Zhaojiang Lin
Pixel-Grounded Retrieval for Knowledgeable Large Multimodal Models
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) often requires coupling fine-grained perception with factual knowledge beyond the input image. Prior multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MM-RAG) systems improve factual grounding but lack an internal policy for when and how to retrieve. We propose PixSearch, the first end-to-end Segmenting Large Multimodal Model (LMM) that unifies region-level perception and retrieval-augmented reasoning. During encoding, PixSearch emits <search> tokens to trigger retrieval, selects query modalities (text, image, or region), and generates pixel-level masks that directly serve as visual queries, eliminating the reliance on modular pipelines (detectors, segmenters, captioners, etc.). A two-stage supervised fine-tuning regimen with search-interleaved supervision teaches retrieval timing and query selection while preserving segmentation ability. On egocentric and entity-centric VQA benchmarks, PixSearch substantially improves factual consistency and generalization, yielding a 19.7% relative gain in accuracy on CRAG-MM compared to whole image retrieval, while retaining competitive reasoning performance on various VQA and text-only QA tasks.
WearVox: An Egocentric Multichannel Voice Assistant Benchmark for Wearables
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Wearable devices such as AI glasses are transforming voice assistants into always-available, hands-free collaborators that integrate seamlessly with daily life, but they also introduce challenges like egocentric audio affected by motion and noise, rapid micro-interactions, and the need to distinguish device-directed speech from background conversations. Existing benchmarks largely overlook these complexities, focusing instead on clean or generic conversational audio. To bridge this gap, we present WearVox, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate voice assistants in realistic wearable scenarios. WearVox comprises 3,842 multi-channel, egocentric audio recordings collected via AI glasses across five diverse tasks including Search-Grounded QA, Closed-Book QA, Side-Talk Rejection, Tool Calling, and Speech Translation, spanning a wide range of indoor and outdoor environments and acoustic conditions. Each recording is accompanied by rich metadata, enabling nuanced analysis of model performance under real-world constraints. We benchmark leading proprietary and open-source speech Large Language Models (SLLMs) and find that most real-time SLLMs achieve accuracies on WearVox ranging from 29% to 59%, with substantial performance degradation on noisy outdoor audio, underscoring the difficulty and realism of the benchmark. Additionally, we conduct a case study with two new SLLMs that perform inference with single-channel and multi-channel audio, demonstrating that multi-channel audio inputs significantly enhance model robustness to environmental noise and improve discrimination between device-directed and background speech. Our results highlight the critical importance of spatial audio cues for context-aware voice assistants and establish WearVox as a comprehensive testbed for advancing wearable voice AI research.
Stream RAG: Instant and Accurate Spoken Dialogue Systems with Streaming Tool Usage
Oct 02, 2025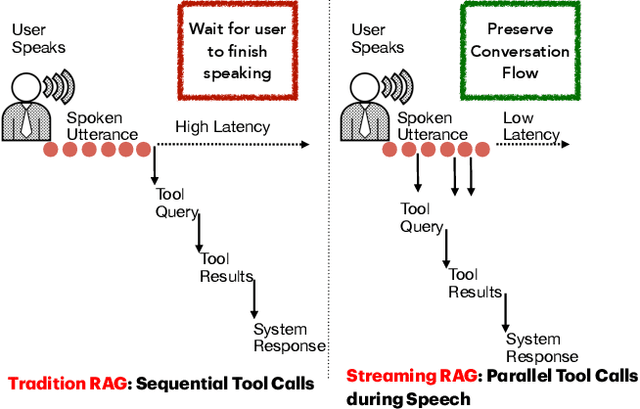
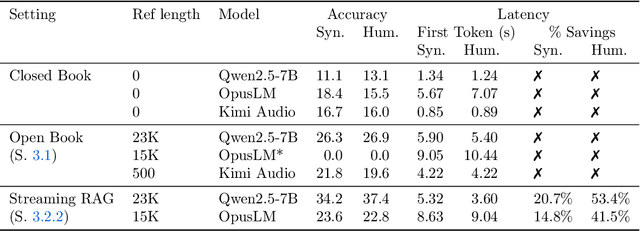
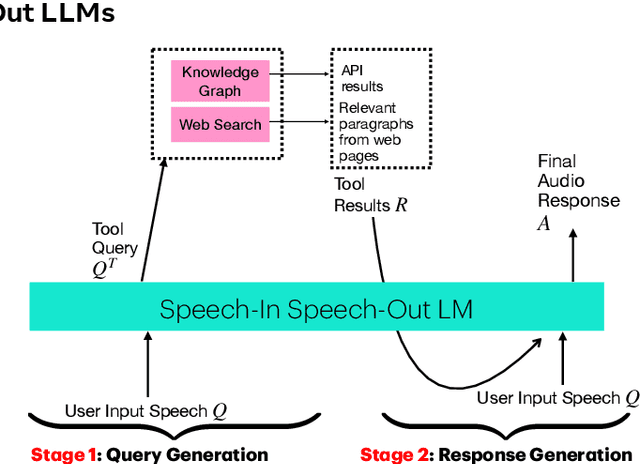
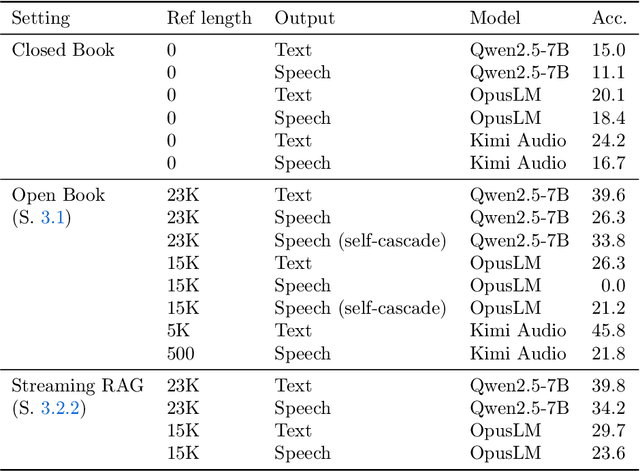
Abstract:End-to-end speech-in speech-out dialogue systems are emerging as a powerful alternative to traditional ASR-LLM-TTS pipelines, generating more natural, expressive responses with significantly lower latency. However, these systems remain prone to hallucinations due to limited factual grounding. While text-based dialogue systems address this challenge by integrating tools such as web search and knowledge graph APIs, we introduce the first approach to extend tool use directly into speech-in speech-out systems. A key challenge is that tool integration substantially increases response latency, disrupting conversational flow. To mitigate this, we propose Streaming Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Streaming RAG), a novel framework that reduces user-perceived latency by predicting tool queries in parallel with user speech, even before the user finishes speaking. Specifically, we develop a post-training pipeline that teaches the model when to issue tool calls during ongoing speech and how to generate spoken summaries that fuse audio queries with retrieved text results, thereby improving both accuracy and responsiveness. To evaluate our approach, we construct AudioCRAG, a benchmark created by converting queries from the publicly available CRAG dataset into speech form. Experimental results demonstrate that our streaming RAG approach increases QA accuracy by up to 200% relative (from 11.1% to 34.2% absolute) and further enhances user experience by reducing tool use latency by 20%. Importantly, our streaming RAG approach is modality-agnostic and can be applied equally to typed input, paving the way for more agentic, real-time AI assistants.
SCRIBES: Web-Scale Script-Based Semi-Structured Data Extraction with Reinforcement Learning
Oct 02, 2025
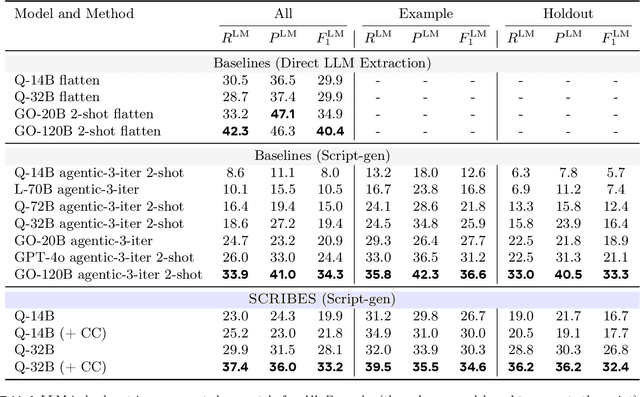

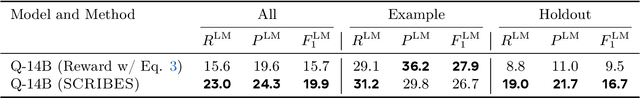
Abstract:Semi-structured content in HTML tables, lists, and infoboxes accounts for a substantial share of factual data on the web, yet the formatting complicates usage, and reliably extracting structured information from them remains challenging. Existing methods either lack generalization or are resource-intensive due to per-page LLM inference. In this paper, we introduce SCRIBES (SCRIpt-Based Semi-Structured Content Extraction at Web-Scale), a novel reinforcement learning framework that leverages layout similarity across webpages within the same site as a reward signal. Instead of processing each page individually, SCRIBES generates reusable extraction scripts that can be applied to groups of structurally similar webpages. Our approach further improves by iteratively training on synthetic annotations from in-the-wild CommonCrawl data. Experiments show that our approach outperforms strong baselines by over 13% in script quality and boosts downstream question answering accuracy by more than 4% for GPT-4o, enabling scalable and resource-efficient web information extraction.
Thinking in Directivity: Speech Large Language Model for Multi-Talker Directional Speech Recognition
Jun 17, 2025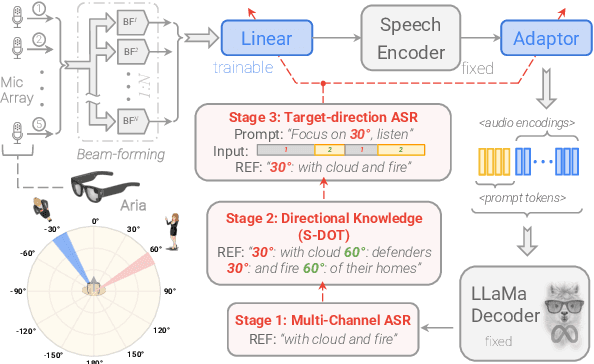
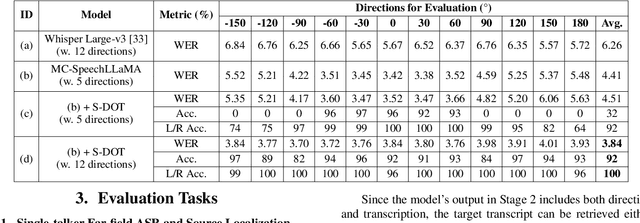
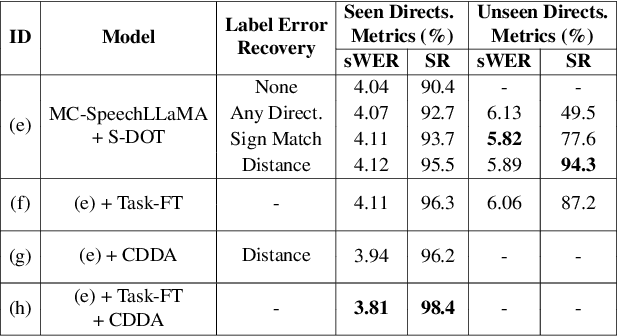
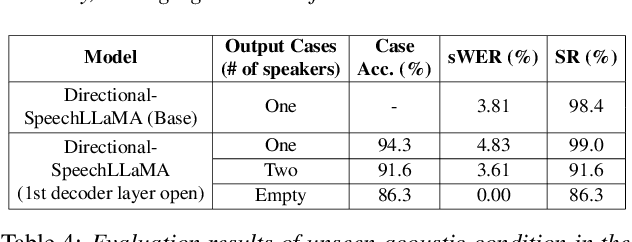
Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated that prompting large language models (LLM) with audio encodings enables effective speech recognition capabilities. However, the ability of Speech LLMs to comprehend and process multi-channel audio with spatial cues remains a relatively uninvestigated area of research. In this work, we present directional-SpeechLlama, a novel approach that leverages the microphone array of smart glasses to achieve directional speech recognition, source localization, and bystander cross-talk suppression. To enhance the model's ability to understand directivity, we propose two key techniques: serialized directional output training (S-DOT) and contrastive direction data augmentation (CDDA). Experimental results show that our proposed directional-SpeechLlama effectively captures the relationship between textual cues and spatial audio, yielding strong performance in both speech recognition and source localization tasks.
Pisces: An Auto-regressive Foundation Model for Image Understanding and Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled multimodal foundation models to tackle both image understanding and generation within a unified framework. Despite these gains, unified models often underperform compared to specialized models in either task. A key challenge in developing unified models lies in the inherent differences between the visual features needed for image understanding versus generation, as well as the distinct training processes required for each modality. In this work, we introduce Pisces, an auto-regressive multimodal foundation model that addresses this challenge through a novel decoupled visual encoding architecture and tailored training techniques optimized for multimodal generation. Combined with meticulous data curation, pretraining, and finetuning, Pisces achieves competitive performance in both image understanding and image generation. We evaluate Pisces on over 20 public benchmarks for image understanding, where it demonstrates strong performance across a wide range of tasks. Additionally, on GenEval, a widely adopted benchmark for image generation, Pisces exhibits robust generative capabilities. Our extensive analysis reveals the synergistic relationship between image understanding and generation, and the benefits of using separate visual encoders, advancing the field of unified multimodal models.
ConfQA: Answer Only If You Are Confident
Jun 08, 2025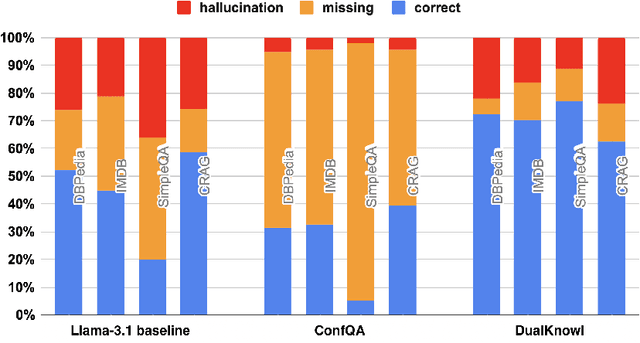
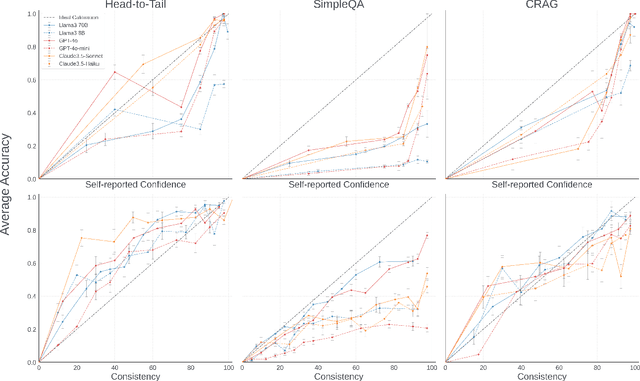
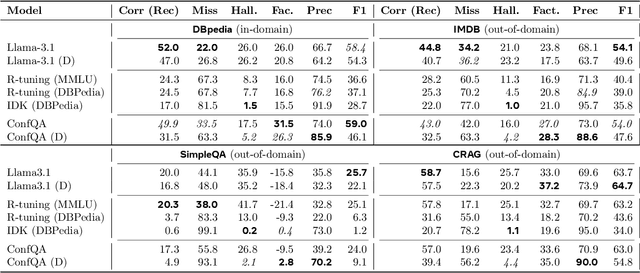
Abstract:Can we teach Large Language Models (LLMs) to refrain from hallucinating factual statements? In this paper we present a fine-tuning strategy that we call ConfQA, which can reduce hallucination rate from 20-40% to under 5% across multiple factuality benchmarks. The core idea is simple: when the LLM answers a question correctly, it is trained to continue with the answer; otherwise, it is trained to admit "I am unsure". But there are two key factors that make the training highly effective. First, we introduce a dampening prompt "answer only if you are confident" to explicitly guide the behavior, without which hallucination remains high as 15%-25%. Second, we leverage simple factual statements, specifically attribute values from knowledge graphs, to help LLMs calibrate the confidence, resulting in robust generalization across domains and question types. Building on this insight, we propose the Dual Neural Knowledge framework, which seamlessly select between internally parameterized neural knowledge and externally recorded symbolic knowledge based on ConfQA's confidence. The framework enables potential accuracy gains to beyond 95%, while reducing unnecessary external retrievals by over 30%.
Proactive Assistant Dialogue Generation from Streaming Egocentric Videos
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in conversational AI have been substantial, but developing real-time systems for perceptual task guidance remains challenging. These systems must provide interactive, proactive assistance based on streaming visual inputs, yet their development is constrained by the costly and labor-intensive process of data collection and system evaluation. To address these limitations, we present a comprehensive framework with three key contributions. First, we introduce a novel data curation pipeline that synthesizes dialogues from annotated egocentric videos, resulting in \dataset, a large-scale synthetic dialogue dataset spanning multiple domains. Second, we develop a suite of automatic evaluation metrics, validated through extensive human studies. Third, we propose an end-to-end model that processes streaming video inputs to generate contextually appropriate responses, incorporating novel techniques for handling data imbalance and long-duration videos. This work lays the foundation for developing real-time, proactive AI assistants capable of guiding users through diverse tasks. Project page: https://pro-assist.github.io/
VisualLens: Personalization through Visual History
Nov 25, 2024
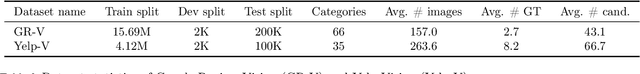
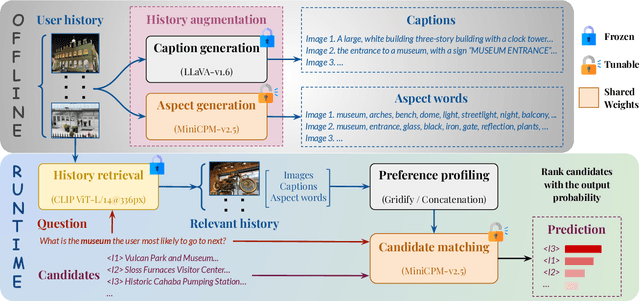
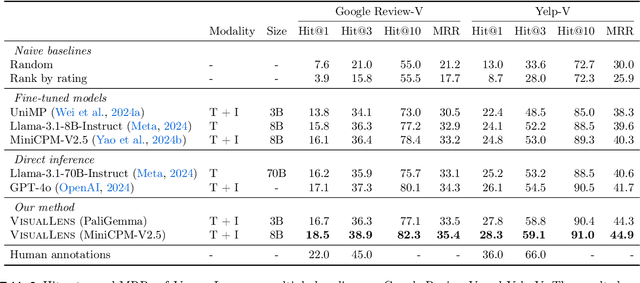
Abstract:We hypothesize that a user's visual history with images reflecting their daily life, offers valuable insights into their interests and preferences, and can be leveraged for personalization. Among the many challenges to achieve this goal, the foremost is the diversity and noises in the visual history, containing images not necessarily related to a recommendation task, not necessarily reflecting the user's interest, or even not necessarily preference-relevant. Existing recommendation systems either rely on task-specific user interaction logs, such as online shopping history for shopping recommendations, or focus on text signals. We propose a novel approach, VisualLens, that extracts, filters, and refines image representations, and leverages these signals for personalization. We created two new benchmarks with task-agnostic visual histories, and show that our method improves over state-of-the-art recommendations by 5-10% on Hit@3, and improves over GPT-4o by 2-5%. Our approach paves the way for personalized recommendations in scenarios where traditional methods fail.
SnapNTell: Enhancing Entity-Centric Visual Question Answering with Retrieval Augmented Multimodal LLM
Mar 07, 2024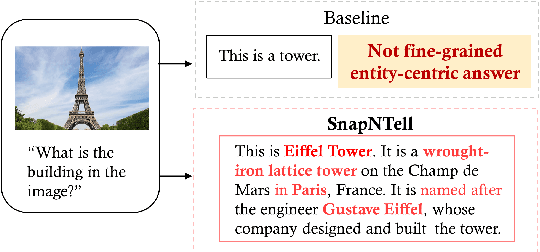
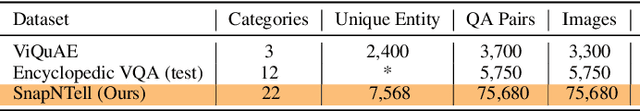
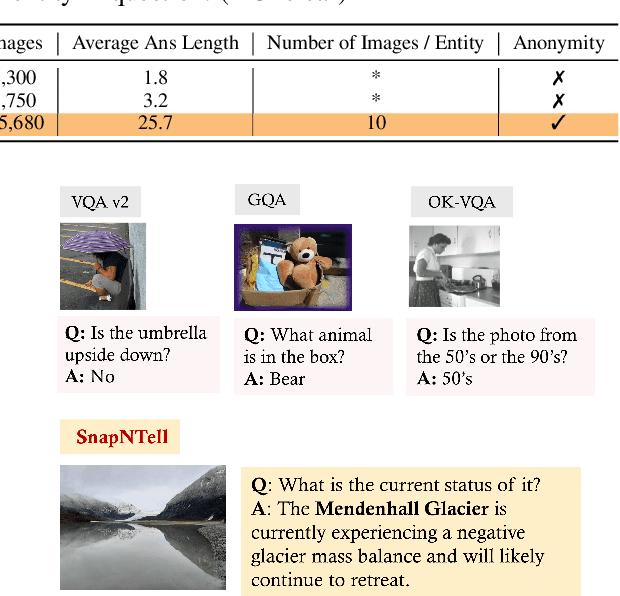
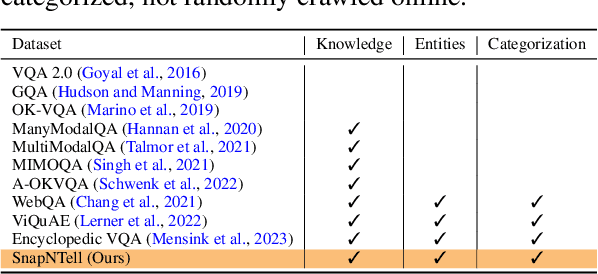
Abstract:Vision-extended LLMs have made significant strides in Visual Question Answering (VQA). Despite these advancements, VLLMs still encounter substantial difficulties in handling queries involving long-tail entities, with a tendency to produce erroneous or hallucinated responses. In this work, we introduce a novel evaluative benchmark named \textbf{SnapNTell}, specifically tailored for entity-centric VQA. This task aims to test the models' capabilities in identifying entities and providing detailed, entity-specific knowledge. We have developed the \textbf{SnapNTell Dataset}, distinct from traditional VQA datasets: (1) It encompasses a wide range of categorized entities, each represented by images and explicitly named in the answers; (2) It features QA pairs that require extensive knowledge for accurate responses. The dataset is organized into 22 major categories, containing 7,568 unique entities in total. For each entity, we curated 10 illustrative images and crafted 10 knowledge-intensive QA pairs. To address this novel task, we devised a scalable, efficient, and transparent retrieval-augmented multimodal LLM. Our approach markedly outperforms existing methods on the SnapNTell dataset, achieving a 66.5\% improvement in the BELURT score. We will soon make the dataset and the source code publicly accessible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge