Zixuan Xu
SaFeR-ToolKit: Structured Reasoning via Virtual Tool Calling for Multimodal Safety
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models remain susceptible to multimodal jailbreaks and over-refusal because safety hinges on both visual evidence and user intent, while many alignment pipelines supervise only the final response. To address this, we present SaFeR-ToolKit, which formalizes safety decision-making as a checkable protocol. Concretely, a planner specifies a persona, a Perception $\to$ Reasoning $\to$ Decision tool set, and a constrained transition graph, while a responder outputs a typed key-value tool trace before the final answer. To make the protocol reliably followed in practice, we train a single policy with a three-stage curriculum (SFT $\to$ DPO $\to$ GRPO), where GRPO directly supervises tool usage beyond answer-level feedback. Our contributions are two-fold: I. Dataset. The first tool-based safety reasoning dataset, comprising 31,654 examples (SFT 6k, DPO 18.6k, GRPO 6k) plus 1k held-out evaluation. II. Experiments. On Qwen2.5-VL, SaFeR-ToolKit significantly improves Safety/Helpfulness/Reasoning Rigor on 3B (29.39/45.04/4.98 $\to$ 84.40/71.13/78.87) and 7B (53.21/52.92/19.26 $\to$ 86.34/80.79/85.34), while preserving general capabilities (3B: 58.67 $\to$ 59.21; 7B: 66.39 $\to$ 66.81). Codes are available at https://github.com/Duebassx/SaFeR_ToolKit.
Correlative Preference Transfer with Hierarchical Hypergraph Network for Multi-Domain Recommendation
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:Advanced recommender systems usually involve multiple domains (scenarios or categories) for various marketing strategies, and users interact with them to satisfy their diverse demands. The goal of multi-domain recommendation is to improve the recommendation performance of all domains simultaneously. Conventional graph neural network based methods usually deal with each domain separately, or train a shared model for serving all domains. The former fails to leverage users' cross-domain behaviors, making the behavior sparseness issue a great obstacle. The latter learns shared user representation with respect to all domains, which neglects users' domain-specific preferences. These shortcomings greatly limit their performance in multi-domain recommendation. To tackle the limitations, an appropriate way is to learn from multi-domain user feedbacks and obtain separate user representations to characterize their domain-specific preferences. In this paper we propose $\mathsf{H^3Trans}$, a hierarchical hypergraph network based correlative preference transfer framework for multi-domain recommendation. $\mathsf{H^3Trans}$ represents multi-domain feedbacks into a unified graph to help preference transfer via taking full advantage of users' multi-domain behaviors. We incorporate two hyperedge-based modules, namely dynamic item transfer module (Hyper-I) and adaptive user aggregation module (Hyper-U). Hyper-I extracts correlative information from multi-domain user-item feedbacks for eliminating domain discrepancy of item representations. Hyper-U aggregates users' scattered preferences in multiple domains and further exploits the high-order (not only pair-wise) connections among them to learn user representations. Experimental results on both public datasets and large-scale production datasets verify the superiority of $\mathsf{H^3Trans}$ for multi-domain recommendation.
Beta R-CNN: Looking into Pedestrian Detection from Another Perspective
Oct 23, 2022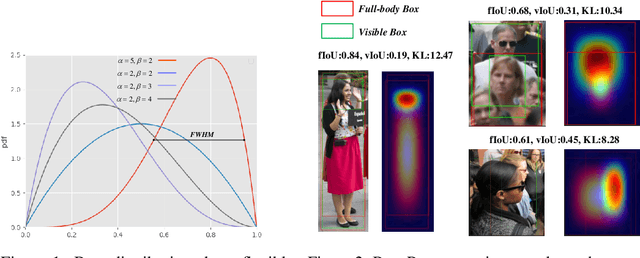
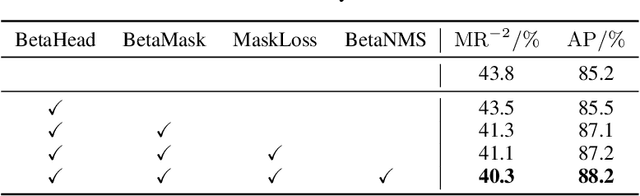
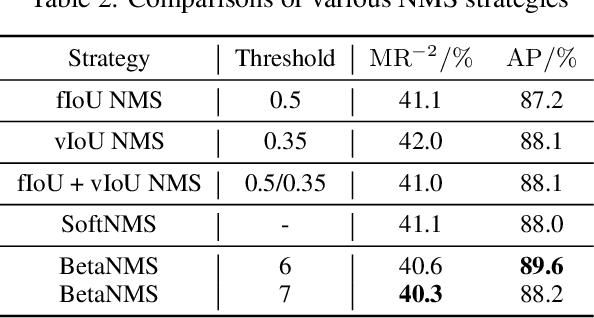
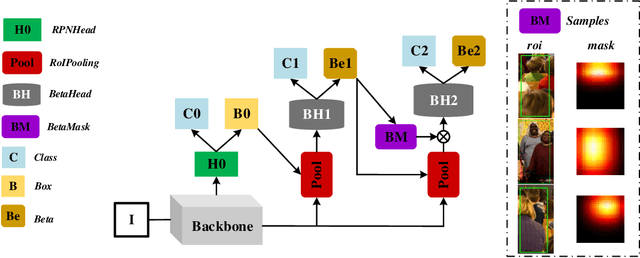
Abstract:Recently significant progress has been made in pedestrian detection, but it remains challenging to achieve high performance in occluded and crowded scenes. It could be attributed mostly to the widely used representation of pedestrians, i.e., 2D axis-aligned bounding box, which just describes the approximate location and size of the object. Bounding box models the object as a uniform distribution within the boundary, making pedestrians indistinguishable in occluded and crowded scenes due to much noise. To eliminate the problem, we propose a novel representation based on 2D beta distribution, named Beta Representation. It pictures a pedestrian by explicitly constructing the relationship between full-body and visible boxes, and emphasizes the center of visual mass by assigning different probability values to pixels. As a result, Beta Representation is much better for distinguishing highly-overlapped instances in crowded scenes with a new NMS strategy named BetaNMS. What's more, to fully exploit Beta Representation, a novel pipeline Beta R-CNN equipped with BetaHead and BetaMask is proposed, leading to high detection performance in occluded and crowded scenes.
UKD: Debiasing Conversion Rate Estimation via Uncertainty-regularized Knowledge Distillation
Jan 20, 2022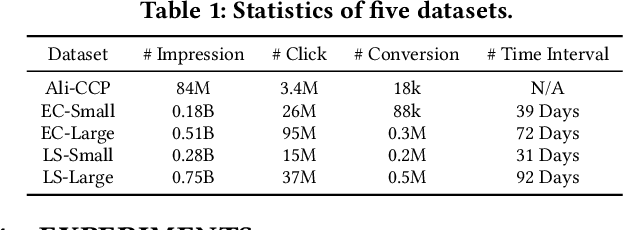
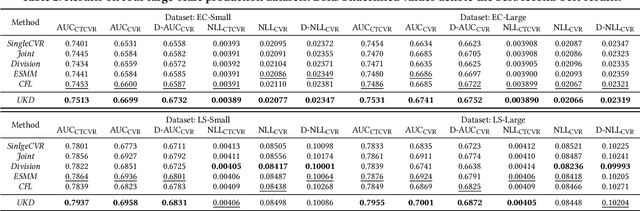

Abstract:In online advertising, conventional post-click conversion rate (CVR) estimation models are trained using clicked samples. However, during online serving the models need to estimate for all impression ads, leading to the sample selection bias (SSB) issue. Intuitively, providing reliable supervision signals for unclicked ads is a feasible way to alleviate the SSB issue. This paper proposes an uncertainty-regularized knowledge distillation (UKD) framework to debias CVR estimation via distilling knowledge from unclicked ads. A teacher model learns click-adaptive representations and produces pseudo-conversion labels on unclicked ads as supervision signals. Then a student model is trained on both clicked and unclicked ads with knowledge distillation, performing uncertainty modeling to alleviate the inherent noise in pseudo-labels. Experiments on billion-scale datasets show that UKD outperforms previous debiasing methods. Online results verify that UKD achieves significant improvements.
Unrestricted Adversarial Attacks on ImageNet Competition
Oct 25, 2021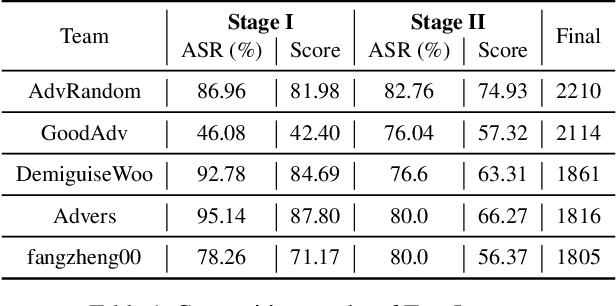
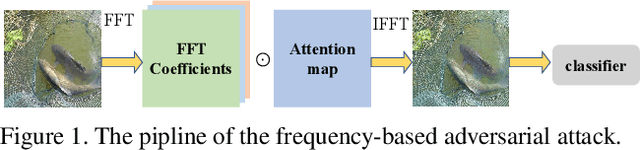
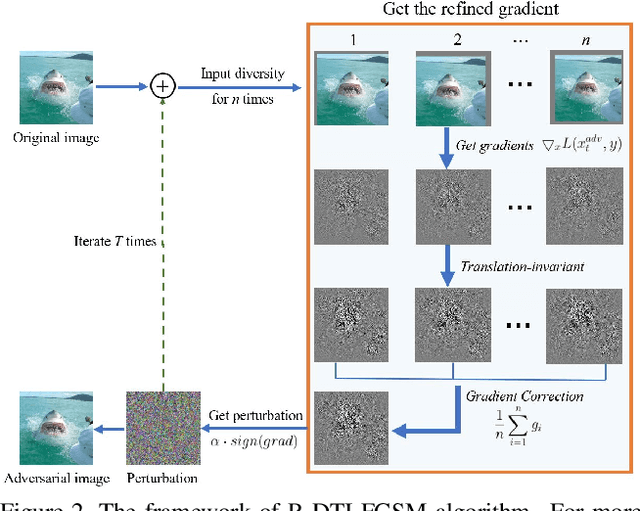
Abstract:Many works have investigated the adversarial attacks or defenses under the settings where a bounded and imperceptible perturbation can be added to the input. However in the real-world, the attacker does not need to comply with this restriction. In fact, more threats to the deep model come from unrestricted adversarial examples, that is, the attacker makes large and visible modifications on the image, which causes the model classifying mistakenly, but does not affect the normal observation in human perspective. Unrestricted adversarial attack is a popular and practical direction but has not been studied thoroughly. We organize this competition with the purpose of exploring more effective unrestricted adversarial attack algorithm, so as to accelerate the academical research on the model robustness under stronger unbounded attacks. The competition is held on the TianChi platform (\url{https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531853/introduction}) as one of the series of AI Security Challengers Program.
MAF-GNN: Multi-adaptive Spatiotemporal-flow Graph Neural Network for Traffic Speed Forecasting
Aug 08, 2021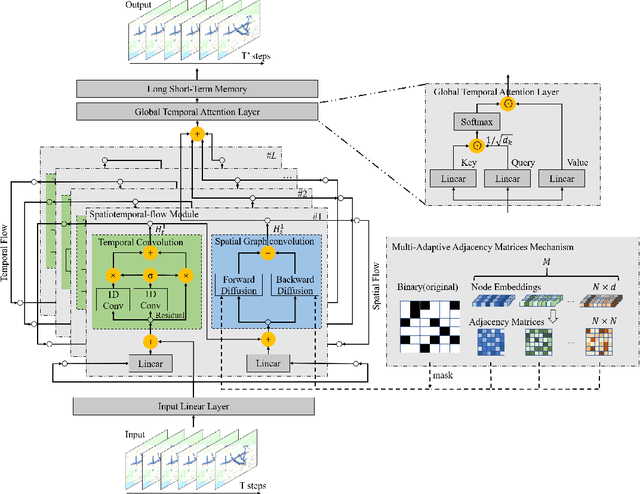
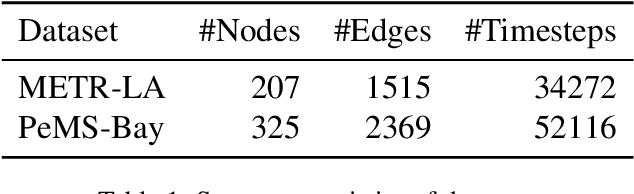
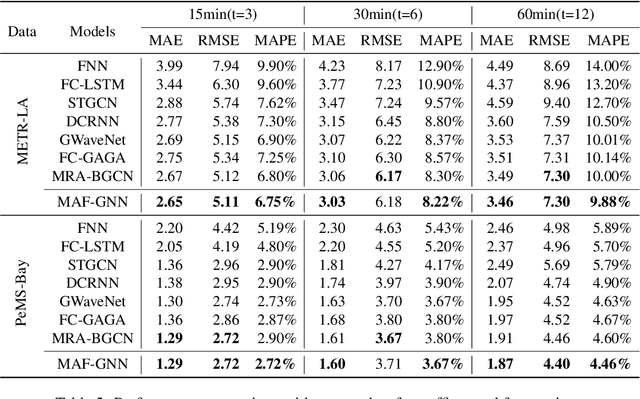
Abstract:Traffic forecasting is a core element of intelligent traffic monitoring system. Approaches based on graph neural networks have been widely used in this task to effectively capture spatial and temporal dependencies of road networks. However, these approaches can not effectively define the complicated network topology. Besides, their cascade network structures have limitations in transmitting distinct features in the time and space dimensions. In this paper, we propose a Multi-adaptive Spatiotemporal-flow Graph Neural Network (MAF-GNN) for traffic speed forecasting. MAF-GNN introduces an effective Multi-adaptive Adjacency Matrices Mechanism to capture multiple latent spatial dependencies between traffic nodes. Additionally, we propose Spatiotemporal-flow Modules aiming to further enhance feature propagation in both time and space dimensions. MAF-GNN achieves better performance than other models on two real-world datasets of public traffic network, METR-LA and PeMS-Bay, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
AnchorFace: An Anchor-based Facial Landmark Detector Across Large Poses
Jul 07, 2020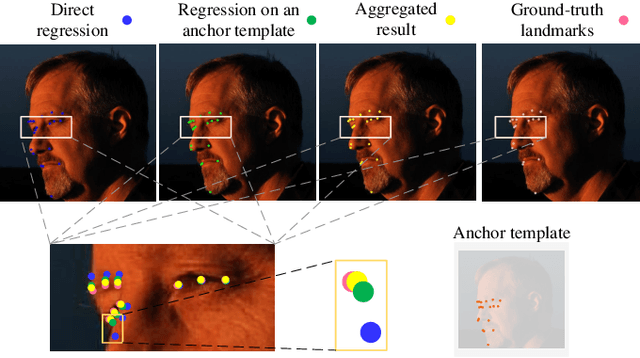
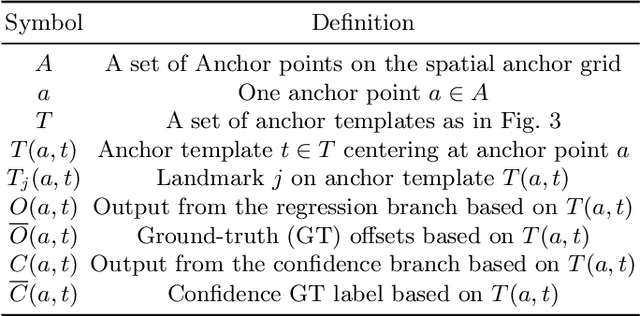
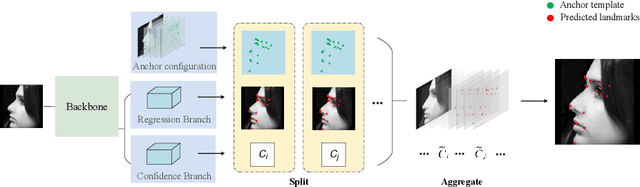
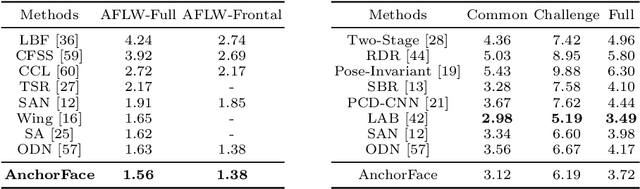
Abstract:Facial landmark localization aims to detect the predefined points of human faces, and the topic has been rapidly improved with the recent development of neural network based methods. However, it remains a challenging task when dealing with faces in unconstrained scenarios, especially with large pose variations. In this paper, we target the problem of facial landmark localization across large poses and address this task based on a split-and-aggregate strategy. To split the search space, we propose a set of anchor templates as references for regression, which well addresses the large variations of face poses. Based on the prediction of each anchor template, we propose to aggregate the results, which can reduce the landmark uncertainty due to the large poses. Overall, our proposed approach, named AnchorFace, obtains state-of-the-art results with extremely efficient inference speed on four challenging benchmarks, i.e. AFLW, 300W, Menpo, and WFLW dataset. Code will be released for reproduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge