Adithya Sagar
MobileLLM-Pro Technical Report
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Efficient on-device language models around 1 billion parameters are essential for powering low-latency AI applications on mobile and wearable devices. However, achieving strong performance in this model class, while supporting long context windows and practical deployment remains a significant challenge. We introduce MobileLLM-Pro, a 1-billion-parameter language model optimized for on-device deployment. MobileLLM-Pro achieves state-of-the-art results across 11 standard benchmarks, significantly outperforming both Gemma 3-1B and Llama 3.2-1B, while supporting context windows of up to 128,000 tokens and showing only minor performance regressions at 4-bit quantization. These improvements are enabled by four core innovations: (1) implicit positional distillation, a novel technique that effectively instills long-context capabilities through knowledge distillation; (2) a specialist model merging framework that fuses multiple domain experts into a compact model without parameter growth; (3) simulation-driven data mixing using utility estimation; and (4) 4-bit quantization-aware training with self-distillation. We release our model weights and code to support future research in efficient on-device language models.
Stream RAG: Instant and Accurate Spoken Dialogue Systems with Streaming Tool Usage
Oct 02, 2025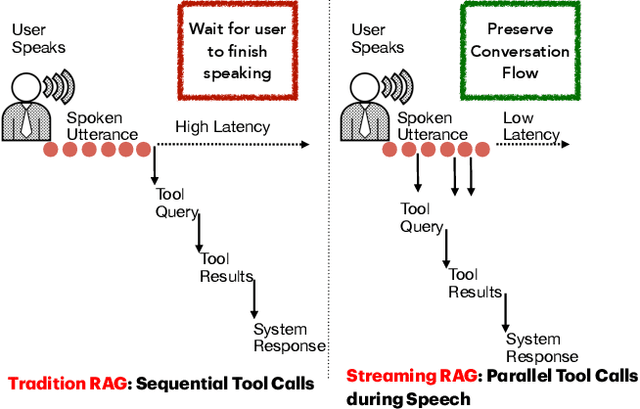
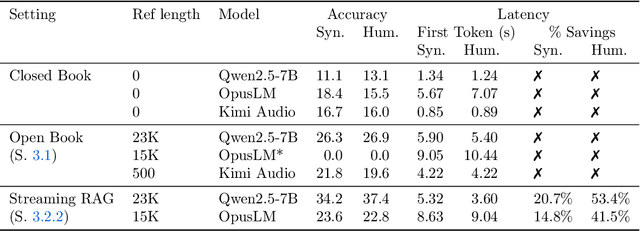
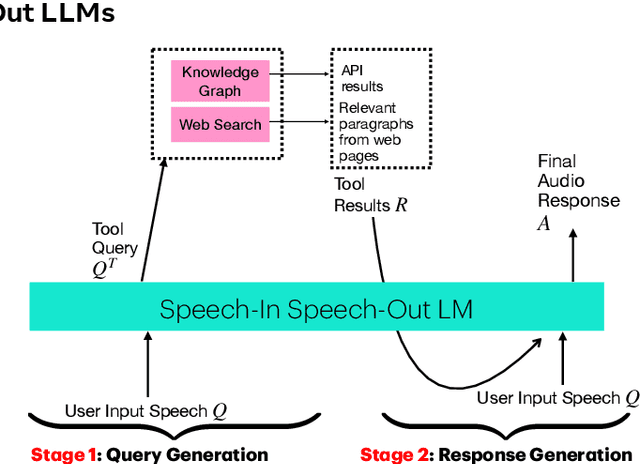
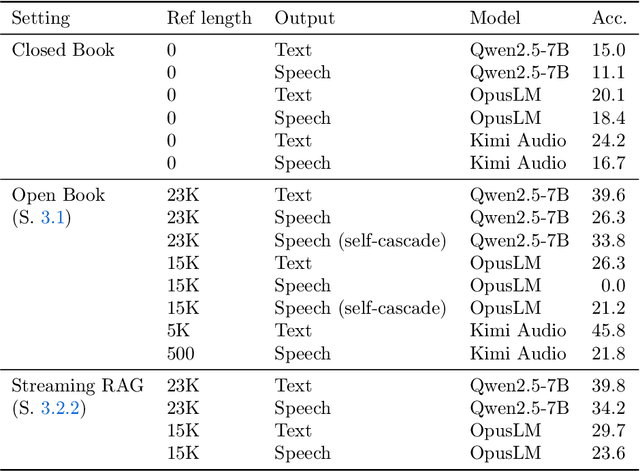
Abstract:End-to-end speech-in speech-out dialogue systems are emerging as a powerful alternative to traditional ASR-LLM-TTS pipelines, generating more natural, expressive responses with significantly lower latency. However, these systems remain prone to hallucinations due to limited factual grounding. While text-based dialogue systems address this challenge by integrating tools such as web search and knowledge graph APIs, we introduce the first approach to extend tool use directly into speech-in speech-out systems. A key challenge is that tool integration substantially increases response latency, disrupting conversational flow. To mitigate this, we propose Streaming Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Streaming RAG), a novel framework that reduces user-perceived latency by predicting tool queries in parallel with user speech, even before the user finishes speaking. Specifically, we develop a post-training pipeline that teaches the model when to issue tool calls during ongoing speech and how to generate spoken summaries that fuse audio queries with retrieved text results, thereby improving both accuracy and responsiveness. To evaluate our approach, we construct AudioCRAG, a benchmark created by converting queries from the publicly available CRAG dataset into speech form. Experimental results demonstrate that our streaming RAG approach increases QA accuracy by up to 200% relative (from 11.1% to 34.2% absolute) and further enhances user experience by reducing tool use latency by 20%. Importantly, our streaming RAG approach is modality-agnostic and can be applied equally to typed input, paving the way for more agentic, real-time AI assistants.
CoDi: Conversational Distillation for Grounded Question Answering
Aug 20, 2024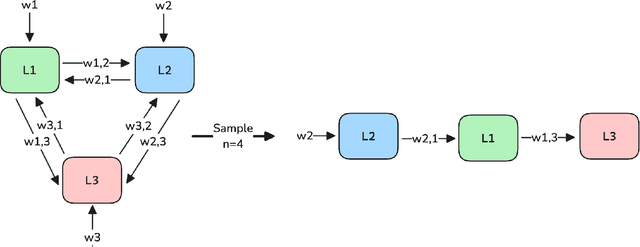
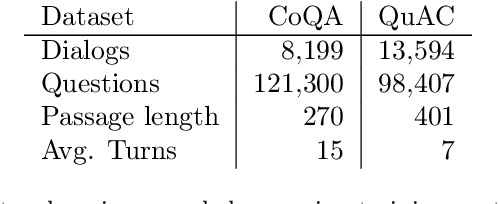
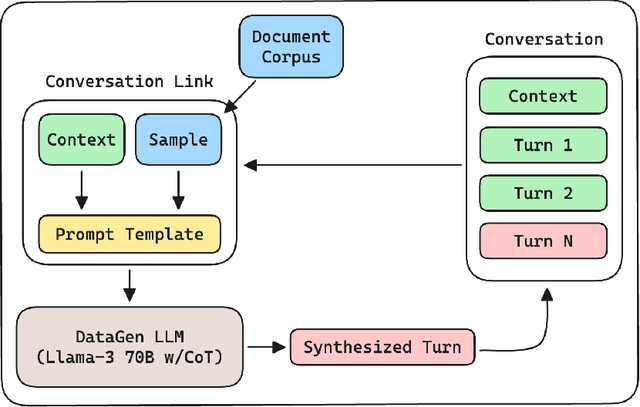
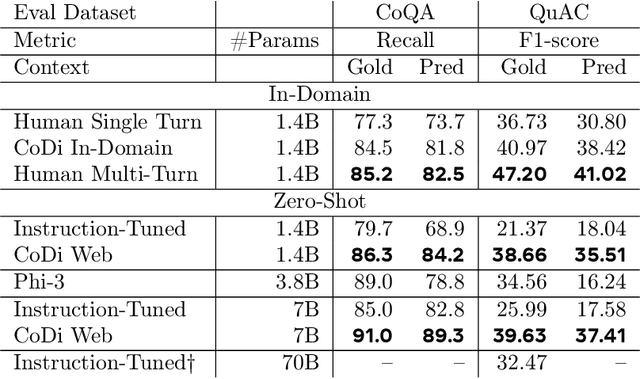
Abstract:Distilling conversational skills into Small Language Models (SLMs) with approximately 1 billion parameters presents significant challenges. Firstly, SLMs have limited capacity in their model parameters to learn extensive knowledge compared to larger models. Secondly, high-quality conversational datasets are often scarce, small, and domain-specific. Addressing these challenges, we introduce a novel data distillation framework named CoDi (short for Conversational Distillation, pronounced "Cody"), allowing us to synthesize large-scale, assistant-style datasets in a steerable and diverse manner. Specifically, while our framework is task agnostic at its core, we explore and evaluate the potential of CoDi on the task of conversational grounded reasoning for question answering. This is a typical on-device scenario for specialist SLMs, allowing for open-domain model responses, without requiring the model to "memorize" world knowledge in its limited weights. Our evaluations show that SLMs trained with CoDi-synthesized data achieve performance comparable to models trained on human-annotated data in standard metrics. Additionally, when using our framework to generate larger datasets from web data, our models surpass larger, instruction-tuned models in zero-shot conversational grounded reasoning tasks.
PRoDeliberation: Parallel Robust Deliberation for End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding
Jun 12, 2024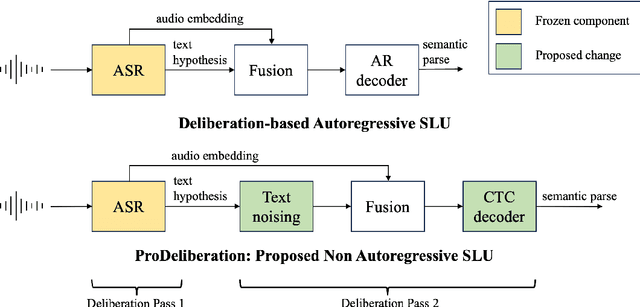
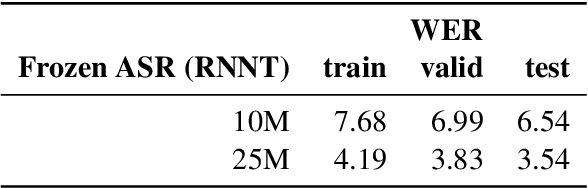
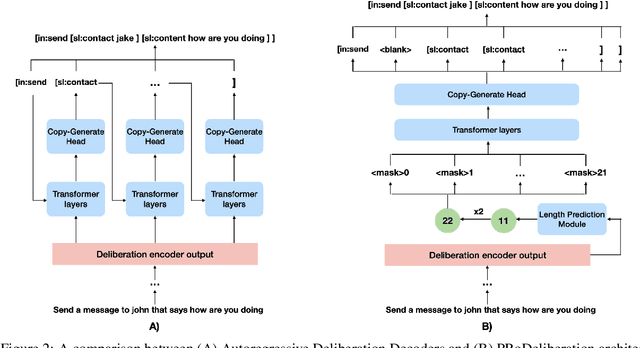
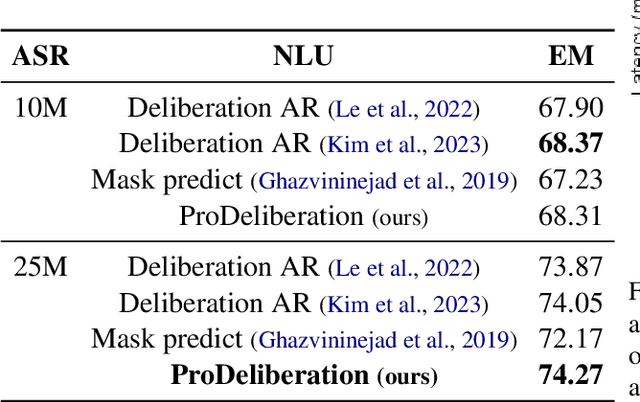
Abstract:Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) is a critical component of voice assistants; it consists of converting speech to semantic parses for task execution. Previous works have explored end-to-end models to improve the quality and robustness of SLU models with Deliberation, however these models have remained autoregressive, resulting in higher latencies. In this work we introduce PRoDeliberation, a novel method leveraging a Connectionist Temporal Classification-based decoding strategy as well as a denoising objective to train robust non-autoregressive deliberation models. We show that PRoDeliberation achieves the latency reduction of parallel decoding (2-10x improvement over autoregressive models) while retaining the ability to correct Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) mistranscriptions of autoregressive deliberation systems. We further show that the design of the denoising training allows PRoDeliberation to overcome the limitations of small ASR devices, and we provide analysis on the necessity of each component of the system.
PrE-Text: Training Language Models on Private Federated Data in the Age of LLMs
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:On-device training is currently the most common approach for training machine learning (ML) models on private, distributed user data. Despite this, on-device training has several drawbacks: (1) most user devices are too small to train large models on-device, (2) on-device training is communication- and computation-intensive, and (3) on-device training can be difficult to debug and deploy. To address these problems, we propose Private Evolution-Text (PrE-Text), a method for generating differentially private (DP) synthetic textual data. First, we show that across multiple datasets, training small models (models that fit on user devices) with PrE-Text synthetic data outperforms small models trained on-device under practical privacy regimes ($\epsilon=1.29$, $\epsilon=7.58$). We achieve these results while using 9$\times$ fewer rounds, 6$\times$ less client computation per round, and 100$\times$ less communication per round. Second, finetuning large models on PrE-Text's DP synthetic data improves large language model (LLM) performance on private data across the same range of privacy budgets. Altogether, these results suggest that training on DP synthetic data can be a better option than training a model on-device on private distributed data. Code is available at https://github.com/houcharlie/PrE-Text.
Large Language Models as Zero-shot Dialogue State Tracker through Function Calling
Feb 16, 2024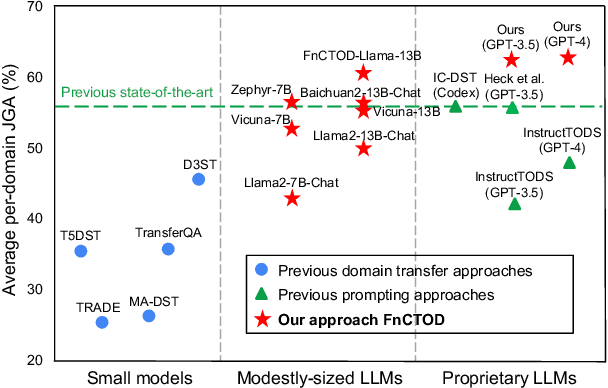

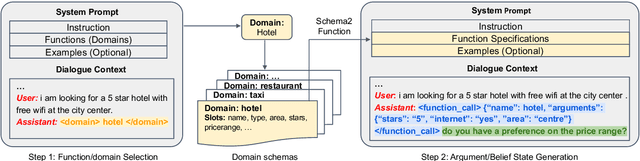
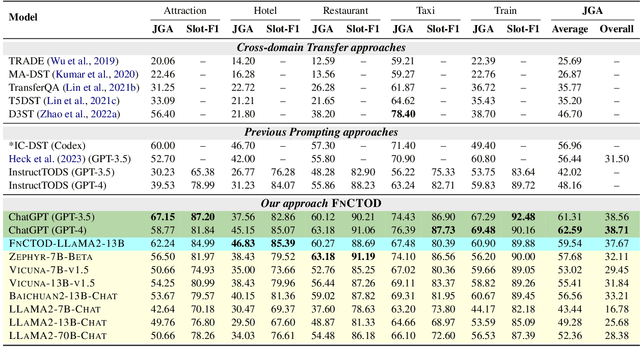
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly prevalent in conversational systems due to their advanced understanding and generative capabilities in general contexts. However, their effectiveness in task-oriented dialogues (TOD), which requires not only response generation but also effective dialogue state tracking (DST) within specific tasks and domains, remains less satisfying. In this work, we propose a novel approach FnCTOD for solving DST with LLMs through function calling. This method improves zero-shot DST, allowing adaptation to diverse domains without extensive data collection or model tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves exceptional performance with both modestly sized open-source and also proprietary LLMs: with in-context prompting it enables various 7B or 13B parameter models to surpass the previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) achieved by ChatGPT, and improves ChatGPT's performance beating the SOTA by 5.6% Avg. JGA. Individual model results for GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 are boosted by 4.8% and 14%, respectively. We also show that by fine-tuning on a small collection of diverse task-oriented dialogues, we can equip modestly sized models, specifically a 13B parameter LLaMA2-Chat model, with function-calling capabilities and DST performance comparable to ChatGPT while maintaining their chat capabilities. We plan to open-source experimental code and model.
Data-Efficiency with a Single GPU: An Exploration of Transfer Methods for Small Language Models
Oct 08, 2022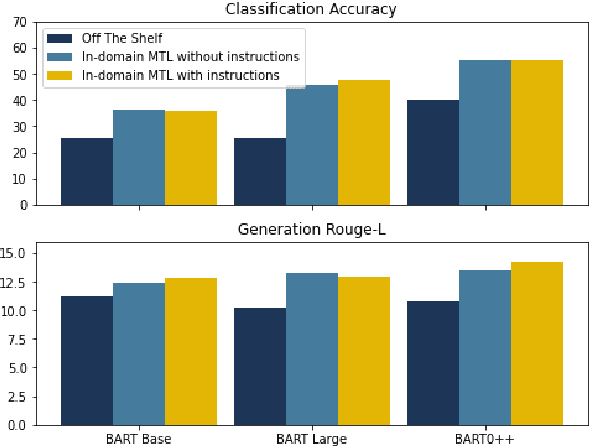
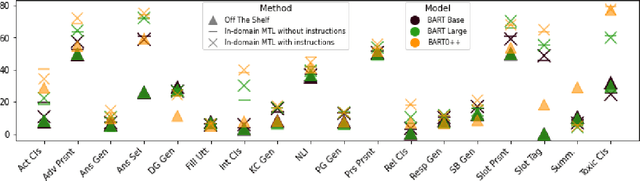
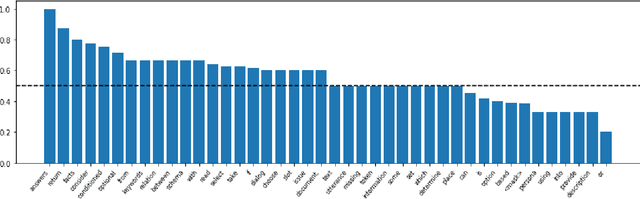
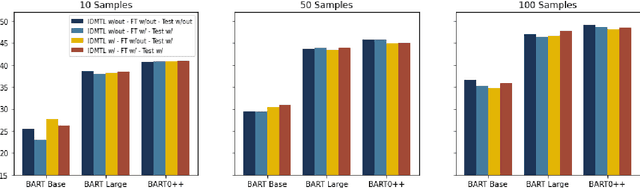
Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL), instruction tuning, and prompting have recently been shown to improve the generalizability of large language models to new tasks. However, the benefits of such methods are less well-documented in smaller language models, with some studies finding contradictory results. In this work, we explore and isolate the effects of (i) model size, (ii) general purpose MTL, (iii) in-domain MTL, (iv) instruction tuning, and (v) few-shot fine-tuning for models with fewer than 500 million parameters. Our experiments in the zero-shot setting demonstrate that models gain 31% relative improvement, on average, from general purpose MTL, with an additional 37.6% relative gain from in-domain MTL. Contradictory to prior works on large models, we find that instruction tuning provides a modest 2% performance improvement for small models.
RETRONLU: Retrieval Augmented Task-Oriented Semantic Parsing
Sep 21, 2021
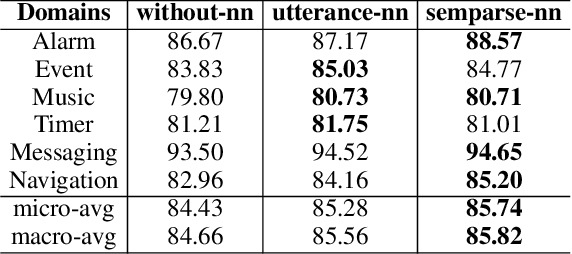
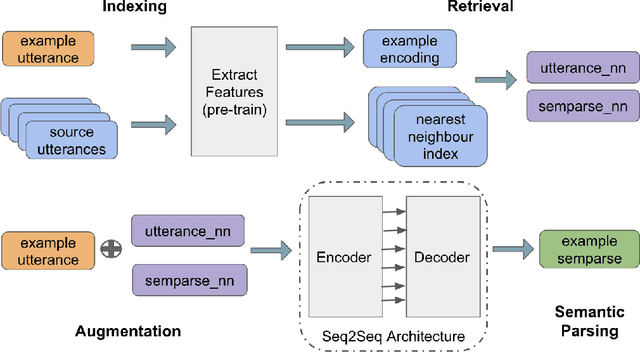
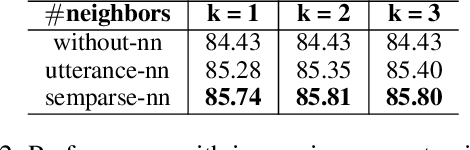
Abstract:While large pre-trained language models accumulate a lot of knowledge in their parameters, it has been demonstrated that augmenting it with non-parametric retrieval-based memory has a number of benefits from accuracy improvements to data efficiency for knowledge-focused tasks, such as question answering. In this paper, we are applying retrieval-based modeling ideas to the problem of multi-domain task-oriented semantic parsing for conversational assistants. Our approach, RetroNLU, extends a sequence-to-sequence model architecture with a retrieval component, used to fetch existing similar examples and provide them as an additional input to the model. In particular, we analyze two settings, where we augment an input with (a) retrieved nearest neighbor utterances (utterance-nn), and (b) ground-truth semantic parses of nearest neighbor utterances (semparse-nn). Our technique outperforms the baseline method by 1.5% absolute macro-F1, especially at the low resource setting, matching the baseline model accuracy with only 40% of the data. Furthermore, we analyze the nearest neighbor retrieval component's quality, model sensitivity and break down the performance for semantic parses of different utterance complexity.
Lattice-based Improvements for Voice Triggering Using Graph Neural Networks
Jan 25, 2020



Abstract:Voice-triggered smart assistants often rely on detection of a trigger-phrase before they start listening for the user request. Mitigation of false triggers is an important aspect of building a privacy-centric non-intrusive smart assistant. In this paper, we address the task of false trigger mitigation (FTM) using a novel approach based on analyzing automatic speech recognition (ASR) lattices using graph neural networks (GNN). The proposed approach uses the fact that decoding lattice of a falsely triggered audio exhibits uncertainties in terms of many alternative paths and unexpected words on the lattice arcs as compared to the lattice of a correctly triggered audio. A pure trigger-phrase detector model doesn't fully utilize the intent of the user speech whereas by using the complete decoding lattice of user audio, we can effectively mitigate speech not intended for the smart assistant. We deploy two variants of GNNs in this paper based on 1) graph convolution layers and 2) self-attention mechanism respectively. Our experiments demonstrate that GNNs are highly accurate in FTM task by mitigating ~87% of false triggers at 99% true positive rate (TPR). Furthermore, the proposed models are fast to train and efficient in parameter requirements.
Active Learning for Domain Classification in a Commercial Spoken Personal Assistant
Aug 29, 2019
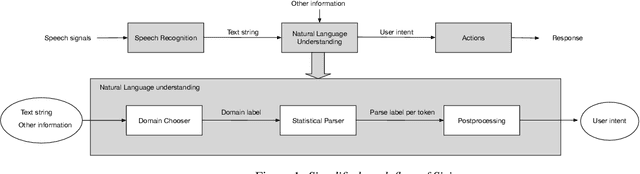
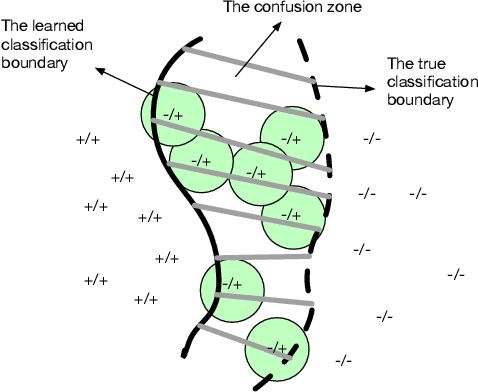
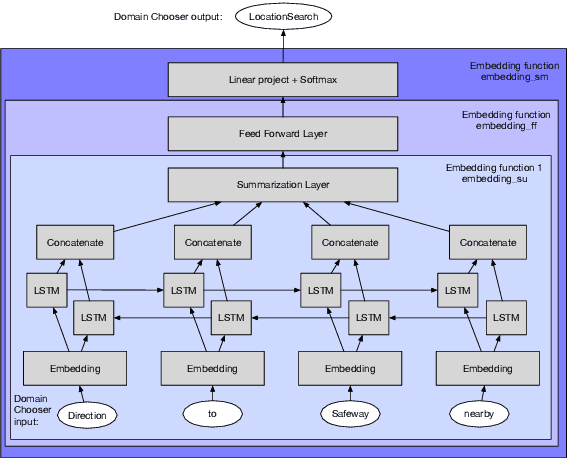
Abstract:We describe a method for selecting relevant new training data for the LSTM-based domain selection component of our personal assistant system. Adding more annotated training data for any ML system typically improves accuracy, but only if it provides examples not already adequately covered in the existing data. However, obtaining, selecting, and labeling relevant data is expensive. This work presents a simple technique that automatically identifies new helpful examples suitable for human annotation. Our experimental results show that the proposed method, compared with random-selection and entropy-based methods, leads to higher accuracy improvements given a fixed annotation budget. Although developed and tested in the setting of a commercial intelligent assistant, the technique is of wider applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge