Yue Lin
Policy-Conditioned Policies for Multi-Agent Task Solving
Dec 24, 2025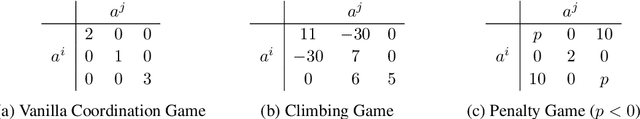
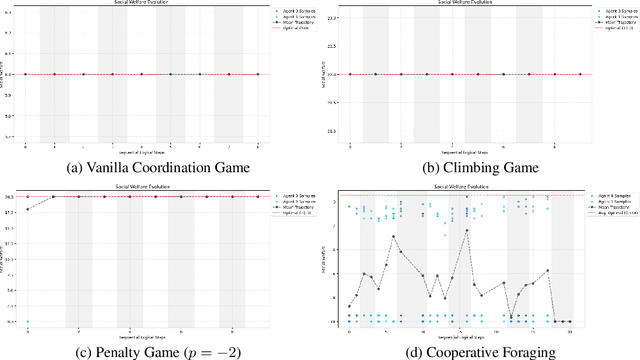
Abstract:In multi-agent tasks, the central challenge lies in the dynamic adaptation of strategies. However, directly conditioning on opponents' strategies is intractable in the prevalent deep reinforcement learning paradigm due to a fundamental ``representational bottleneck'': neural policies are opaque, high-dimensional parameter vectors that are incomprehensible to other agents. In this work, we propose a paradigm shift that bridges this gap by representing policies as human-interpretable source code and utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) as approximate interpreters. This programmatic representation allows us to operationalize the game-theoretic concept of \textit{Program Equilibrium}. We reformulate the learning problem by utilizing LLMs to perform optimization directly in the space of programmatic policies. The LLM functions as a point-wise best-response operator that iteratively synthesizes and refines the ego agent's policy code to respond to the opponent's strategy. We formalize this process as \textit{Programmatic Iterated Best Response (PIBR)}, an algorithm where the policy code is optimized by textual gradients, using structured feedback derived from game utility and runtime unit tests. We demonstrate that this approach effectively solves several standard coordination matrix games and a cooperative Level-Based Foraging environment.
Information Bargaining: Bilateral Commitment in Bayesian Persuasion
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Bayesian persuasion, an extension of cheap-talk communication, involves an informed sender committing to a signaling scheme to influence a receiver's actions. Compared to cheap talk, this sender's commitment enables the receiver to verify the incentive compatibility of signals beforehand, facilitating cooperation. While effective in one-shot scenarios, Bayesian persuasion faces computational complexity (NP-hardness) when extended to long-term interactions, where the receiver may adopt dynamic strategies conditional on past outcomes and future expectations. To address this complexity, we introduce the bargaining perspective, which allows: (1) a unified framework and well-structured solution concept for long-term persuasion, with desirable properties such as fairness and Pareto efficiency; (2) a clear distinction between two previously conflated advantages: the sender's informational advantage and first-proposer advantage. With only modest modifications to the standard setting, this perspective makes explicit the common knowledge of the game structure and grants the receiver comparable commitment capabilities, thereby reinterpreting classic one-sided persuasion as a balanced information bargaining framework. The framework is validated through a two-stage validation-and-inference paradigm: We first demonstrate that GPT-o3 and DeepSeek-R1, out of publicly available LLMs, reliably handle standard tasks; We then apply them to persuasion scenarios to test that the outcomes align with what our information-bargaining framework suggests. All code, results, and terminal logs are publicly available at github.com/YueLin301/InformationBargaining.
Bayesian Persuasion as a Bargaining Game
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Bayesian persuasion, an extension of cheap-talk communication, involves an informed sender committing to a signaling scheme to influence a receiver's actions. Compared to cheap talk, this sender's commitment enables the receiver to verify the incentive compatibility of signals beforehand, facilitating cooperation. While effective in one-shot scenarios, Bayesian persuasion faces computational complexity (NP-hardness) when extended to long-term interactions, where the receiver may adopt dynamic strategies conditional on past outcomes and future expectations. To address this complexity, we introduce the bargaining perspective, which allows: (1) a unified framework and well-structured solution concept for long-term persuasion, with desirable properties such as fairness and Pareto efficiency; (2) a clear distinction between two previously conflated advantages: the sender's informational advantage and first-proposer advantage. With only modest modifications to the standard setting, this perspective makes explicit the common knowledge of the game structure and grants the receiver comparable commitment capabilities, thereby reinterpreting classic one-sided persuasion as a balanced information bargaining framework. The framework is validated through a two-stage validation-and-inference paradigm: We first demonstrate that GPT-o3 and DeepSeek-R1, out of publicly available LLMs, reliably handle standard tasks; We then apply them to persuasion scenarios to test that the outcomes align with what our information-bargaining framework suggests. All code, results, and terminal logs are publicly available at github.com/YueLin301/InformationBargaining.
We Care Each Pixel: Calibrating on Medical Segmentation Model
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Medical image segmentation is fundamental for computer-aided diagnostics, providing accurate delineation of anatomical structures and pathological regions. While common metrics such as Accuracy, DSC, IoU, and HD primarily quantify spatial agreement between predictions and ground-truth labels, they do not assess the calibration quality of segmentation models, which is crucial for clinical reliability. To address this limitation, we propose pixel-wise Expected Calibration Error (pECE), a novel metric that explicitly measures miscalibration at the pixel level, thereby ensuring both spatial precision and confidence reliability. We further introduce a morphological adaptation strategy that applies morphological operations to ground-truth masks before computing calibration losses, particularly benefiting margin-based losses such as Margin SVLS and NACL. Additionally, we present the Signed Distance Calibration Loss (SDC), which aligns boundary geometry with calibration objectives by penalizing discrepancies between predicted and ground-truth signed distance functions (SDFs). Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method not only enhances segmentation performance but also improves calibration quality, yielding more trustworthy confidence estimates. Code is available at: https://github.com/EagleAdelaide/SDC-Loss.
Verbalized Bayesian Persuasion
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Information design (ID) explores how a sender influence the optimal behavior of receivers to achieve specific objectives. While ID originates from everyday human communication, existing game-theoretic and machine learning methods often model information structures as numbers, which limits many applications to toy games. This work leverages LLMs and proposes a verbalized framework in Bayesian persuasion (BP), which extends classic BP to real-world games involving human dialogues for the first time. Specifically, we map the BP to a verbalized mediator-augmented extensive-form game, where LLMs instantiate the sender and receiver. To efficiently solve the verbalized game, we propose a generalized equilibrium-finding algorithm combining LLM and game solver. The algorithm is reinforced with techniques including verbalized commitment assumptions, verbalized obedience constraints, and information obfuscation. Numerical experiments in dialogue scenarios, such as recommendation letters, courtroom interactions, and law enforcement, validate that our framework can both reproduce theoretical results in classic BP and discover effective persuasion strategies in more complex natural language and multi-stage scenarios.
Effective Unsupervised Constrained Text Generation based on Perturbed Masking
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised constrained text generation aims to generate text under a given set of constraints without any supervised data. Current state-of-the-art methods stochastically sample edit positions and actions, which may cause unnecessary search steps. In this paper, we propose PMCTG to improve effectiveness by searching for the best edit position and action in each step. Specifically, PMCTG extends perturbed masking technique to effectively search for the most incongruent token to edit. Then it introduces four multi-aspect scoring functions to select edit action to further reduce search difficulty. Since PMCTG does not require supervised data, it could be applied to different generation tasks. We show that under the unsupervised setting, PMCTG achieves new state-of-the-art results in two representative tasks, namely keywords-to-sentence generation and paraphrasing.
A Comprehensive Survey for Evaluation Methodologies of AI-Generated Music
Aug 26, 2023Abstract:In recent years, AI-generated music has made significant progress, with several models performing well in multimodal and complex musical genres and scenes. While objective metrics can be used to evaluate generative music, they often lack interpretability for musical evaluation. Therefore, researchers often resort to subjective user studies to assess the quality of the generated works, which can be resource-intensive and less reproducible than objective metrics. This study aims to comprehensively evaluate the subjective, objective, and combined methodologies for assessing AI-generated music, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Ultimately, this study provides a valuable reference for unifying generative AI in the field of music evaluation.
General Image-to-Image Translation with One-Shot Image Guidance
Aug 05, 2023Abstract:Large-scale text-to-image models pre-trained on massive text-image pairs show excellent performance in image synthesis recently. However, image can provide more intuitive visual concepts than plain text. People may ask: how can we integrate the desired visual concept into an existing image, such as our portrait? Current methods are inadequate in meeting this demand as they lack the ability to preserve content or translate visual concepts effectively. Inspired by this, we propose a novel framework named visual concept translator (VCT) with the ability to preserve content in the source image and translate the visual concepts guided by a single reference image. The proposed VCT contains a content-concept inversion (CCI) process to extract contents and concepts, and a content-concept fusion (CCF) process to gather the extracted information to obtain the target image. Given only one reference image, the proposed VCT can complete a wide range of general image-to-image translation tasks with excellent results. Extensive experiments are conducted to prove the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed methods. Codes are available at https://github.com/CrystalNeuro/visual-concept-translator.
Information Design in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
May 08, 2023Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) mimics how humans and animals interact with the environment. The setting is somewhat idealized because, in actual tasks, other agents in the environment have their own goals and behave adaptively to the ego agent. To thrive in those environments, the agent needs to influence other agents so their actions become more helpful and less harmful. Research in computational economics distills two ways to influence others directly: by providing tangible goods (mechanism design) and by providing information (information design). This work investigates information design problems for a group of RL agents. The main challenges are two-fold. One is the information provided will immediately affect the transition of the agent trajectories, which introduces additional non-stationarity. The other is the information can be ignored, so the sender must provide information that the receivers are willing to respect. We formulate the Markov signaling game, and develop the notions of signaling gradient and the extended obedience constraints that address these challenges. Our algorithm is efficient on various mixed-motive tasks and provides further insights into computational economics. Our code is available at https://github.com/YueLin301/InformationDesignMARL.
Let the Chart Spark: Embedding Semantic Context into Chart with Text-to-Image Generative Model
Apr 28, 2023



Abstract:Pictorial visualization seamlessly integrates data and semantic context into visual representation, conveying complex information in a manner that is both engaging and informative. Extensive studies have been devoted to developing authoring tools to simplify the creation of pictorial visualizations. However, mainstream works mostly follow a retrieving-and-editing pipeline that heavily relies on retrieved visual elements from a dedicated corpus, which often compromise the data integrity. Text-guided generation methods are emerging, but may have limited applicability due to its predefined recognized entities. In this work, we propose ChartSpark, a novel system that embeds semantic context into chart based on text-to-image generative model. ChartSpark generates pictorial visualizations conditioned on both semantic context conveyed in textual inputs and data information embedded in plain charts. The method is generic for both foreground and background pictorial generation, satisfying the design practices identified from an empirical research into existing pictorial visualizations. We further develop an interactive visual interface that integrates a text analyzer, editing module, and evaluation module to enable users to generate, modify, and assess pictorial visualizations. We experimentally demonstrate the usability of our tool, and conclude with a discussion of the potential of using text-to-image generative model combined with interactive interface for visualization design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge