Deqing Fu
Are LLM Decisions Faithful to Verbal Confidence?
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) can produce surprisingly sophisticated estimates of their own uncertainty. However, it remains unclear to what extent this expressed confidence is tied to the reasoning, knowledge, or decision making of the model. To test this, we introduce $\textbf{RiskEval}$: a framework designed to evaluate whether models adjust their abstention policies in response to varying error penalties. Our evaluation of several frontier models reveals a critical dissociation: models are neither cost-aware when articulating their verbal confidence, nor strategically responsive when deciding whether to engage or abstain under high-penalty conditions. Even when extreme penalties render frequent abstention the mathematically optimal strategy, models almost never abstain, resulting in utility collapse. This indicates that calibrated verbal confidence scores may not be sufficient to create trustworthy and interpretable AI systems, as current models lack the strategic agency to convert uncertainty signals into optimal and risk-sensitive decisions.
Zebra-CoT: A Dataset for Interleaved Vision Language Reasoning
Jul 22, 2025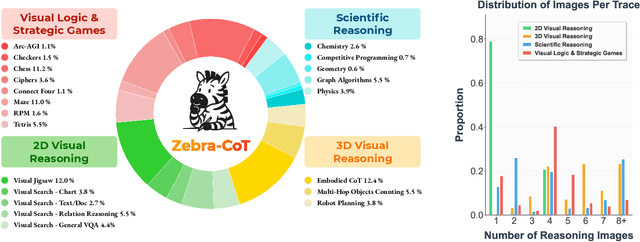
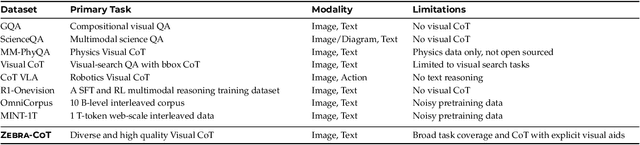
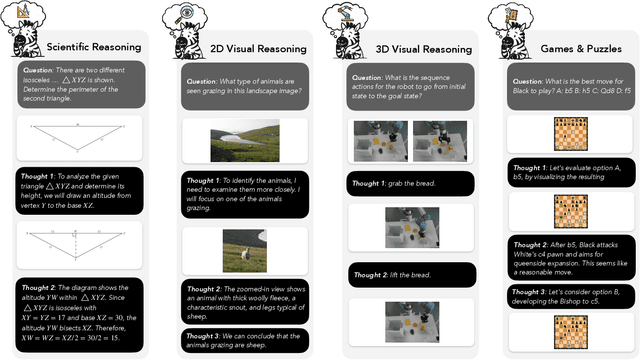

Abstract:Humans often use visual aids, for example diagrams or sketches, when solving complex problems. Training multimodal models to do the same, known as Visual Chain of Thought (Visual CoT), is challenging due to: (1) poor off-the-shelf visual CoT performance, which hinders reinforcement learning, and (2) the lack of high-quality visual CoT training data. We introduce $\textbf{Zebra-CoT}$, a diverse large-scale dataset with 182,384 samples, containing logically coherent interleaved text-image reasoning traces. We focus on four categories of tasks where sketching or visual reasoning is especially natural, spanning scientific questions such as geometry, physics, and algorithms; 2D visual reasoning tasks like visual search and jigsaw puzzles; 3D reasoning tasks including 3D multi-hop inference, embodied and robot planning; visual logic problems and strategic games like chess. Fine-tuning the Anole-7B model on the Zebra-CoT training corpus results in an improvement of +12% in our test-set accuracy and yields up to +13% performance gain on standard VLM benchmark evaluations. Fine-tuning Bagel-7B yields a model that generates high-quality interleaved visual reasoning chains, underscoring Zebra-CoT's effectiveness for developing multimodal reasoning abilities. We open-source our dataset and models to support development and evaluation of visual CoT.
Resa: Transparent Reasoning Models via SAEs
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:How cost-effectively can we elicit strong reasoning in language models by leveraging their underlying representations? We answer this question with Resa, a family of 1.5B reasoning models trained via a novel and efficient sparse autoencoder tuning (SAE-Tuning) procedure. This method first trains an SAE to capture reasoning abilities from a source model, and then uses the trained SAE to guide a standard supervised fine-tuning process to elicit such abilities in a target model, all using verified question-answer data without any reasoning traces. Notably, when applied to certain base models before further RL post-training, SAE-Tuning retains >97% of its RL-trained counterpart's reasoning performance while reducing training costs by >2000x to roughly \$1 and training time by >450x to around 20 minutes. Furthermore, when applied to lightly RL-trained models (e.g., within 1 hour on 2 GPUs), it enables reasoning performance such as 43.33% Pass@1 on AIME24 and 90% Pass@1 on AMC23 for only around \$1 additional cost. Surprisingly, the reasoning abilities extracted via SAEs are potentially both generalizable and modular. Generality means abilities extracted from one dataset still elevate performance on a larger and overlapping corpus. Modularity means abilities extracted from Qwen or Qwen-Math can be attached to the R1-Distill model at test time, without any retraining, and yield comparable gains. Extensive ablations validate these findings and all artifacts are fully open-sourced.
Textual Steering Vectors Can Improve Visual Understanding in Multimodal Large Language Models
May 20, 2025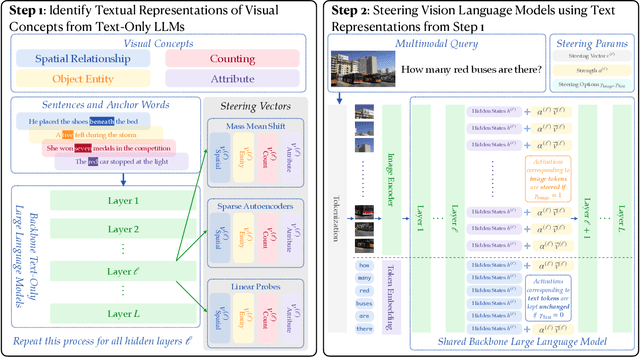
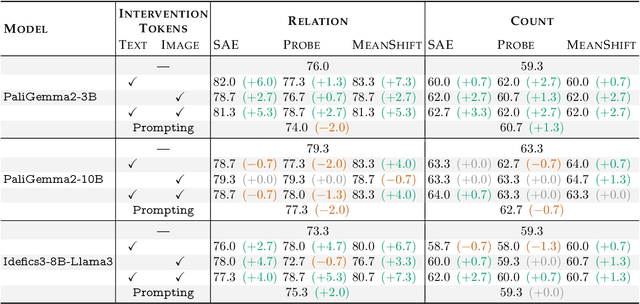
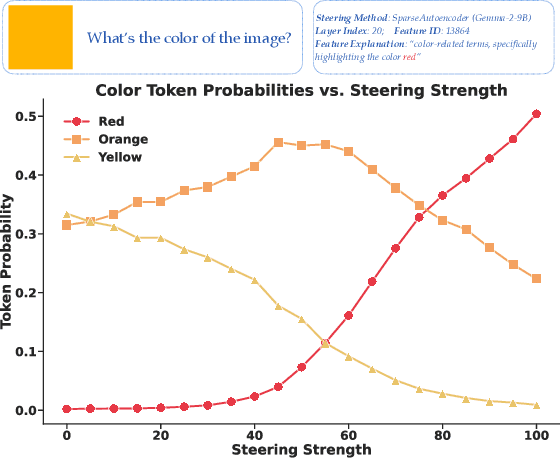
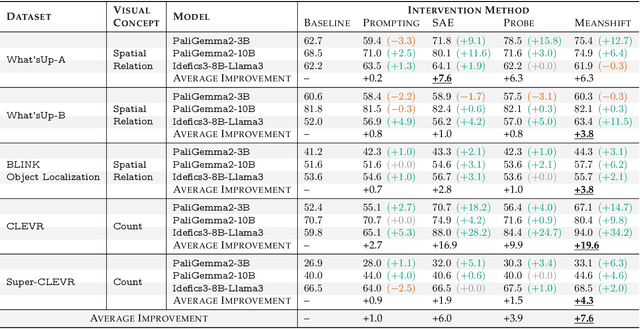
Abstract:Steering methods have emerged as effective and targeted tools for guiding large language models' (LLMs) behavior without modifying their parameters. Multimodal large language models (MLLMs), however, do not currently enjoy the same suite of techniques, due in part to their recency and architectural diversity. Inspired by this gap, we investigate whether MLLMs can be steered using vectors derived from their text-only LLM backbone, via sparse autoencoders (SAEs), mean shift, and linear probing. We find that text-derived steering consistently enhances multimodal accuracy across diverse MLLM architectures and visual tasks. In particular, mean shift boosts spatial relationship accuracy on CV-Bench by up to +7.3% and counting accuracy by up to +3.3%, outperforming prompting and exhibiting strong generalization to out-of-distribution datasets. These results highlight textual steering vectors as a powerful, efficient mechanism for enhancing grounding in MLLMs with minimal additional data collection and computational overhead.
VisualLens: Personalization through Visual History
Nov 25, 2024
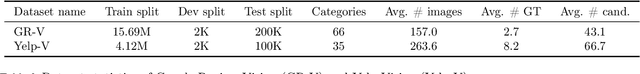
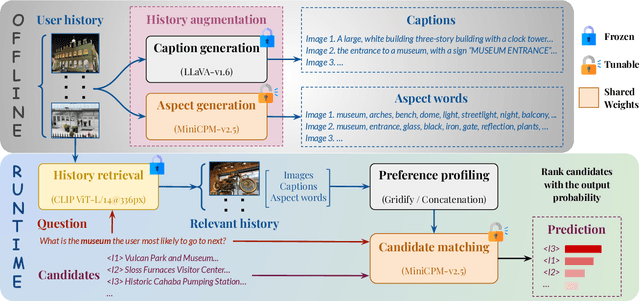
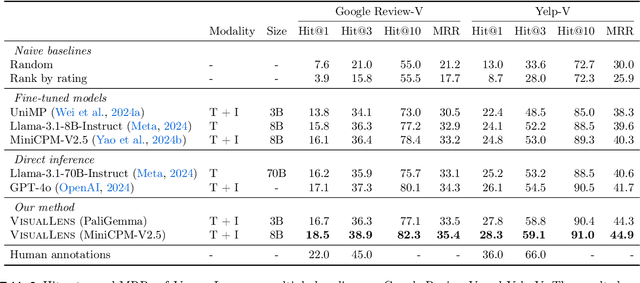
Abstract:We hypothesize that a user's visual history with images reflecting their daily life, offers valuable insights into their interests and preferences, and can be leveraged for personalization. Among the many challenges to achieve this goal, the foremost is the diversity and noises in the visual history, containing images not necessarily related to a recommendation task, not necessarily reflecting the user's interest, or even not necessarily preference-relevant. Existing recommendation systems either rely on task-specific user interaction logs, such as online shopping history for shopping recommendations, or focus on text signals. We propose a novel approach, VisualLens, that extracts, filters, and refines image representations, and leverages these signals for personalization. We created two new benchmarks with task-agnostic visual histories, and show that our method improves over state-of-the-art recommendations by 5-10% on Hit@3, and improves over GPT-4o by 2-5%. Our approach paves the way for personalized recommendations in scenarios where traditional methods fail.
TLDR: Token-Level Detective Reward Model for Large Vision Language Models
Oct 07, 2024


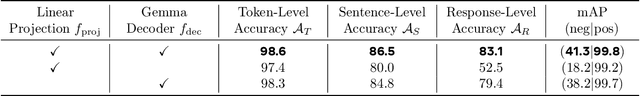
Abstract:Although reward models have been successful in improving multimodal large language models, the reward models themselves remain brutal and contain minimal information. Notably, existing reward models only mimic human annotations by assigning only one binary feedback to any text, no matter how long the text is. In the realm of multimodal language models, where models are required to process both images and texts, a naive reward model may learn implicit biases toward texts and become less grounded in images. In this paper, we propose a $\textbf{T}$oken-$\textbf{L}$evel $\textbf{D}$etective $\textbf{R}$eward Model ($\textbf{TLDR}$) to provide fine-grained annotations to each text token. We first introduce a perturbation-based method to generate synthetic hard negatives and their token-level labels to train TLDR models. Then we show the rich usefulness of TLDR models both in assisting off-the-shelf models to self-correct their generations, and in serving as a hallucination evaluation tool. Finally, we show that TLDR models can significantly speed up human annotation by 3 times to acquire a broader range of high-quality vision language data.
Pre-trained Large Language Models Use Fourier Features to Compute Addition
Jun 05, 2024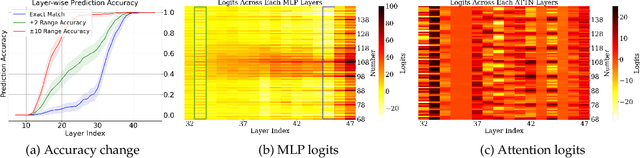
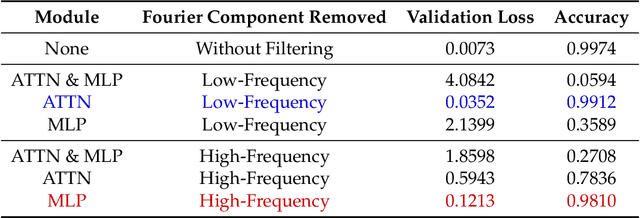
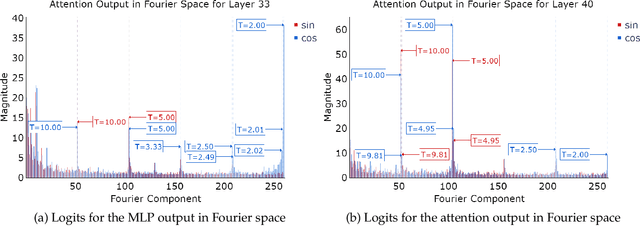
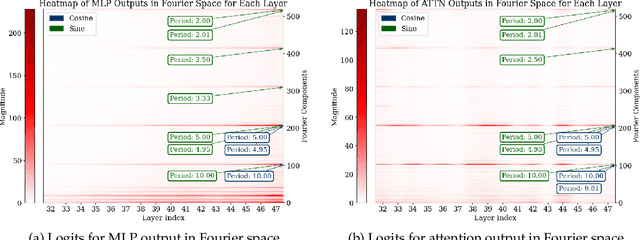
Abstract:Pre-trained large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive mathematical reasoning capabilities, yet how they compute basic arithmetic, such as addition, remains unclear. This paper shows that pre-trained LLMs add numbers using Fourier features -- dimensions in the hidden state that represent numbers via a set of features sparse in the frequency domain. Within the model, MLP and attention layers use Fourier features in complementary ways: MLP layers primarily approximate the magnitude of the answer using low-frequency features, while attention layers primarily perform modular addition (e.g., computing whether the answer is even or odd) using high-frequency features. Pre-training is crucial for this mechanism: models trained from scratch to add numbers only exploit low-frequency features, leading to lower accuracy. Introducing pre-trained token embeddings to a randomly initialized model rescues its performance. Overall, our analysis demonstrates that appropriate pre-trained representations (e.g., Fourier features) can unlock the ability of Transformers to learn precise mechanisms for algorithmic tasks.
IsoBench: Benchmarking Multimodal Foundation Models on Isomorphic Representations
Apr 02, 2024
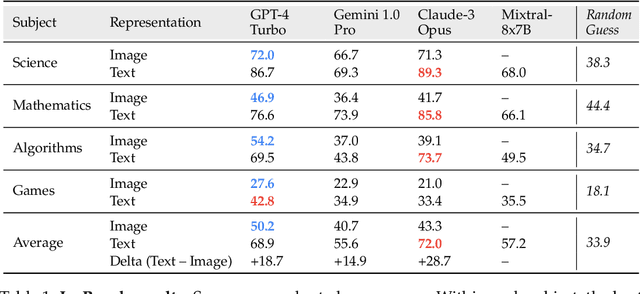
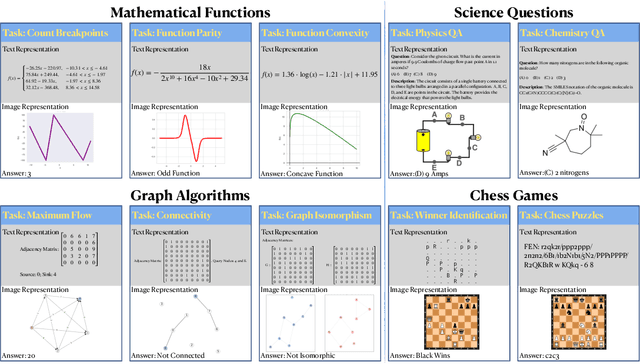
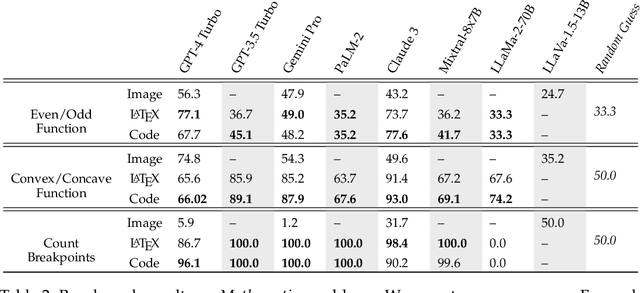
Abstract:Current foundation models exhibit impressive capabilities when prompted either with text only or with both image and text inputs. But do their capabilities change depending on the input modality? In this work, we propose $\textbf{IsoBench}$, a benchmark dataset containing problems from four major areas: math, science, algorithms, and games. Each example is presented with multiple $\textbf{isomorphic representations}$ of inputs, such as visual, textual, and mathematical presentations. IsoBench provides fine-grained feedback to diagnose performance gaps caused by the form of the representation. Across various foundation models, we observe that on the same problem, models have a consistent preference towards textual representations. Most prominently, when evaluated on all IsoBench problems, Claude-3 Opus performs 28.7 points worse when provided with images instead of text; similarly, GPT-4 Turbo is 18.7 points worse and Gemini Pro is 14.9 points worse. Finally, we present two prompting techniques, $\textit{IsoCombination}$ and $\textit{IsoScratchPad}$, which improve model performance by considering combinations of, and translations between, different input representations.
Simplicity Bias of Transformers to Learn Low Sensitivity Functions
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Transformers achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and robustness across many tasks, but an understanding of the inductive biases that they have and how those biases are different from other neural network architectures remains elusive. Various neural network architectures such as fully connected networks have been found to have a simplicity bias towards simple functions of the data; one version of this simplicity bias is a spectral bias to learn simple functions in the Fourier space. In this work, we identify the notion of sensitivity of the model to random changes in the input as a notion of simplicity bias which provides a unified metric to explain the simplicity and spectral bias of transformers across different data modalities. We show that transformers have lower sensitivity than alternative architectures, such as LSTMs, MLPs and CNNs, across both vision and language tasks. We also show that low-sensitivity bias correlates with improved robustness; furthermore, it can also be used as an efficient intervention to further improve the robustness of transformers.
DeLLMa: A Framework for Decision Making Under Uncertainty with Large Language Models
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used across society, including in domains like business, engineering, and medicine. These fields often grapple with decision-making under uncertainty, a critical yet challenging task. In this paper, we show that directly prompting LLMs on these types of decision-making problems yields poor results, especially as the problem complexity increases. To overcome this limitation, we propose DeLLMa (Decision-making Large Language Model assistant), a framework designed to enhance decision-making accuracy in uncertain environments. DeLLMa involves a multi-step scaffolding procedure, drawing upon principles from decision theory and utility theory, to provide an optimal and human-auditable decision-making process. We validate our framework on decision-making environments involving real agriculture and finance data. Our results show that DeLLMa can significantly improve LLM decision-making performance, achieving up to a 40% increase in accuracy over competing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge