Zuoyu Tian
Science Out of Its Ivory Tower: Improving Accessibility with Reinforcement Learning
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:A vast amount of scholarly work is published daily, yet much of it remains inaccessible to the general public due to dense jargon and complex language. To address this challenge in science communication, we introduce a reinforcement learning framework that fine-tunes a language model to rewrite scholarly abstracts into more comprehensible versions. Guided by a carefully balanced combination of word- and sentence-level accessibility rewards, our language model effectively substitutes technical terms with more accessible alternatives, a task which models supervised fine-tuned or guided by conventional readability measures struggle to accomplish. Our best model adjusts the readability level of scholarly abstracts by approximately six U.S. grade levels -- in other words, from a postgraduate to a high school level. This translates to roughly a 90% relative boost over the supervised fine-tuning baseline, all while maintaining factual accuracy and high-quality language. An in-depth analysis of our approach shows that balanced rewards lead to systematic modifications in the base model, likely contributing to smoother optimization and superior performance. We envision this work as a step toward bridging the gap between scholarly research and the general public, particularly younger readers and those without a college degree.
Bootstrapping meaning through listening: Unsupervised learning of spoken sentence embeddings
Oct 23, 2022Abstract:Inducing semantic representations directly from speech signals is a highly challenging task but has many useful applications in speech mining and spoken language understanding. This study tackles the unsupervised learning of semantic representations for spoken utterances. Through converting speech signals into hidden units generated from acoustic unit discovery, we propose WavEmbed, a multimodal sequential autoencoder that predicts hidden units from a dense representation of speech. Secondly, we also propose S-HuBERT to induce meaning through knowledge distillation, in which a sentence embedding model is first trained on hidden units and passes its knowledge to a speech encoder through contrastive learning. The best performing model achieves a moderate correlation (0.5~0.6) with human judgments, without relying on any labels or transcriptions. Furthermore, these models can also be easily extended to leverage textual transcriptions of speech to learn much better speech embeddings that are strongly correlated with human annotations. Our proposed methods are applicable to the development of purely data-driven systems for speech mining, indexing and search.
Investigating Transfer Learning in Multilingual Pre-trained Language Models through Chinese Natural Language Inference
Jun 07, 2021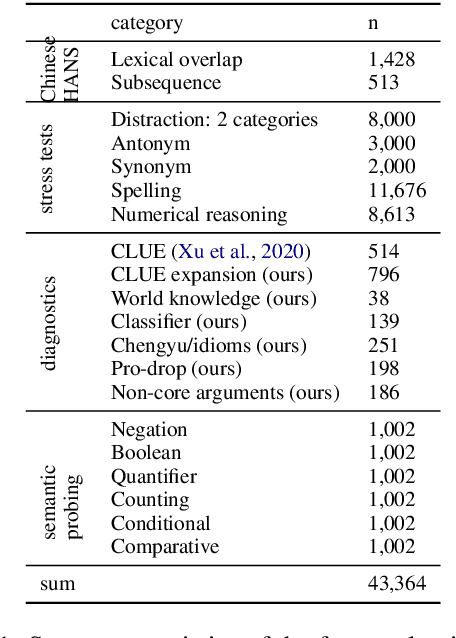

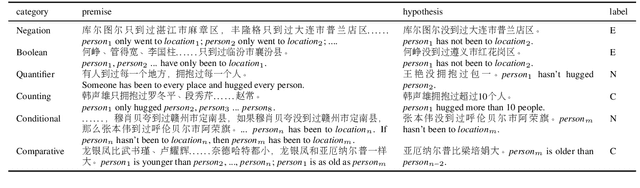
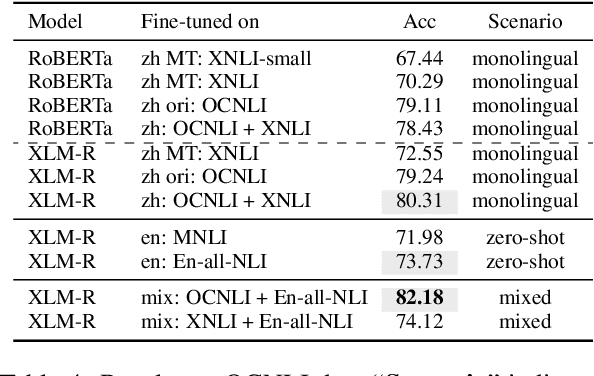
Abstract:Multilingual transformers (XLM, mT5) have been shown to have remarkable transfer skills in zero-shot settings. Most transfer studies, however, rely on automatically translated resources (XNLI, XQuAD), making it hard to discern the particular linguistic knowledge that is being transferred, and the role of expert annotated monolingual datasets when developing task-specific models. We investigate the cross-lingual transfer abilities of XLM-R for Chinese and English natural language inference (NLI), with a focus on the recent large-scale Chinese dataset OCNLI. To better understand linguistic transfer, we created 4 categories of challenge and adversarial tasks (totaling 17 new datasets) for Chinese that build on several well-known resources for English (e.g., HANS, NLI stress-tests). We find that cross-lingual models trained on English NLI do transfer well across our Chinese tasks (e.g., in 3/4 of our challenge categories, they perform as well/better than the best monolingual models, even on 3/5 uniquely Chinese linguistic phenomena such as idioms, pro drop). These results, however, come with important caveats: cross-lingual models often perform best when trained on a mixture of English and high-quality monolingual NLI data (OCNLI), and are often hindered by automatically translated resources (XNLI-zh). For many phenomena, all models continue to struggle, highlighting the need for our new diagnostics to help benchmark Chinese and cross-lingual models. All new datasets/code are released at https://github.com/huhailinguist/ChineseNLIProbing.
CLUE: A Chinese Language Understanding Evaluation Benchmark
Apr 14, 2020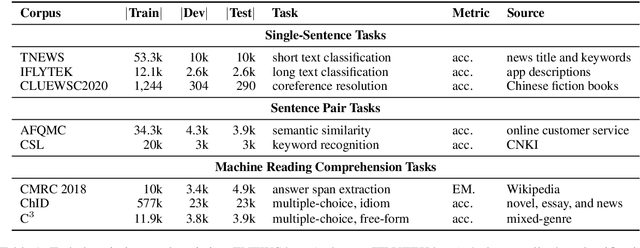
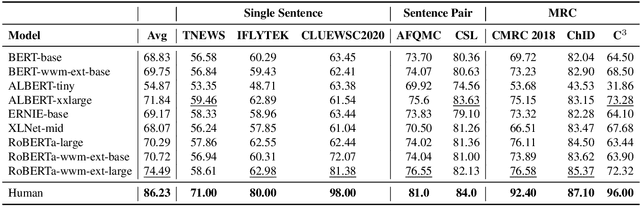
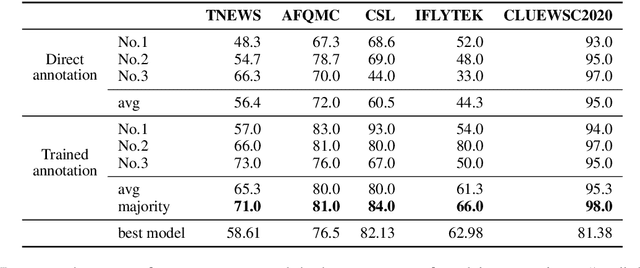
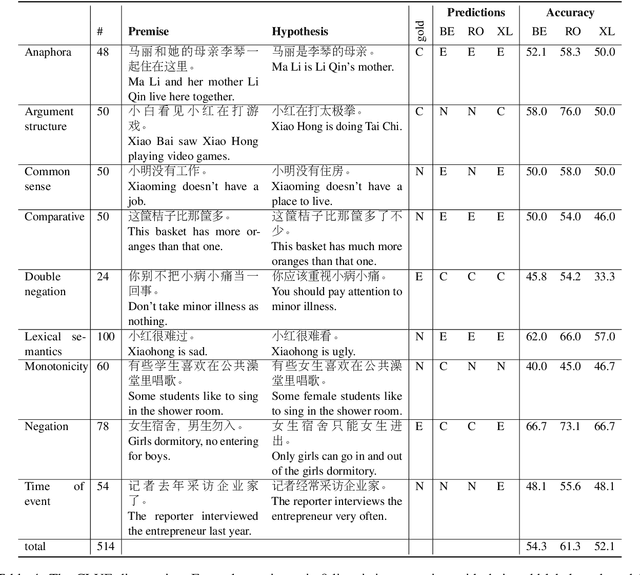
Abstract:We introduce CLUE, a Chinese Language Understanding Evaluation benchmark. It contains eight different tasks, including single-sentence classification, sentence pair classification, and machine reading comprehension. We evaluate CLUE on a number of existing full-network pre-trained models for Chinese. We also include a small hand-crafted diagnostic test set designed to probe specific linguistic phenomena using different models, some of which are unique to Chinese. Along with CLUE, we release a large clean crawled raw text corpus that can be used for model pre-training. We release CLUE, baselines and pre-training dataset on Github.
UM-IU@LING at SemEval-2019 Task 6: Identifying Offensive Tweets Using BERT and SVMs
Apr 06, 2019



Abstract:This paper describes the UM-IU@LING's system for the SemEval 2019 Task 6: OffensEval. We take a mixed approach to identify and categorize hate speech in social media. In subtask A, we fine-tuned a BERT based classifier to detect abusive content in tweets, achieving a macro F1 score of 0.8136 on the test data, thus reaching the 3rd rank out of 103 submissions. In subtasks B and C, we used a linear SVM with selected character n-gram features. For subtask C, our system could identify the target of abuse with a macro F1 score of 0.5243, ranking it 27th out of 65 submissions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge