Yue Hao
DQO-MAP: Dual Quadrics Multi-Object mapping with Gaussian Splatting
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Accurate object perception is essential for robotic applications such as object navigation. In this paper, we propose DQO-MAP, a novel object-SLAM system that seamlessly integrates object pose estimation and reconstruction. We employ 3D Gaussian Splatting for high-fidelity object reconstruction and leverage quadrics for precise object pose estimation. Both of them management is handled on the CPU, while optimization is performed on the GPU, significantly improving system efficiency. By associating objects with unique IDs, our system enables rapid object extraction from the scene. Extensive experimental results on object reconstruction and pose estimation demonstrate that DQO-MAP achieves outstanding performance in terms of precision, reconstruction quality, and computational efficiency. The code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/LiHaoy-ux/DQO-MAP.
Prior-mean-assisted Bayesian optimization application on FRIB Front-End tunning
Nov 11, 2022Abstract:Bayesian optimization~(BO) is often used for accelerator tuning due to its high sample efficiency. However, the computational scalability of training over large data-set can be problematic and the adoption of historical data in a computationally efficient way is not trivial. Here, we exploit a neural network model trained over historical data as a prior mean of BO for FRIB Front-End tuning.
Spiking SiamFC++: Deep Spiking Neural Network for Object Tracking
Sep 24, 2022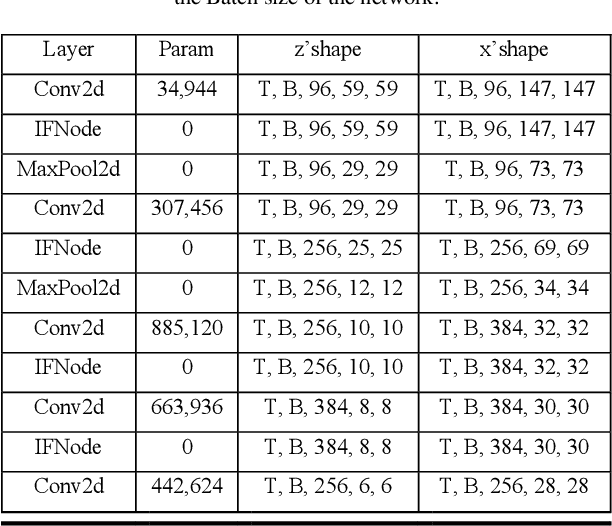
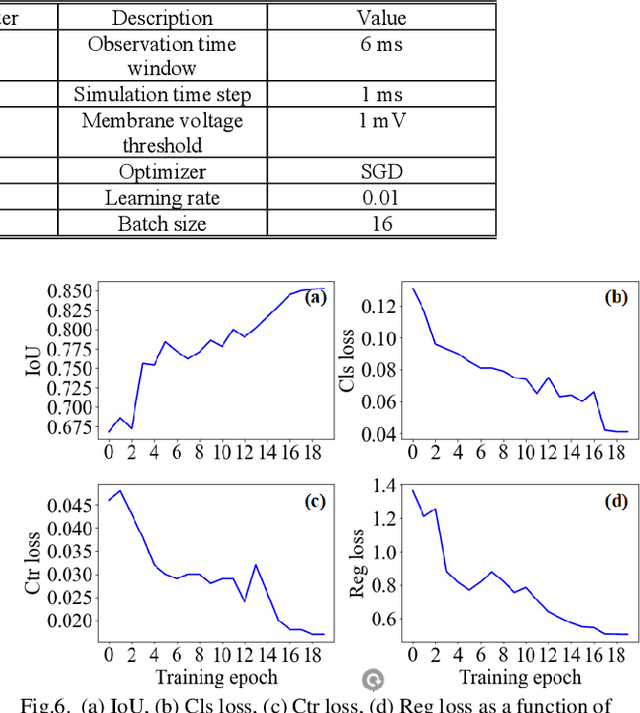
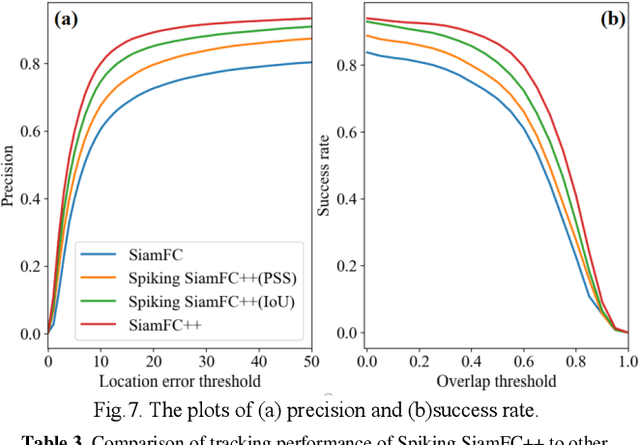
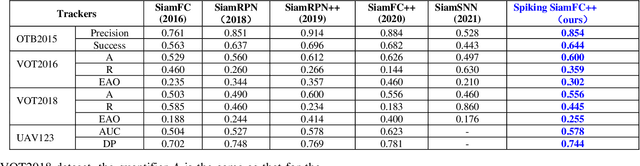
Abstract:Spiking neural network (SNN) is a biologically-plausible model and exhibits advantages of high computational capability and low power consumption. While the training of deep SNN is still an open problem, which limits the real-world applications of deep SNN. Here we propose a deep SNN architecture named Spiking SiamFC++ for object tracking with end-to-end direct training. Specifically, the AlexNet network is extended in the time domain to extract the feature, and the surrogate gradient function is adopted to realize direct supervised training of the deep SNN. To examine the performance of the Spiking SiamFC++, several tracking benchmarks including OTB2013, OTB2015, VOT2015, VOT2016, and UAV123 are considered. It is found that, the precision loss is small compared with the original SiamFC++. Compared with the existing SNN-based target tracker, e.g., the SiamSNN, the precision (succession) of the proposed Spiking SiamFC++ reaches 85.24% (64.37%), which is much higher than that of 52.78% (44.32%) achieved by the SiamSNN. To our best knowledge, the performance of the Spiking SiamFC++ outperforms the existing state-of-the-art approaches in SNN-based object tracking, which provides a novel path for SNN application in the field of target tracking. This work may further promote the development of SNN algorithms and neuromorphic chips.
Origami-based Zygote structure enables pluripotent shape-transforming deployable structure
Aug 08, 2022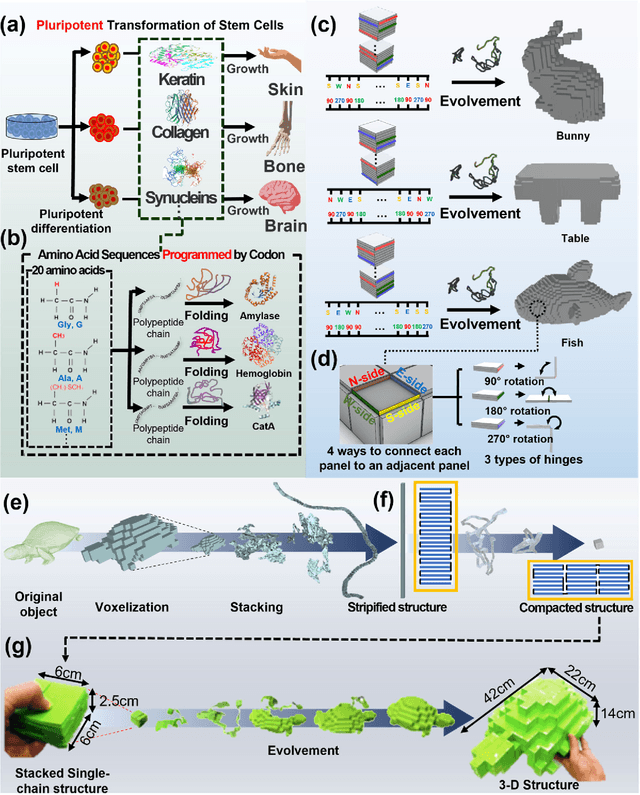


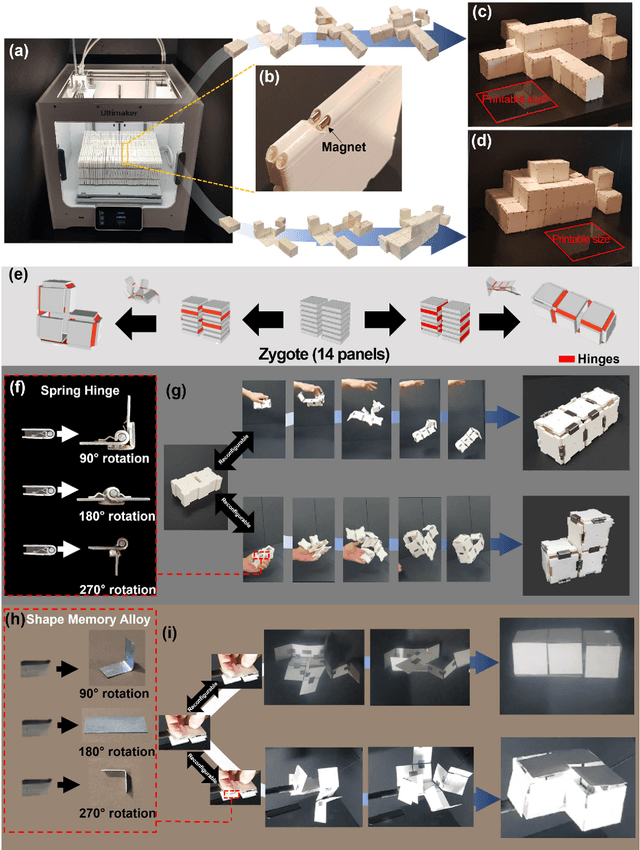
Abstract:We propose an algorithmic framework of a pluripotent structure evolving from a simple compact structure into diverse complex 3-D structures for designing the shape transformable, reconfigurable, and deployable structures and robots. Our algorithmic approach suggests a way of transforming a compact structure consisting of uniform building blocks into a large, desired 3-D shape. Analogous to the pluripotent stem cells that can grow into a preprogrammed shape according to coded information, which we call DNA, compactly stacked panels named the zygote structure can evolve into arbitrary 3-D structures by programming their connection path. Our stacking algorithm obtains this coded sequence by inversely stacking the voxelized surface of the desired structure into a tree. Applying the connection path obtained by the stacking algorithm, the compactly stacked panels named the zygote structure can be deployed into diverse large 3-D structures. We conceptually demonstrated our pluripotent evolving structure by energy releasing commercial spring hinges and thermally actuated shape memory alloy (SMA) hinges, respectively. We also show that the proposed concept enables the fabrication of large structures in a significantly smaller workspace.
Metal Blossom: Laser Forming Complex and Freeform Metal Structures Imitating Flower Blooming
Nov 30, 2021
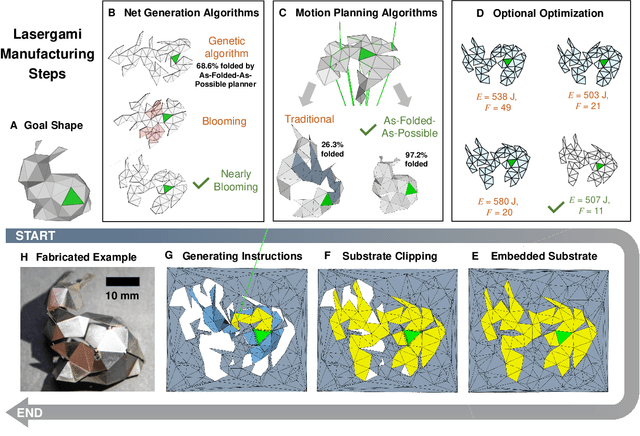
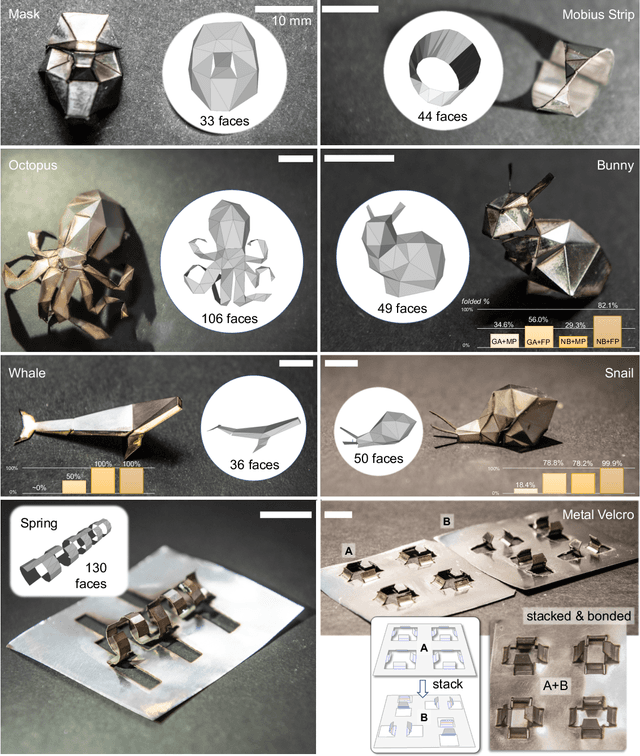
Abstract:For centuries, human civilizations devised metal forming techniques to make tools and items; yet, customized metal forming remains costly and intricate. Laser-forming origami} (lasergami) is a metal forming process where a laser beam cuts and folds a planar metal sheet to form a three-dimensional (3D) shape. Designing foldable structures formable by lasers, however, has long been a trial-and-error practice that requires significant mental effort and hinders the possibility of creating practical structures. This work demonstrates for the first time that lasergami can form a freeform set of metallic structures previously believed to have been impossible to be laser-formed. This technological breakthrough is enabled by new computational origami methods that imitate flower blooming and optimize laser folding instructions. Combined with new ideas that address laser line of sight and minimize fabrication energy, we report a low-cost manufacturing framework that can be readily adopted by hobbyists and professionals alike.
Planning Folding Motion with Simulation in the Loop Using Laser Forming Origami and Thermal Behaviors as an Example
Nov 20, 2020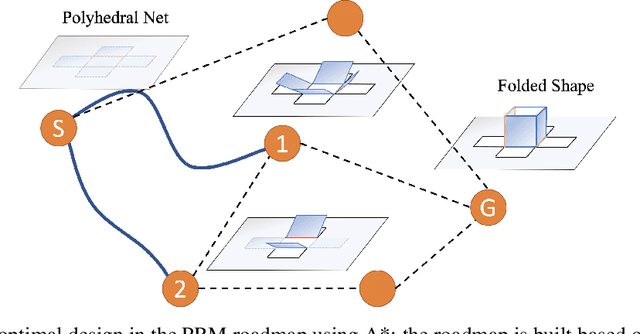
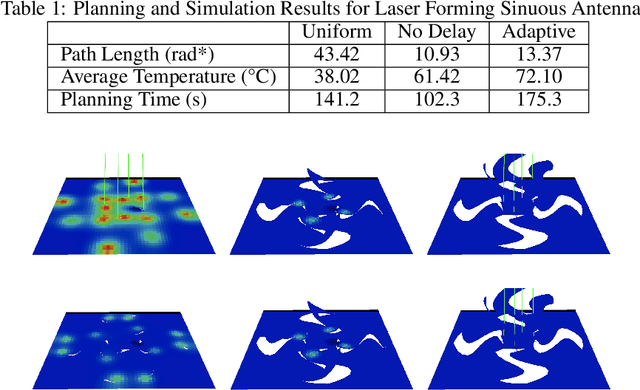

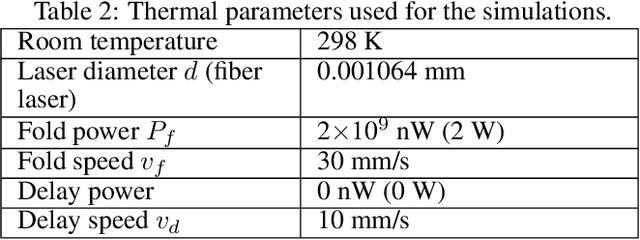
Abstract:Designing a robot or structure that can fold itself into a target shape is a process that involves challenges originated from multiple sources. For example, the designer of rigid self-folding robots must consider foldability from geometric and kinematic aspects to avoid self-intersection and undesired deformations. Recent works have shown success in estimating foldability of a design using robot motion planners. However, many foldable structures are actuated using physically coupled reactions (i.e., folding originated from thermal, chemical, or electromagnetic loads). Therefore, a reliable foldability analysis must consider additional constraints that resulted from these critical phenomena. This work investigates the idea of efficiently incorporating computationally expensive physics simulation within the folding motion planner to provide a better estimation of the foldability. In this paper, we will use laser forming origami as an example to demonstrate the benefits of considering the properties beyond geometry. We show that the design produced by the proposed method can be folded more efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge