unbiased estimate of the mean of the target "strong" rating, subject to some total annotation budget. Building on recent work in active and prediction-powered statistical inference, we derive a family of cost-optimal policies for allocating a given annotation budget between weak and strong raters so as to maximize statistical efficiency. Using synthetic and real-world data, we empirically characterize the conditions under which these policies yield improvements over prior methods. We find that, especially in tasks where there is high variability in the difficulty of examples, our policies can achieve the same estimation precision at a far lower total annotation budget than standard evaluation methods.
Rethinking the Global Convergence of Softmax Policy Gradient with Linear Function Approximation
May 06, 2025Abstract:Policy gradient (PG) methods have played an essential role in the empirical successes of reinforcement learning. In order to handle large state-action spaces, PG methods are typically used with function approximation. In this setting, the approximation error in modeling problem-dependent quantities is a key notion for characterizing the global convergence of PG methods. We focus on Softmax PG with linear function approximation (referred to as $\texttt{Lin-SPG}$) and demonstrate that the approximation error is irrelevant to the algorithm's global convergence even for the stochastic bandit setting. Consequently, we first identify the necessary and sufficient conditions on the feature representation that can guarantee the asymptotic global convergence of $\texttt{Lin-SPG}$. Under these feature conditions, we prove that $T$ iterations of $\texttt{Lin-SPG}$ with a problem-specific learning rate result in an $O(1/T)$ convergence to the optimal policy. Furthermore, we prove that $\texttt{Lin-SPG}$ with any arbitrary constant learning rate can ensure asymptotic global convergence to the optimal policy.
Ordering-based Conditions for Global Convergence of Policy Gradient Methods
Apr 02, 2025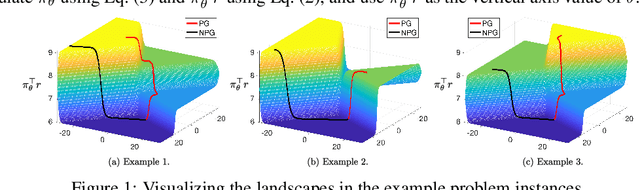
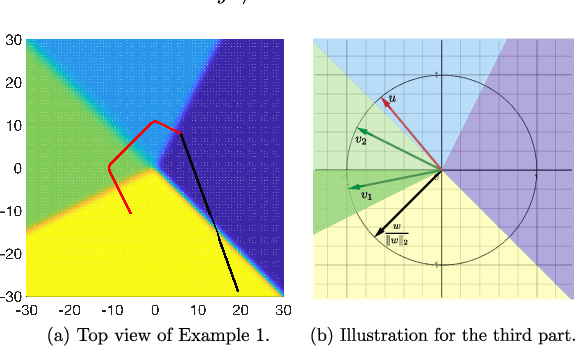
Abstract:We prove that, for finite-arm bandits with linear function approximation, the global convergence of policy gradient (PG) methods depends on inter-related properties between the policy update and the representation. textcolor{blue}{First}, we establish a few key observations that frame the study: \textbf{(i)} Global convergence can be achieved under linear function approximation without policy or reward realizability, both for the standard Softmax PG and natural policy gradient (NPG). \textbf{(ii)} Approximation error is not a key quantity for characterizing global convergence in either algorithm. \textbf{(iii)} The conditions on the representation that imply global convergence are different between these two algorithms. Overall, these observations call into question approximation error as an appropriate quantity for characterizing the global convergence of PG methods under linear function approximation. \textcolor{blue}{Second}, motivated by these observations, we establish new general results: \textbf{(i)} NPG with linear function approximation achieves global convergence \emph{if and only if} the projection of the reward onto the representable space preserves the optimal action's rank, a quantity that is not strongly related to approximation error. \textbf{(ii)} The global convergence of Softmax PG occurs if the representation satisfies a non-domination condition and can preserve the ranking of rewards, which goes well beyond policy or reward realizability. We provide experimental results to support these theoretical findings.
Mitigating Preference Hacking in Policy Optimization with Pessimism
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:This work tackles the problem of overoptimization in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), a prevalent technique for aligning models with human preferences. RLHF relies on reward or preference models trained on \emph{fixed preference datasets}, and these models are unreliable when evaluated outside the support of this preference data, leading to the common reward or preference hacking phenomenon. We propose novel, pessimistic objectives for RLHF which are provably robust to overoptimization through the use of pessimism in the face of uncertainty, and design practical algorithms, P3O and PRPO, to optimize these objectives. Our approach is derived for the general preference optimization setting, but can be used with reward models as well. We evaluate P3O and PRPO on the tasks of fine-tuning language models for document summarization and creating helpful assistants, demonstrating remarkable resilience to overoptimization.
Optimizing Pre-Training Data Mixtures with Mixtures of Data Expert Models
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:We propose a method to optimize language model pre-training data mixtures through efficient approximation of the cross-entropy loss corresponding to each candidate mixture via a Mixture of Data Experts (MDE). We use this approximation as a source of additional features in a regression model, trained from observations of model loss for a small number of mixtures. Experiments with Transformer decoder-only language models in the range of 70M to 1B parameters on the SlimPajama dataset show that our method achieves significantly better performance than approaches that train regression models using only the mixture rates as input features. Combining this improved optimization method with an objective that takes into account cross-entropy on end task data leads to superior performance on few-shot downstream evaluations. We also provide theoretical insights on why aggregation of data expert predictions can provide good approximations to model losses for data mixtures.
Small steps no more: Global convergence of stochastic gradient bandits for arbitrary learning rates
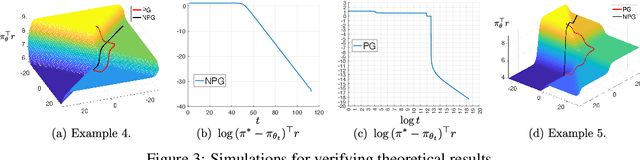
Feb 11, 2025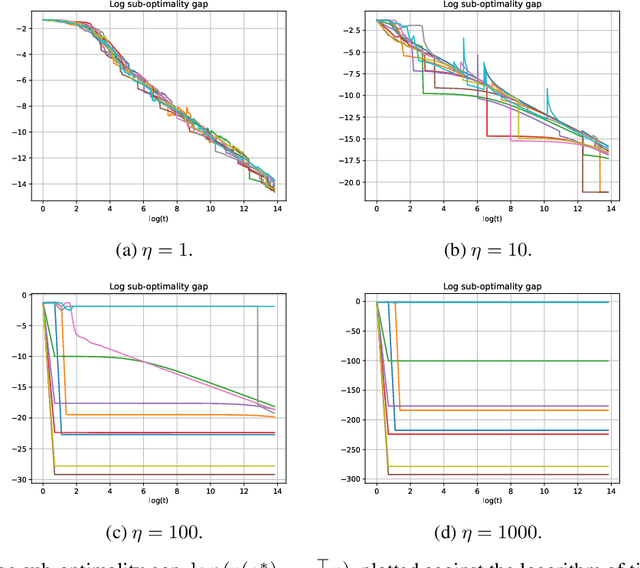
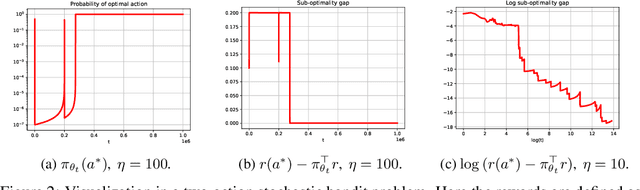
Abstract:We provide a new understanding of the stochastic gradient bandit algorithm by showing that it converges to a globally optimal policy almost surely using \emph{any} constant learning rate. This result demonstrates that the stochastic gradient algorithm continues to balance exploration and exploitation appropriately even in scenarios where standard smoothness and noise control assumptions break down. The proofs are based on novel findings about action sampling rates and the relationship between cumulative progress and noise, and extend the current understanding of how simple stochastic gradient methods behave in bandit settings.
Design Considerations in Offline Preference-based RL
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Offline algorithms for Reinforcement Learning from Human Preferences (RLHF), which use only a fixed dataset of sampled responses given an input, and preference feedback among these responses, have gained increasing prominence in the literature on aligning language models. In this paper, we study how the different design choices made in methods such as DPO, IPO, SLiC and many variants influence the quality of the learned policy, from a theoretical perspective. Our treatment yields insights into the choices of loss function, the policy which is used to normalize log-likelihoods, and also the role of the data sampling policy. Notably, our results do not rely on the standard reparameterization-style arguments used to motivate some of the algorithms in this family, which allows us to give a unified treatment to a broad class of methods. We also conduct a small empirical study to verify some of the theoretical findings on a standard summarization benchmark.
Catoni Contextual Bandits are Robust to Heavy-tailed Rewards
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Typical contextual bandit algorithms assume that the rewards at each round lie in some fixed range $[0, R]$, and their regret scales polynomially with this reward range $R$. However, many practical scenarios naturally involve heavy-tailed rewards or rewards where the worst-case range can be substantially larger than the variance. In this paper, we develop an algorithmic approach building on Catoni's estimator from robust statistics, and apply it to contextual bandits with general function approximation. When the variance of the reward at each round is known, we use a variance-weighted regression approach and establish a regret bound that depends only on the cumulative reward variance and logarithmically on the reward range $R$ as well as the number of rounds $T$. For the unknown-variance case, we further propose a careful peeling-based algorithm and remove the need for cumbersome variance estimation. With additional dependence on the fourth moment, our algorithm also enjoys a variance-based bound with logarithmic reward-range dependence. Moreover, we demonstrate the optimality of the leading-order term in our regret bound through a matching lower bound.
Preserving Expert-Level Privacy in Offline Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:The offline reinforcement learning (RL) problem aims to learn an optimal policy from historical data collected by one or more behavioural policies (experts) by interacting with an environment. However, the individual experts may be privacy-sensitive in that the learnt policy may retain information about their precise choices. In some domains like personalized retrieval, advertising and healthcare, the expert choices are considered sensitive data. To provably protect the privacy of such experts, we propose a novel consensus-based expert-level differentially private offline RL training approach compatible with any existing offline RL algorithm. We prove rigorous differential privacy guarantees, while maintaining strong empirical performance. Unlike existing work in differentially private RL, we supplement the theory with proof-of-concept experiments on classic RL environments featuring large continuous state spaces, demonstrating substantial improvements over a natural baseline across multiple tasks.
Rewarding Progress: Scaling Automated Process Verifiers for LLM Reasoning
Oct 10, 2024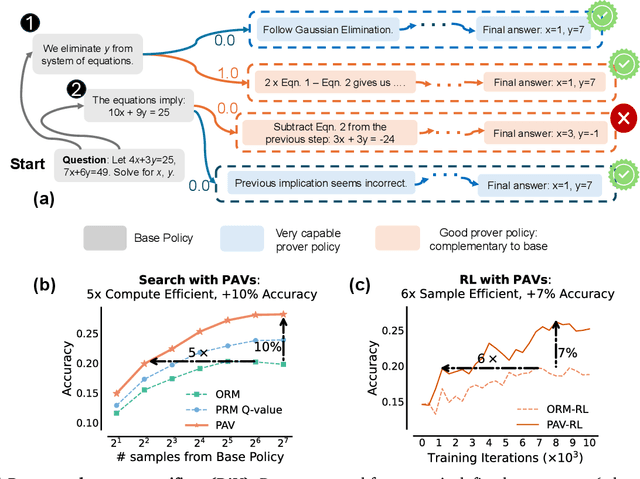
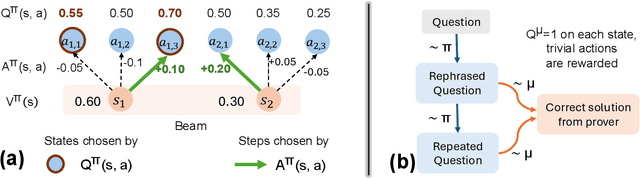
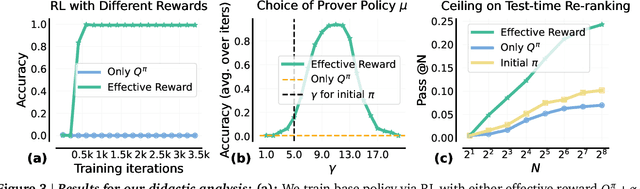
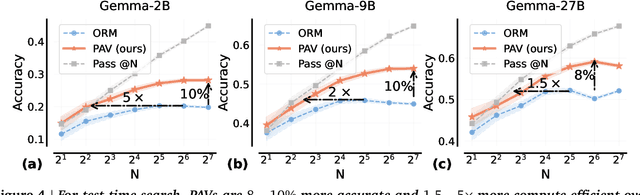
Abstract:A promising approach for improving reasoning in large language models is to use process reward models (PRMs). PRMs provide feedback at each step of a multi-step reasoning trace, potentially improving credit assignment over outcome reward models (ORMs) that only provide feedback at the final step. However, collecting dense, per-step human labels is not scalable, and training PRMs from automatically-labeled data has thus far led to limited gains. To improve a base policy by running search against a PRM or using it as dense rewards for reinforcement learning (RL), we ask: "How should we design process rewards?". Our key insight is that, to be effective, the process reward for a step should measure progress: a change in the likelihood of producing a correct response in the future, before and after taking the step, corresponding to the notion of step-level advantages in RL. Crucially, this progress should be measured under a prover policy distinct from the base policy. We theoretically characterize the set of good provers and our results show that optimizing process rewards from such provers improves exploration during test-time search and online RL. In fact, our characterization shows that weak prover policies can substantially improve a stronger base policy, which we also observe empirically. We validate our claims by training process advantage verifiers (PAVs) to predict progress under such provers, and show that compared to ORMs, test-time search against PAVs is $>8\%$ more accurate, and $1.5-5\times$ more compute-efficient. Online RL with dense rewards from PAVs enables one of the first results with $5-6\times$ gain in sample efficiency, and $>6\%$ gain in accuracy, over ORMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge