Sen Zhang
Enhancing Diffusion-Based Quantitatively Controllable Image Generation via Matrix-Form EDM and Adaptive Vicinal Training
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Continuous Conditional Diffusion Model (CCDM) is a diffusion-based framework designed to generate high-quality images conditioned on continuous regression labels. Although CCDM has demonstrated clear advantages over prior approaches across a range of datasets, it still exhibits notable limitations and has recently been surpassed by a GAN-based method, namely CcGAN-AVAR. These limitations mainly arise from its reliance on an outdated diffusion framework and its low sampling efficiency due to long sampling trajectories. To address these issues, we propose an improved CCDM framework, termed iCCDM, which incorporates the more advanced \textit{Elucidated Diffusion Model} (EDM) framework with substantial modifications to improve both generation quality and sampling efficiency. Specifically, iCCDM introduces a novel matrix-form EDM formulation together with an adaptive vicinal training strategy. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets, spanning image resolutions from $64\times64$ to $256\times256$, demonstrate that iCCDM consistently outperforms existing methods, including state-of-the-art large-scale text-to-image diffusion models (e.g., Stable Diffusion 3, FLUX.1, and Qwen-Image), achieving higher generation quality while significantly reducing sampling cost.
Large Sign Language Models: Toward 3D American Sign Language Translation
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:We present Large Sign Language Models (LSLM), a novel framework for translating 3D American Sign Language (ASL) by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) as the backbone, which can benefit hearing-impaired individuals' virtual communication. Unlike existing sign language recognition methods that rely on 2D video, our approach directly utilizes 3D sign language data to capture rich spatial, gestural, and depth information in 3D scenes. This enables more accurate and resilient translation, enhancing digital communication accessibility for the hearing-impaired community. Beyond the task of ASL translation, our work explores the integration of complex, embodied multimodal languages into the processing capabilities of LLMs, moving beyond purely text-based inputs to broaden their understanding of human communication. We investigate both direct translation from 3D gesture features to text and an instruction-guided setting where translations can be modulated by external prompts, offering greater flexibility. This work provides a foundational step toward inclusive, multimodal intelligent systems capable of understanding diverse forms of language.
Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Neural Operators for Parametric PDEs: A Human-AI Collaborative Analysis
Nov 06, 2025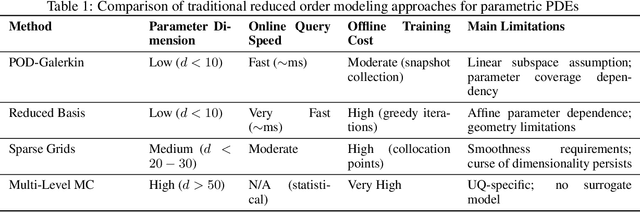
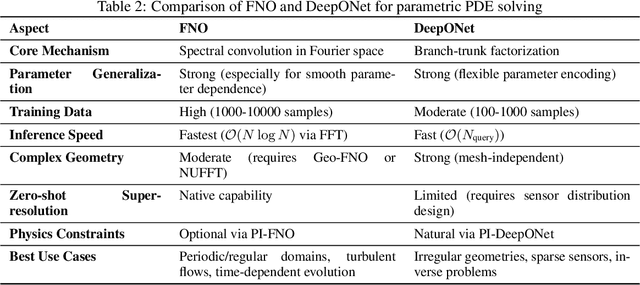
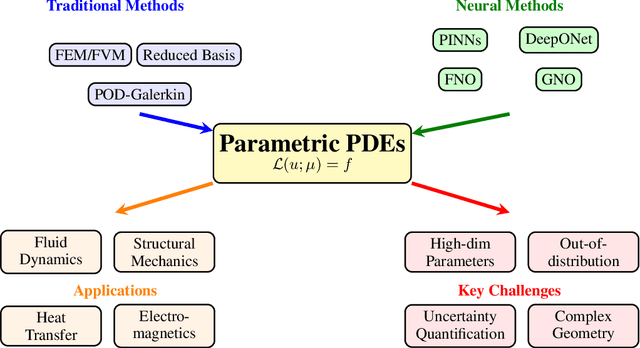
Abstract:PDEs arise ubiquitously in science and engineering, where solutions depend on parameters (physical properties, boundary conditions, geometry). Traditional numerical methods require re-solving the PDE for each parameter, making parameter space exploration prohibitively expensive. Recent machine learning advances, particularly physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) and neural operators, have revolutionized parametric PDE solving by learning solution operators that generalize across parameter spaces. We critically analyze two main paradigms: (1) PINNs, which embed physical laws as soft constraints and excel at inverse problems with sparse data, and (2) neural operators (e.g., DeepONet, Fourier Neural Operator), which learn mappings between infinite-dimensional function spaces and achieve unprecedented generalization. Through comparisons across fluid dynamics, solid mechanics, heat transfer, and electromagnetics, we show neural operators can achieve computational speedups of $10^3$ to $10^5$ times faster than traditional solvers for multi-query scenarios, while maintaining comparable accuracy. We provide practical guidance for method selection, discuss theoretical foundations (universal approximation, convergence), and identify critical open challenges: high-dimensional parameters, complex geometries, and out-of-distribution generalization. This work establishes a unified framework for understanding parametric PDE solvers via operator learning, offering a comprehensive, incrementally updated resource for this rapidly evolving field
One-shot Face Sketch Synthesis in the Wild via Generative Diffusion Prior and Instruction Tuning
Jun 18, 2025
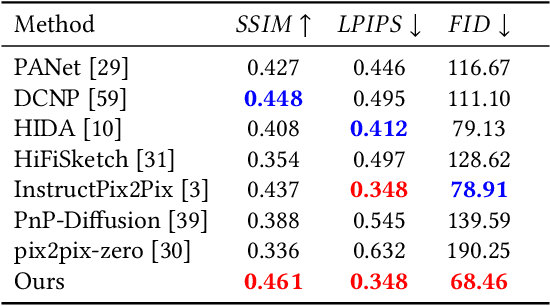
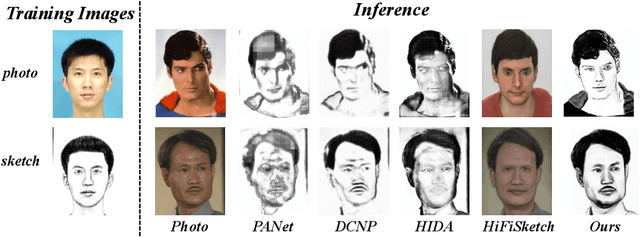
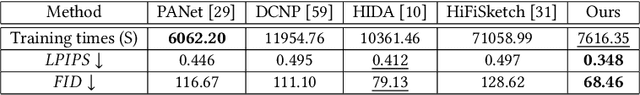
Abstract:Face sketch synthesis is a technique aimed at converting face photos into sketches. Existing face sketch synthesis research mainly relies on training with numerous photo-sketch sample pairs from existing datasets. However, these large-scale discriminative learning methods will have to face problems such as data scarcity and high human labor costs. Once the training data becomes scarce, their generative performance significantly degrades. In this paper, we propose a one-shot face sketch synthesis method based on diffusion models. We optimize text instructions on a diffusion model using face photo-sketch image pairs. Then, the instructions derived through gradient-based optimization are used for inference. To simulate real-world scenarios more accurately and evaluate method effectiveness more comprehensively, we introduce a new benchmark named One-shot Face Sketch Dataset (OS-Sketch). The benchmark consists of 400 pairs of face photo-sketch images, including sketches with different styles and photos with different backgrounds, ages, sexes, expressions, illumination, etc. For a solid out-of-distribution evaluation, we select only one pair of images for training at each time, with the rest used for inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can convert various photos into realistic and highly consistent sketches in a one-shot context. Compared to other methods, our approach offers greater convenience and broader applicability. The dataset will be available at: https://github.com/HanWu3125/OS-Sketch
Regularized Adaptive Graph Learning for Large-Scale Traffic Forecasting
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Traffic prediction is a critical task in spatial-temporal forecasting with broad applications in travel planning and urban management. Adaptive graph convolution networks have emerged as mainstream solutions due to their ability to learn node embeddings in a data-driven manner and capture complex latent dependencies. However, existing adaptive graph learning methods for traffic forecasting often either ignore the regularization of node embeddings, which account for a significant proportion of model parameters, or face scalability issues from expensive graph convolution operations. To address these challenges, we propose a Regularized Adaptive Graph Learning (RAGL) model. First, we introduce a regularized adaptive graph learning framework that synergizes Stochastic Shared Embedding (SSE) and adaptive graph convolution via a residual difference mechanism, achieving both embedding regularization and noise suppression. Second, to ensure scalability on large road networks, we develop the Efficient Cosine Operator (ECO), which performs graph convolution based on the cosine similarity of regularized embeddings with linear time complexity. Extensive experiments on four large-scale real-world traffic datasets show that RAGL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of prediction accuracy and exhibits competitive computational efficiency.
Neuron-level Balance between Stability and Plasticity in Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:In contrast to the human ability to continuously acquire knowledge, agents struggle with the stability-plasticity dilemma in deep reinforcement learning (DRL), which refers to the trade-off between retaining existing skills (stability) and learning new knowledge (plasticity). Current methods focus on balancing these two aspects at the network level, lacking sufficient differentiation and fine-grained control of individual neurons. To overcome this limitation, we propose Neuron-level Balance between Stability and Plasticity (NBSP) method, by taking inspiration from the observation that specific neurons are strongly relevant to task-relevant skills. Specifically, NBSP first (1) defines and identifies RL skill neurons that are crucial for knowledge retention through a goal-oriented method, and then (2) introduces a framework by employing gradient masking and experience replay techniques targeting these neurons to preserve the encoded existing skills while enabling adaptation to new tasks. Numerous experimental results on the Meta-World and Atari benchmarks demonstrate that NBSP significantly outperforms existing approaches in balancing stability and plasticity.
AdvSGM: Differentially Private Graph Learning via Adversarial Skip-gram Model
Mar 27, 2025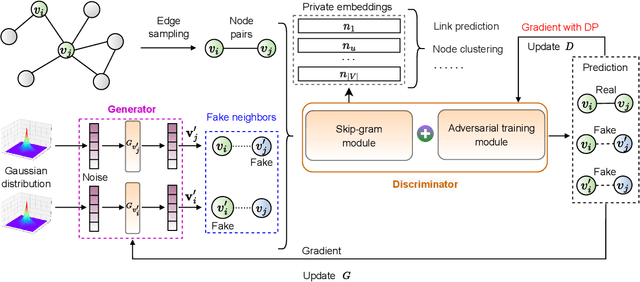
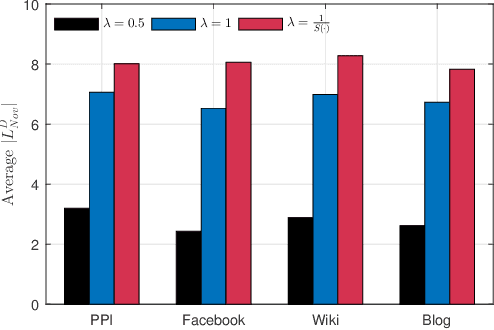
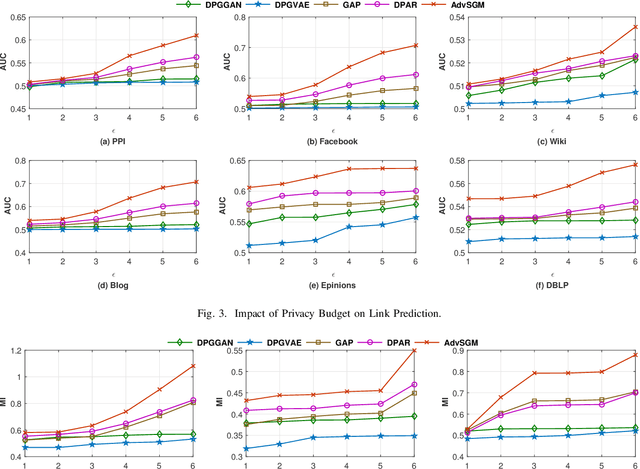
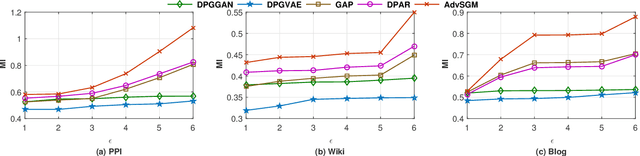
Abstract:The skip-gram model (SGM), which employs a neural network to generate node vectors, serves as the basis for numerous popular graph embedding techniques. However, since the training datasets contain sensitive linkage information, the parameters of a released SGM may encode private information and pose significant privacy risks. Differential privacy (DP) is a rigorous standard for protecting individual privacy in data analysis. Nevertheless, when applying differential privacy to skip-gram in graphs, it becomes highly challenging due to the complex link relationships, which potentially result in high sensitivity and necessitate substantial noise injection. To tackle this challenge, we present AdvSGM, a differentially private skip-gram for graphs via adversarial training. Our core idea is to leverage adversarial training to privatize skip-gram while improving its utility. Towards this end, we develop a novel adversarial training module by devising two optimizable noise terms that correspond to the parameters of a skip-gram. By fine-tuning the weights between modules within AdvSGM, we can achieve differentially private gradient updates without additional noise injection. Extensive experimental results on six real-world graph datasets show that AdvSGM preserves high data utility across different downstream tasks.
GraphSparseNet: a Novel Method for Large Scale Trafffic Flow Prediction
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Traffic flow forecasting is a critical spatio-temporal data mining task with wide-ranging applications in intelligent route planning and dynamic traffic management. Recent advancements in deep learning, particularly through Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), have significantly enhanced the accuracy of these forecasts by capturing complex spatio-temporal dynamics. However, the scalability of GNNs remains a challenge due to their exponential growth in model complexity with increasing nodes in the graph. Existing methods to address this issue, including sparsification, decomposition, and kernel-based approaches, either do not fully resolve the complexity issue or risk compromising predictive accuracy. This paper introduces GraphSparseNet (GSNet), a novel framework designed to improve both the scalability and accuracy of GNN-based traffic forecasting models. GraphSparseNet is comprised of two core modules: the Feature Extractor and the Relational Compressor. These modules operate with linear time and space complexity, thereby reducing the overall computational complexity of the model to a linear scale. Our extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that GraphSparseNet not only significantly reduces training time by 3.51x compared to state-of-the-art linear models but also maintains high predictive performance.
Cardiverse: Harnessing LLMs for Novel Card Game Prototyping
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:The prototyping of computer games, particularly card games, requires extensive human effort in creative ideation and gameplay evaluation. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) offer opportunities to automate and streamline these processes. However, it remains challenging for LLMs to design novel game mechanics beyond existing databases, generate consistent gameplay environments, and develop scalable gameplay AI for large-scale evaluations. This paper addresses these challenges by introducing a comprehensive automated card game prototyping framework. The approach highlights a graph-based indexing method for generating novel game designs, an LLM-driven system for consistent game code generation validated by gameplay records, and a gameplay AI constructing method that uses an ensemble of LLM-generated action-value functions optimized through self-play. These contributions aim to accelerate card game prototyping, reduce human labor, and lower barriers to entry for game developers.
Generative Adversarial Networks Bridging Art and Machine Intelligence
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have greatly influenced the development of computer vision and artificial intelligence in the past decade and also connected art and machine intelligence together. This book begins with a detailed introduction to the fundamental principles and historical development of GANs, contrasting them with traditional generative models and elucidating the core adversarial mechanisms through illustrative Python examples. The text systematically addresses the mathematical and theoretical underpinnings including probability theory, statistics, and game theory providing a solid framework for understanding the objectives, loss functions, and optimisation challenges inherent to GAN training. Subsequent chapters review classic variants such as Conditional GANs, DCGANs, InfoGAN, and LAPGAN before progressing to advanced training methodologies like Wasserstein GANs, GANs with gradient penalty, least squares GANs, and spectral normalisation techniques. The book further examines architectural enhancements and task-specific adaptations in generators and discriminators, showcasing practical implementations in high resolution image generation, artistic style transfer, video synthesis, text to image generation and other multimedia applications. The concluding sections offer insights into emerging research trends, including self-attention mechanisms, transformer-based generative models, and a comparative analysis with diffusion models, thus charting promising directions for future developments in both academic and applied settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge