Weitang Liu
Model-diff: A Tool for Comparative Study of Language Models in the Input Space
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Comparing two (large) language models (LMs) side-by-side and pinpointing their prediction similarities and differences on the same set of inputs are crucial in many real-world scenarios, e.g., one can test if a licensed model was potentially plagiarized by another. Traditional analysis compares the LMs' outputs on some benchmark datasets, which only cover a limited number of inputs of designed perspectives for the intended applications. The benchmark datasets cannot prepare data to cover the test cases from unforeseen perspectives which can help us understand differences between models unbiasedly. In this paper, we propose a new model comparative analysis setting that considers a large input space where brute-force enumeration would be infeasible. The input space can be simply defined as all token sequences that a LM would produce low perplexity on -- we follow this definition in the paper as it would produce the most human-understandable inputs. We propose a novel framework \our that uses text generation by sampling and deweights the histogram of sampling statistics to estimate prediction differences between two LMs in this input space efficiently and unbiasedly. Our method achieves this by drawing and counting the inputs at each prediction difference value in negative log-likelihood. Experiments reveal for the first time the quantitative prediction differences between LMs in a large input space, potentially facilitating the model analysis for applications such as model plagiarism.
OMNIINPUT: A Model-centric Evaluation Framework through Output Distribution
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:We propose a novel model-centric evaluation framework, OmniInput, to evaluate the quality of an AI/ML model's predictions on all possible inputs (including human-unrecognizable ones), which is crucial for AI safety and reliability. Unlike traditional data-centric evaluation based on pre-defined test sets, the test set in OmniInput is self-constructed by the model itself and the model quality is evaluated by investigating its output distribution. We employ an efficient sampler to obtain representative inputs and the output distribution of the trained model, which, after selective annotation, can be used to estimate the model's precision and recall at different output values and a comprehensive precision-recall curve. Our experiments demonstrate that OmniInput enables a more fine-grained comparison between models, especially when their performance is almost the same on pre-defined datasets, leading to new findings and insights for how to train more robust, generalizable models.
WOT-Class: Weakly Supervised Open-world Text Classification
May 21, 2023



Abstract:State-of-the-art weakly supervised text classification methods, while significantly reduced the required human supervision, still requires the supervision to cover all the classes of interest. This is never easy to meet in practice when human explore new, large corpora without complete pictures. In this paper, we work on a novel yet important problem of weakly supervised open-world text classification, where supervision is only needed for a few examples from a few known classes and the machine should handle both known and unknown classes in test time. General open-world classification has been studied mostly using image classification; however, existing methods typically assume the availability of sufficient known-class supervision and strong unknown-class prior knowledge (e.g., the number and/or data distribution). We propose a novel framework WOT-Class that lifts those strong assumptions. Specifically, it follows an iterative process of (a) clustering text to new classes, (b) mining and ranking indicative words for each class, and (c) merging redundant classes by using the overlapped indicative words as a bridge. Extensive experiments on 7 popular text classification datasets demonstrate that WOT-Class outperforms strong baselines consistently with a large margin, attaining 23.33% greater average absolute macro-F1 over existing approaches across all datasets. Such competent accuracy illuminates the practical potential of further reducing human effort for text classification.
Gradient-based Wang-Landau Algorithm: A Novel Sampler for Output Distribution of Neural Networks over the Input Space
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:The output distribution of a neural network (NN) over the entire input space captures the complete input-output mapping relationship, offering insights toward a more comprehensive NN understanding. Exhaustive enumeration or traditional Monte Carlo methods for the entire input space can exhibit impractical sampling time, especially for high-dimensional inputs. To make such difficult sampling computationally feasible, in this paper, we propose a novel Gradient-based Wang-Landau (GWL) sampler. We first draw the connection between the output distribution of a NN and the density of states (DOS) of a physical system. Then, we renovate the classic sampler for the DOS problem, the Wang-Landau algorithm, by replacing its random proposals with gradient-based Monte Carlo proposals. This way, our GWL sampler investigates the under-explored subsets of the input space much more efficiently. Extensive experiments have verified the accuracy of the output distribution generated by GWL and also showcased several interesting findings - for example, in a binary image classification task, both CNN and ResNet mapped the majority of human unrecognizable images to very negative logit values.
Can multi-label classification networks know what they don't know?
Sep 29, 2021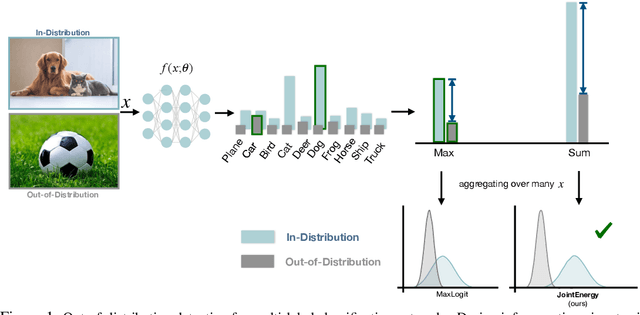
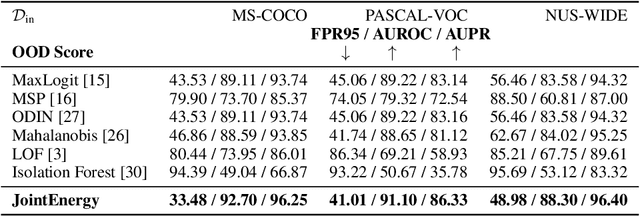
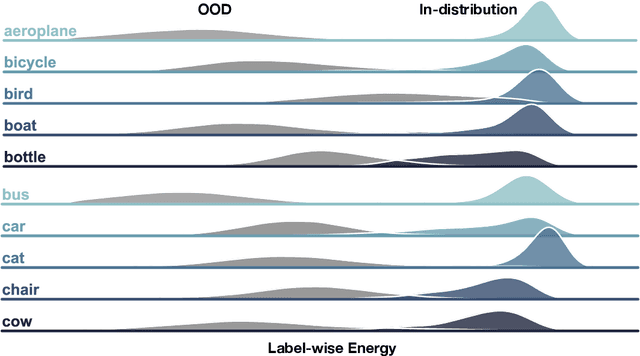
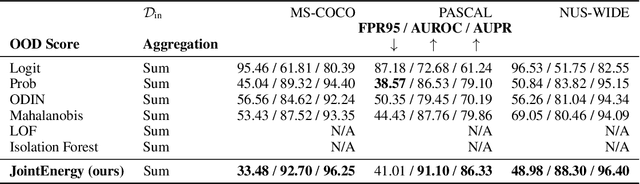
Abstract:Estimating out-of-distribution (OOD) uncertainty is a central challenge for safely deploying machine learning models in the open-world environment. Improved methods for OOD detection in multi-class classification have emerged, while OOD detection methods for multi-label classification remain underexplored and use rudimentary techniques. We propose JointEnergy, a simple and effective method, which estimates the OOD indicator scores by aggregating energy scores from multiple labels. We show that JointEnergy can be mathematically interpreted from a joint likelihood perspective. Our results show consistent improvement over previous methods that are based on the maximum-valued scores, which fail to capture joint information from multiple labels. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on three common multi-label classification benchmarks, including MS-COCO, PASCAL-VOC, and NUS-WIDE. We show that JointEnergy can reduce the FPR95 by up to 10.05% compared to the previous best baseline, establishing state-of-the-art performance.
MAF-GNN: Multi-adaptive Spatiotemporal-flow Graph Neural Network for Traffic Speed Forecasting
Aug 08, 2021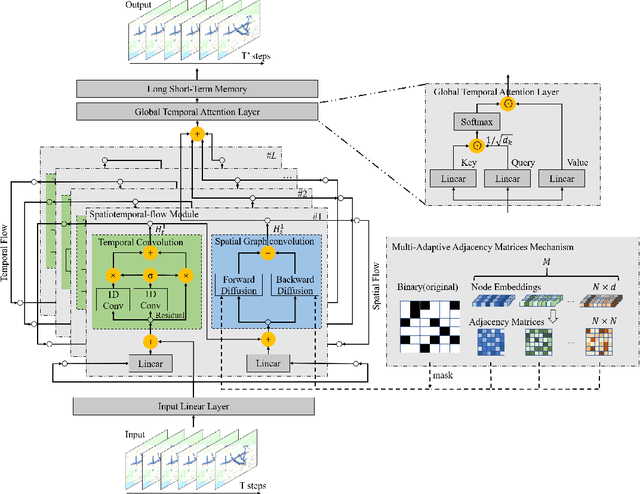
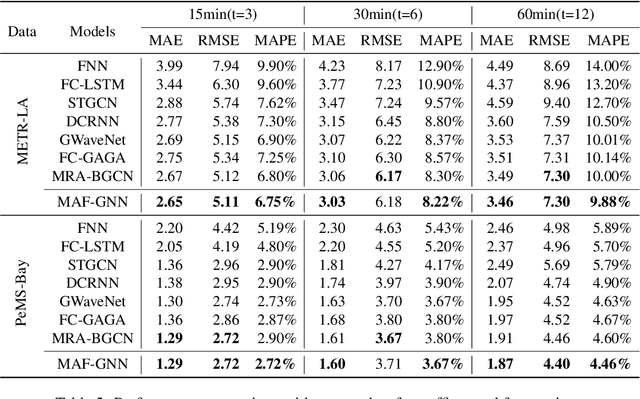
Abstract:Traffic forecasting is a core element of intelligent traffic monitoring system. Approaches based on graph neural networks have been widely used in this task to effectively capture spatial and temporal dependencies of road networks. However, these approaches can not effectively define the complicated network topology. Besides, their cascade network structures have limitations in transmitting distinct features in the time and space dimensions. In this paper, we propose a Multi-adaptive Spatiotemporal-flow Graph Neural Network (MAF-GNN) for traffic speed forecasting. MAF-GNN introduces an effective Multi-adaptive Adjacency Matrices Mechanism to capture multiple latent spatial dependencies between traffic nodes. Additionally, we propose Spatiotemporal-flow Modules aiming to further enhance feature propagation in both time and space dimensions. MAF-GNN achieves better performance than other models on two real-world datasets of public traffic network, METR-LA and PeMS-Bay, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Energy-based Out-of-distribution Detection
Oct 13, 2020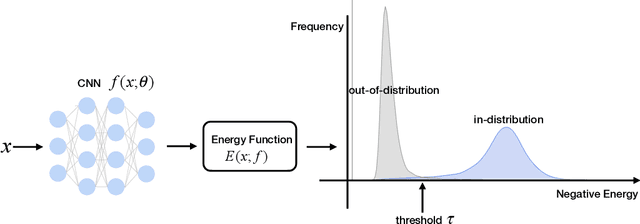
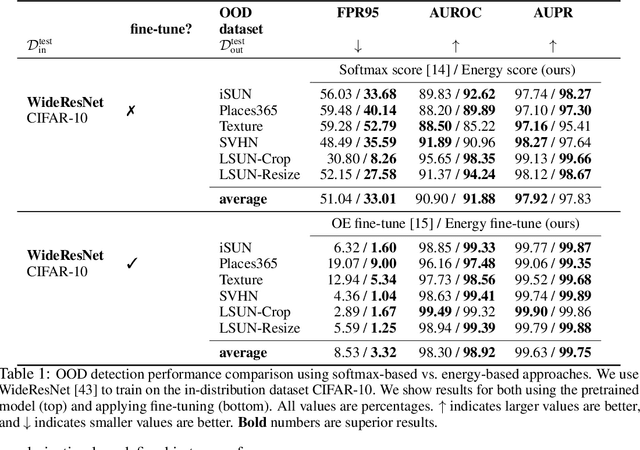
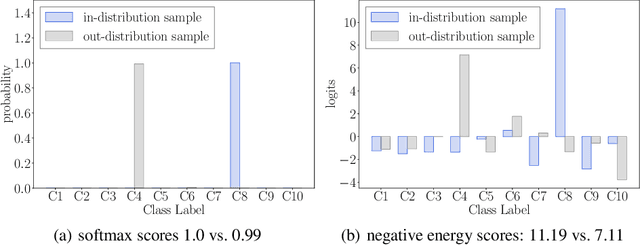
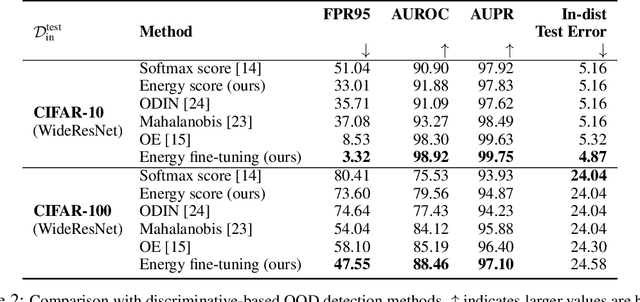
Abstract:Determining whether inputs are out-of-distribution (OOD) is an essential building block for safely deploying machine learning models in the open world. However, previous methods relying on the softmax confidence score suffer from overconfident posterior distributions for OOD data. We propose a unified framework for OOD detection that uses an energy score. We show that energy scores better distinguish in- and out-of-distribution samples than the traditional approach using the softmax scores. Unlike softmax confidence scores, energy scores are theoretically aligned with the probability density of the inputs and are less susceptible to the overconfidence issue. Within this framework, energy can be flexibly used as a scoring function for any pre-trained neural classifier as well as a trainable cost function to shape the energy surface explicitly for OOD detection. On a CIFAR-10 pre-trained WideResNet, using the energy score reduces the average FPR (at TPR 95%) by 18.03% compared to the softmax confidence score. With energy-based training, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art on common benchmarks.
CLUE: A Chinese Language Understanding Evaluation Benchmark
Apr 14, 2020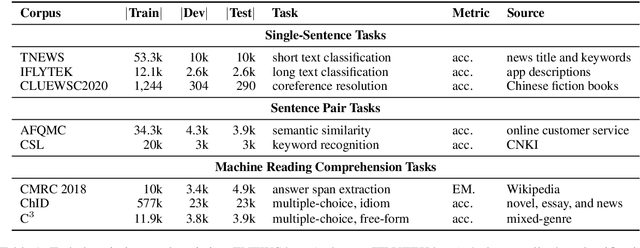
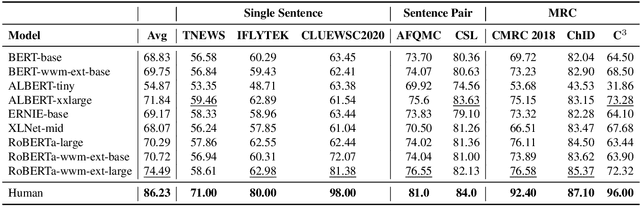
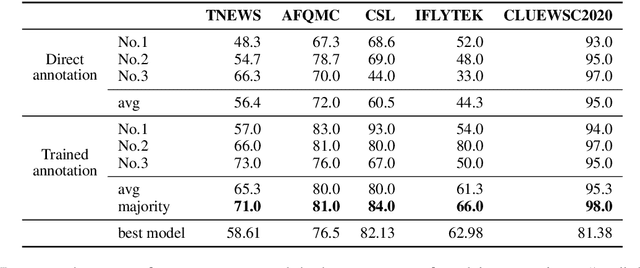
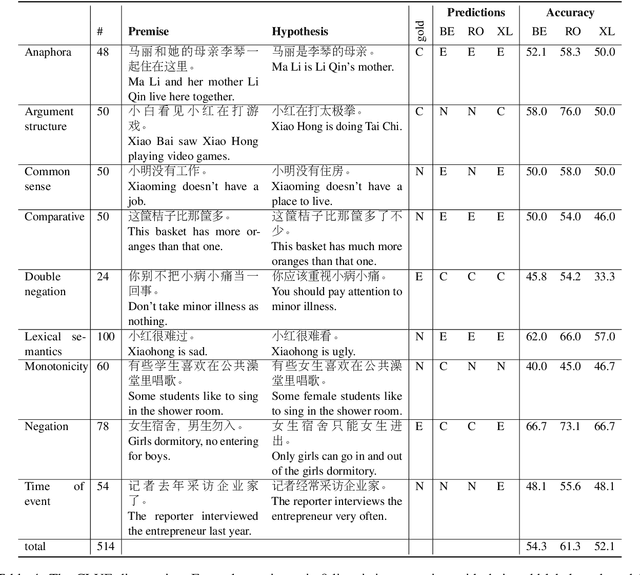
Abstract:We introduce CLUE, a Chinese Language Understanding Evaluation benchmark. It contains eight different tasks, including single-sentence classification, sentence pair classification, and machine reading comprehension. We evaluate CLUE on a number of existing full-network pre-trained models for Chinese. We also include a small hand-crafted diagnostic test set designed to probe specific linguistic phenomena using different models, some of which are unique to Chinese. Along with CLUE, we release a large clean crawled raw text corpus that can be used for model pre-training. We release CLUE, baselines and pre-training dataset on Github.
CLUENER2020: Fine-grained Named Entity Recognition Dataset and Benchmark for Chinese
Jan 20, 2020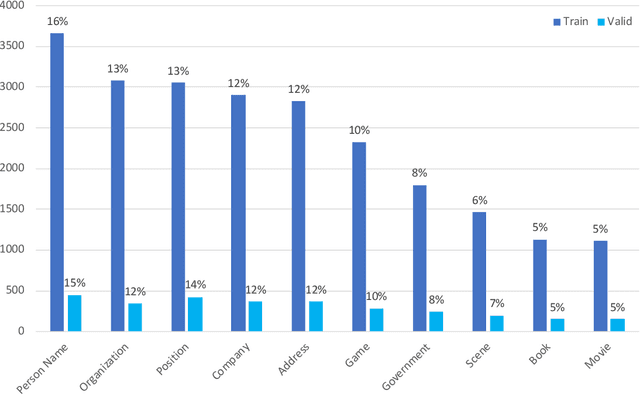

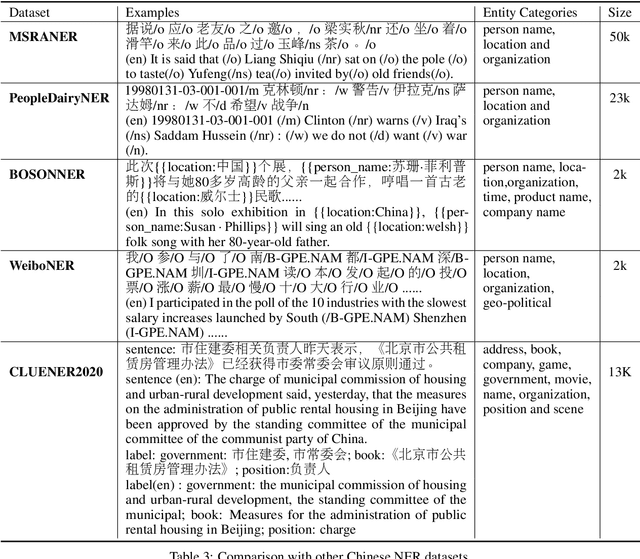
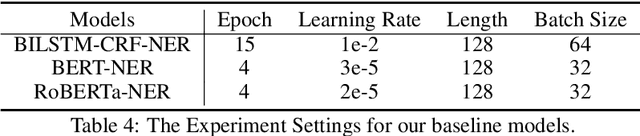
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the NER dataset from CLUE organization (CLUENER2020), a well-defined fine-grained dataset for named entity recognition in Chinese. CLUENER2020 contains 10 categories. Apart from common labels like person, organization, and location, it contains more diverse categories. It is more challenging than current other Chinese NER datasets and could better reflect real-world applications. For comparison, we implement several state-of-the-art baselines as sequence labeling tasks and report human performance, as well as its analysis. To facilitate future work on fine-grained NER for Chinese, we release our dataset, baselines, and leader-board.
Unsupervised Object Segmentation with Explicit Localization Module
Nov 21, 2019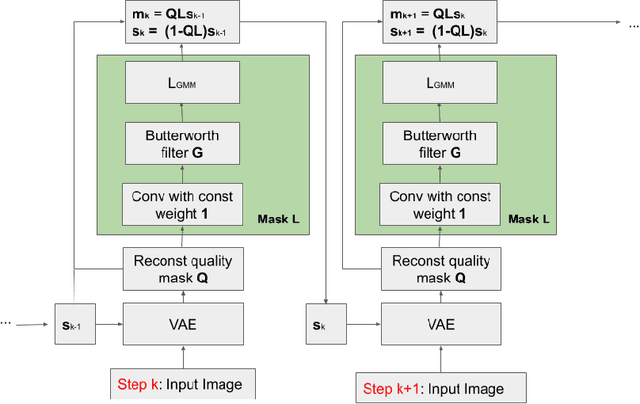

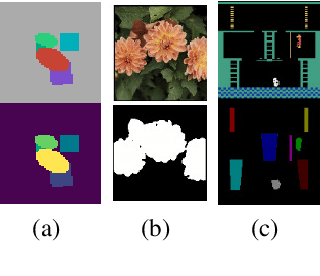
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel architecture that iteratively discovers and segments out the objects of a scene based on the image reconstruction quality. Different from other approaches, our model uses an explicit localization module that localizes objects of the scene based on the pixel-level reconstruction qualities at each iteration, where simpler objects tend to be reconstructed better at earlier iterations and thus are segmented out first. We show that our localization module improves the quality of the segmentation, especially on a challenging background.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge