Jianjun Wei
Enhancing Robot Route Optimization in Smart Logistics with Transformer and GNN Integration
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:This research delves into advanced route optimization for robots in smart logistics, leveraging a fusion of Transformer architectures, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). The approach utilizes a graph-based representation encompassing geographical data, cargo allocation, and robot dynamics, addressing both spatial and resource limitations to refine route efficiency. Through extensive testing with authentic logistics datasets, the proposed method achieves notable improvements, including a 15% reduction in travel distance, a 20% boost in time efficiency, and a 10% decrease in energy consumption. These findings highlight the algorithm's effectiveness, promoting enhanced performance in intelligent logistics operations.
Few-Shot Learning with Adaptive Weight Masking in Conditional GANs
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning has revolutionized various fields, yet its efficacy is hindered by overfitting and the requirement of extensive annotated data, particularly in few-shot learning scenarios where limited samples are available. This paper introduces a novel approach to few-shot learning by employing a Residual Weight Masking Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (RWM-CGAN) for data augmentation. The proposed model integrates residual units within the generator to enhance network depth and sample quality, coupled with a weight mask regularization technique in the discriminator to improve feature learning from small-sample categories. This method addresses the core issues of robustness and generalization in few-shot learning by providing a controlled and clear augmentation of the sample space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RWM-CGAN not only expands the sample space effectively but also enriches the diversity and quality of generated samples, leading to significant improvements in detection and classification accuracy on public datasets. The paper contributes to the advancement of few-shot learning by offering a practical solution to the challenges posed by data scarcity and the need for rapid generalization to new tasks or categories.
Self-Supervised Graph Neural Networks for Enhanced Feature Extraction in Heterogeneous Information Networks
Oct 23, 2024Abstract:This paper explores the applications and challenges of graph neural networks (GNNs) in processing complex graph data brought about by the rapid development of the Internet. Given the heterogeneity and redundancy problems that graph data often have, traditional GNN methods may be overly dependent on the initial structure and attribute information of the graph, which limits their ability to accurately simulate more complex relationships and patterns in the graph. Therefore, this study proposes a graph neural network model under a self-supervised learning framework, which can flexibly combine different types of additional information of the attribute graph and its nodes, so as to better mine the deep features in the graph data. By introducing a self-supervisory mechanism, it is expected to improve the adaptability of existing models to the diversity and complexity of graph data and improve the overall performance of the model.
A Recommendation Model Utilizing Separation Embedding and Self-Attention for Feature Mining
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:With the explosive growth of Internet data, users are facing the problem of information overload, which makes it a challenge to efficiently obtain the required resources. Recommendation systems have emerged in this context. By filtering massive amounts of information, they provide users with content that meets their needs, playing a key role in scenarios such as advertising recommendation and product recommendation. However, traditional click-through rate prediction and TOP-K recommendation mechanisms are gradually unable to meet the recommendations needs in modern life scenarios due to high computational complexity, large memory consumption, long feature selection time, and insufficient feature interaction. This paper proposes a recommendations system model based on a separation embedding cross-network. The model uses an embedding neural network layer to transform sparse feature vectors into dense embedding vectors, and can independently perform feature cross operations on different dimensions, thereby improving the accuracy and depth of feature mining. Experimental results show that the model shows stronger adaptability and higher prediction accuracy in processing complex data sets, effectively solving the problems existing in existing models.
Optimizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Elasticsearch for Enhanced Question-Answering Systems
Oct 18, 2024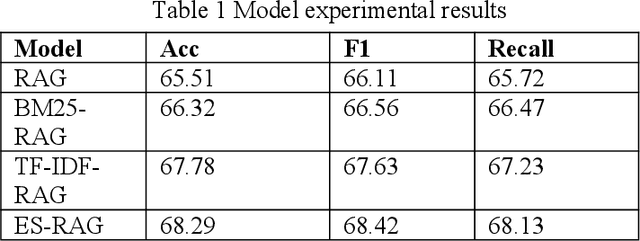
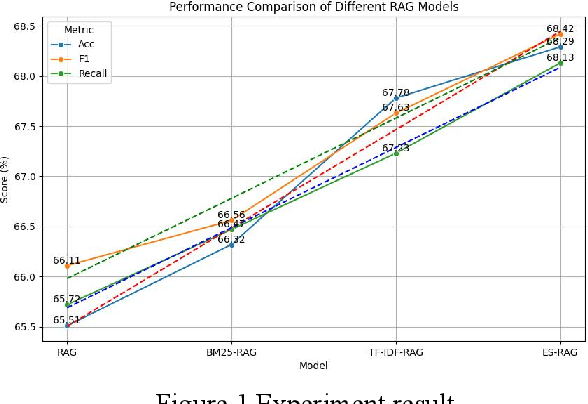
Abstract:This study aims to improve the accuracy and quality of large-scale language models (LLMs) in answering questions by integrating Elasticsearch into the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework. The experiment uses the Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) version 2.0 as the test dataset and compares the performance of different retrieval methods, including traditional methods based on keyword matching or semantic similarity calculation, BM25-RAG and TF-IDF- RAG, and the newly proposed ES-RAG scheme. The results show that ES-RAG not only has obvious advantages in retrieval efficiency but also performs well in key indicators such as accuracy, which is 0.51 percentage points higher than TF-IDF-RAG. In addition, Elasticsearch's powerful search capabilities and rich configuration options enable the entire question-answering system to better handle complex queries and provide more flexible and efficient responses based on the diverse needs of users. Future research directions can further explore how to optimize the interaction mechanism between Elasticsearch and LLM, such as introducing higher-level semantic understanding and context-awareness capabilities, to achieve a more intelligent and humanized question-answering experience.
Data-Driven Spatiotemporal Feature Representation and Mining in Multidimensional Time Series
Sep 22, 2024
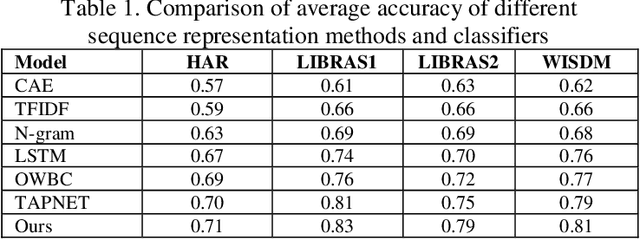
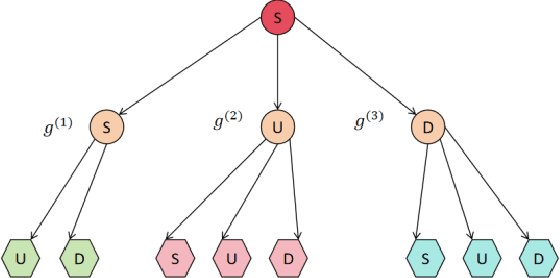

Abstract:This paper explores a new method for time series data analysis, aiming to overcome the limitations of traditional mining techniques when dealing with multidimensional time series data. Time series data are extensively utilized in diverse fields, including backend services for monitoring and optimizing IT infrastructure, medical diagnosis through continuous patient monitoring and health trend analysis, and internet business for tracking user behavior and forecasting sales. However, since the effective information in time series data is often hidden in sequence fragments, the uncertainty of their length, quantity, and morphological variables brings challenges to mining. To this end, this paper proposes a new spatiotemporal feature representation method, which converts multidimensional time series (MTS) into one-dimensional event sequences by transforming spatially varying events, and uses a series of event symbols to represent the spatial structural information of multidimensional coupling in the sequence, which has good interpretability. Then, this paper introduces a variable-length tuple mining method to extract non-redundant key event subsequences in event sequences as spatiotemporal structural features of motion sequences. This method is an unsupervised method that does not rely on large-scale training samples and defines a new model for representing the spatiotemporal structural features of multidimensional time series. The superior performance of the STEM model is verified by pattern classification experiments on a variety of motion sequences. The research results of this paper provide an important theoretical basis and technical support for understanding and predicting human behavior patterns, and have far-reaching practical application value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge