Mohammad Kachuee
ConfQA: Answer Only If You Are Confident
Jun 08, 2025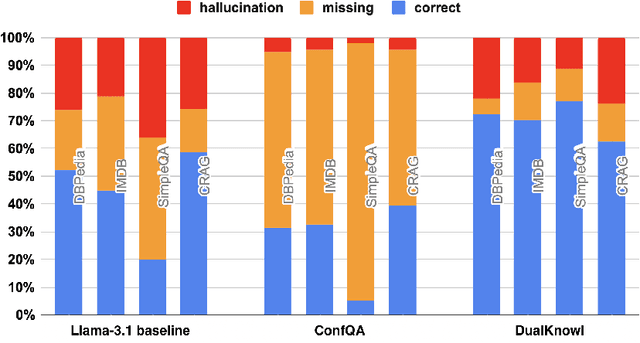
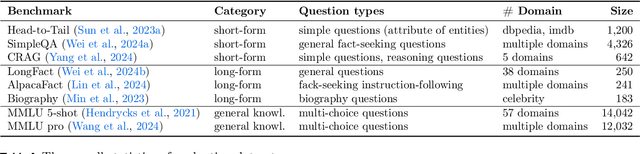
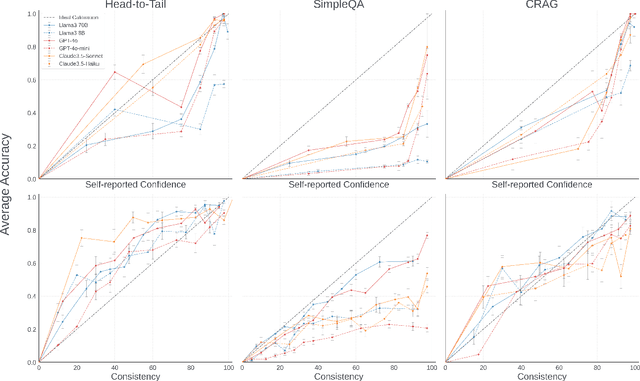
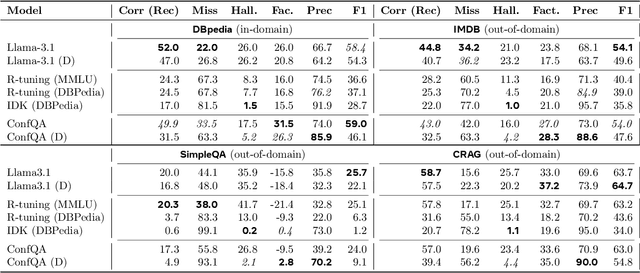
Abstract:Can we teach Large Language Models (LLMs) to refrain from hallucinating factual statements? In this paper we present a fine-tuning strategy that we call ConfQA, which can reduce hallucination rate from 20-40% to under 5% across multiple factuality benchmarks. The core idea is simple: when the LLM answers a question correctly, it is trained to continue with the answer; otherwise, it is trained to admit "I am unsure". But there are two key factors that make the training highly effective. First, we introduce a dampening prompt "answer only if you are confident" to explicitly guide the behavior, without which hallucination remains high as 15%-25%. Second, we leverage simple factual statements, specifically attribute values from knowledge graphs, to help LLMs calibrate the confidence, resulting in robust generalization across domains and question types. Building on this insight, we propose the Dual Neural Knowledge framework, which seamlessly select between internally parameterized neural knowledge and externally recorded symbolic knowledge based on ConfQA's confidence. The framework enables potential accuracy gains to beyond 95%, while reducing unnecessary external retrievals by over 30%.
Skin-in-the-Game: Decision Making via Multi-Stakeholder Alignment in LLMs
May 21, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in tasks such as summarization, arithmetic reasoning, and question answering. However, they encounter significant challenges in the domain of moral reasoning and ethical decision-making, especially in complex scenarios with multiple stakeholders. This paper introduces the Skin-in-the-Game (SKIG) framework, aimed at enhancing moral reasoning in LLMs by exploring decisions' consequences from multiple stakeholder perspectives. Central to SKIG's mechanism is simulating accountability for actions, which, alongside empathy exercises and risk assessment, is pivotal to its effectiveness. We validate SKIG's performance across various moral reasoning benchmarks with proprietary and opensource LLMs, and investigate its crucial components through extensive ablation analyses.
GrounDial: Human-norm Grounded Safe Dialog Response Generation
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Current conversational AI systems based on large language models (LLMs) are known to generate unsafe responses, agreeing to offensive user input or including toxic content. Previous research aimed to alleviate the toxicity, by fine-tuning LLM with manually annotated safe dialogue histories. However, the dependency on additional tuning requires substantial costs. To remove the dependency, we propose GrounDial, where response safety is achieved by grounding responses to commonsense social rules without requiring fine-tuning. A hybrid approach of in-context learning and human-norm-guided decoding of GrounDial enables the response to be quantitatively and qualitatively safer even without additional data or tuning.
Data Augmentation for Improving Tail-traffic Robustness in Skill-routing for Dialogue Systems
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:Large-scale conversational systems typically rely on a skill-routing component to route a user request to an appropriate skill and interpretation to serve the request. In such system, the agent is responsible for serving thousands of skills and interpretations which create a long-tail distribution due to the natural frequency of requests. For example, the samples related to play music might be a thousand times more frequent than those asking for theatre show times. Moreover, inputs used for ML-based skill routing are often a heterogeneous mix of strings, embedding vectors, categorical and scalar features which makes employing augmentation-based long-tail learning approaches challenging. To improve the skill-routing robustness, we propose an augmentation of heterogeneous skill-routing data and training targeted for robust operation in long-tail data regimes. We explore a variety of conditional encoder-decoder generative frameworks to perturb original data fields and create synthetic training data. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct extensive experiments using real-world data from a commercial conversational system. Based on the experiment results, the proposed approach improves more than 80% (51 out of 63) of intents with less than 10K of traffic instances in the skill-routing replication task.
Scalable and Safe Remediation of Defective Actions in Self-Learning Conversational Systems
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Off-Policy reinforcement learning has been a driving force for the state-of-the-art conversational AIs leading to more natural humanagent interactions and improving the user satisfaction for goal-oriented agents. However, in large-scale commercial settings, it is often challenging to balance between policy improvements and experience continuity on the broad spectrum of applications handled by such system. In the literature, off-policy evaluation and guard-railing on aggregate statistics has been commonly used to address this problem. In this paper, we propose a method for curating and leveraging high-precision samples sourced from historical regression incident reports to validate, safe-guard, and improve policies prior to the online deployment. We conducted extensive experiments using data from a real-world conversational system and actual regression incidents. The proposed method is currently deployed in our production system to protect customers against broken experiences and enable long-term policy improvements.
Constrained Policy Optimization for Controlled Self-Learning in Conversational AI Systems
Sep 17, 2022
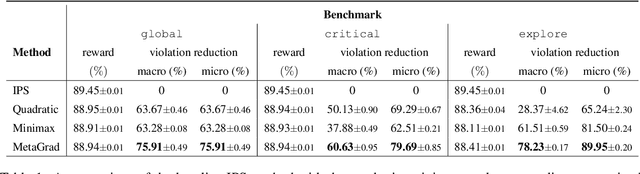

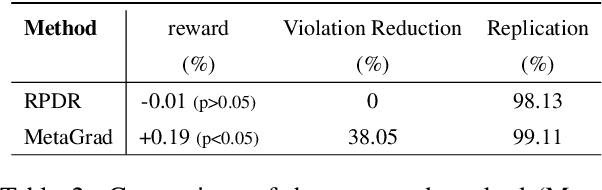
Abstract:Recently, self-learning methods based on user satisfaction metrics and contextual bandits have shown promising results to enable consistent improvements in conversational AI systems. However, directly targeting such metrics by off-policy bandit learning objectives often increases the risk of making abrupt policy changes that break the current user experience. In this study, we introduce a scalable framework for supporting fine-grained exploration targets for individual domains via user-defined constraints. For example, we may want to ensure fewer policy deviations in business-critical domains such as shopping, while allocating more exploration budget to domains such as music. Furthermore, we present a novel meta-gradient learning approach that is scalable and practical to address this problem. The proposed method adjusts constraint violation penalty terms adaptively through a meta objective that encourages balanced constraint satisfaction across domains. We conduct extensive experiments using data from a real-world conversational AI on a set of realistic constraint benchmarks. Based on the experimental results, we demonstrate that the proposed approach is capable of achieving the best balance between the policy value and constraint satisfaction rate.
Scalable and Robust Self-Learning for Skill Routing in Large-Scale Conversational AI Systems
Apr 14, 2022



Abstract:Skill routing is an important component in large-scale conversational systems. In contrast to traditional rule-based skill routing, state-of-the-art systems use a model-based approach to enable natural conversations. To provide supervision signal required to train such models, ideas such as human annotation, replication of a rule-based system, relabeling based on user paraphrases, and bandit-based learning were suggested. However, these approaches: (a) do not scale in terms of the number of skills and skill on-boarding, (b) require a very costly expert annotation/rule-design, (c) introduce risks in the user experience with each model update. In this paper, we present a scalable self-learning approach to explore routing alternatives without causing abrupt policy changes that break the user experience, learn from the user interaction, and incrementally improve the routing via frequent model refreshes. To enable such robust frequent model updates, we suggest a simple and effective approach that ensures controlled policy updates for individual domains, followed by an off-policy evaluation for making deployment decisions without any need for lengthy A/B experimentation. We conduct various offline and online A/B experiments on a commercial large-scale conversational system to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in real-world production settings.
Domain-Aware Contrastive Knowledge Transfer for Multi-domain Imbalanced Data
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:In many real-world machine learning applications, samples belong to a set of domains e.g., for product reviews each review belongs to a product category. In this paper, we study multi-domain imbalanced learning (MIL), the scenario that there is imbalance not only in classes but also in domains. In the MIL setting, different domains exhibit different patterns and there is a varying degree of similarity and divergence among domains posing opportunities and challenges for transfer learning especially when faced with limited or insufficient training data. We propose a novel domain-aware contrastive knowledge transfer method called DCMI to (1) identify the shared domain knowledge to encourage positive transfer among similar domains (in particular from head domains to tail domains); (2) isolate the domain-specific knowledge to minimize the negative transfer from dissimilar domains. We evaluated the performance of DCMI on three different datasets showing significant improvements in different MIL scenarios.
Real-Time Decentralized knowledge Transfer at the Edge
Nov 11, 2020



Abstract:Proliferation of edge networks creates islands of learning agents working on local streams of data. Transferring knowledge between these agents in real-time without exposing private data allows for collaboration to decrease learning time, and increase model confidence. Incorporating knowledge from data that was not seen by a local model creates an ability to debias a local model, or add to classification abilities on data never before seen. Transferring knowledge in a decentralized approach allows for models to retain their local insights, in turn allowing for local flavors of a machine learning model. This approach suits the decentralized architecture of edge networks, as a local edge node will serve a community of learning agents that will likely encounter similar data. We propose a method based on knowledge distillation for pairwise knowledge transfer pipelines, and compare to other popular knowledge transfer methods. Additionally, we test different scenarios of knowledge transfer network construction and show the practicality of our approach. Based on our experiments we show knowledge transfer using our model outperforms common methods in a real time transfer scenario.
Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning for Efficient User Satisfaction Prediction in Conversational Agents
Oct 21, 2020



Abstract:Turn-level user satisfaction is one of the most important performance metrics for conversational agents. It can be used to monitor the agent's performance and provide insights about defective user experiences. Moreover, a powerful satisfaction model can be used as an objective function that a conversational agent continuously optimizes for. While end-to-end deep learning has shown promising results, having access to a large number of reliable annotated samples required by these methods remains challenging. In a large-scale conversational system, there is a growing number of newly developed skills, making the traditional data collection, annotation, and modeling process impractical due to the required annotation costs as well as the turnaround times. In this paper, we suggest a self-supervised contrastive learning approach that leverages the pool of unlabeled data to learn user-agent interactions. We show that the pre-trained models using the self-supervised objective are transferable to the user satisfaction prediction. In addition, we propose a novel few-shot transfer learning approach that ensures better transferability for very small sample sizes. The suggested few-shot method does not require any inner loop optimization process and is scalable to very large datasets and complex models. Based on our experiments using real-world data from a large-scale commercial system, the suggested approach is able to significantly reduce the required number of annotations, while improving the generalization on unseen out-of-domain skills.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge