Zhonghong Ou
OmniRAG-Agent: Agentic Omnimodal Reasoning for Low-Resource Long Audio-Video Question Answering
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Long-horizon omnimodal question answering answers questions by reasoning over text, images, audio, and video. Despite recent progress on OmniLLMs, low-resource long audio-video QA still suffers from costly dense encoding, weak fine-grained retrieval, limited proactive planning, and no clear end-to-end optimization.To address these issues, we propose OmniRAG-Agent, an agentic omnimodal QA method for budgeted long audio-video reasoning. It builds an image-audio retrieval-augmented generation module that lets an OmniLLM fetch short, relevant frames and audio snippets from external banks. Moreover, it uses an agent loop that plans, calls tools across turns, and merges retrieved evidence to answer complex queries. Furthermore, we apply group relative policy optimization to jointly improve tool use and answer quality over time. Experiments on OmniVideoBench, WorldSense, and Daily-Omni show that OmniRAG-Agent consistently outperforms prior methods under low-resource settings and achieves strong results, with ablations validating each component.
CreBench: Human-Aligned Creativity Evaluation from Idea to Process to Product
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Human-defined creativity is highly abstract, posing a challenge for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to comprehend and assess creativity that aligns with human judgments. The absence of an existing benchmark further exacerbates this dilemma. To this end, we propose CreBench, which consists of two key components: 1) an evaluation benchmark covering the multiple dimensions from creative idea to process to products; 2) CreMIT (Creativity Multimodal Instruction Tuning dataset), a multimodal creativity evaluation dataset, consisting of 2.2K diverse-sourced multimodal data, 79.2K human feedbacks and 4.7M multi-typed instructions. Specifically, to ensure MLLMs can handle diverse creativity-related queries, we prompt GPT to refine these human feedbacks to activate stronger creativity assessment capabilities. CreBench serves as a foundation for building MLLMs that understand human-aligned creativity. Based on the CreBench, we fine-tune open-source general MLLMs, resulting in CreExpert, a multimodal creativity evaluation expert model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed CreExpert models achieve significantly better alignment with human creativity evaluation compared to state-of-the-art MLLMs, including the most advanced GPT-4V and Gemini-Pro-Vision.
A Foundation Model for Chest X-ray Interpretation with Grounded Reasoning via Online Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Medical foundation models (FMs) have shown tremendous promise amid the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. However, current medical FMs typically generate answers in a black-box manner, lacking transparent reasoning processes and locally grounded interpretability, which hinders their practical clinical deployments. To this end, we introduce DeepMedix-R1, a holistic medical FM for chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation. It leverages a sequential training pipeline: initially fine-tuned on curated CXR instruction data to equip with fundamental CXR interpretation capabilities, then exposed to high-quality synthetic reasoning samples to enable cold-start reasoning, and finally refined via online reinforcement learning to enhance both grounded reasoning quality and generation performance. Thus, the model produces both an answer and reasoning steps tied to the image's local regions for each query. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates substantial improvements in report generation (e.g., 14.54% and 31.32% over LLaVA-Rad and MedGemma) and visual question answering (e.g., 57.75% and 23.06% over MedGemma and CheXagent) tasks. To facilitate robust assessment, we propose Report Arena, a benchmarking framework using advanced language models to evaluate answer quality, further highlighting the superiority of DeepMedix-R1. Expert review of generated reasoning steps reveals greater interpretability and clinical plausibility compared to the established Qwen2.5-VL-7B model (0.7416 vs. 0.2584 overall preference). Collectively, our work advances medical FM development toward holistic, transparent, and clinically actionable modeling for CXR interpretation.
Efficient Robotic Policy Learning via Latent Space Backward Planning
May 11, 2025Abstract:Current robotic planning methods often rely on predicting multi-frame images with full pixel details. While this fine-grained approach can serve as a generic world model, it introduces two significant challenges for downstream policy learning: substantial computational costs that hinder real-time deployment, and accumulated inaccuracies that can mislead action extraction. Planning with coarse-grained subgoals partially alleviates efficiency issues. However, their forward planning schemes can still result in off-task predictions due to accumulation errors, leading to misalignment with long-term goals. This raises a critical question: Can robotic planning be both efficient and accurate enough for real-time control in long-horizon, multi-stage tasks? To address this, we propose a Latent Space Backward Planning scheme (LBP), which begins by grounding the task into final latent goals, followed by recursively predicting intermediate subgoals closer to the current state. The grounded final goal enables backward subgoal planning to always remain aware of task completion, facilitating on-task prediction along the entire planning horizon. The subgoal-conditioned policy incorporates a learnable token to summarize the subgoal sequences and determines how each subgoal guides action extraction. Through extensive simulation and real-robot long-horizon experiments, we show that LBP outperforms existing fine-grained and forward planning methods, achieving SOTA performance. Project Page: https://lbp-authors.github.io
SQL-o1: A Self-Reward Heuristic Dynamic Search Method for Text-to-SQL
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:The Text-to-SQL(Text2SQL) task aims to convert natural language queries into executable SQL queries. Thanks to the application of large language models (LLMs), significant progress has been made in this field. However, challenges such as model scalability, limited generation space, and coherence issues in SQL generation still persist. To address these issues, we propose SQL-o1, a Self-Reward-based heuristic search method designed to enhance the reasoning ability of LLMs in SQL query generation. SQL-o1 combines Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) for heuristic process-level search and constructs a Schema-Aware dataset to help the model better understand database schemas. Extensive experiments on the Bird and Spider datasets demonstrate that SQL-o1 improves execution accuracy by 10.8\% on the complex Bird dataset compared to the latest baseline methods, even outperforming GPT-4-based approaches. Additionally, SQL-o1 excels in few-shot learning scenarios and shows strong cross-model transferability. Our code is publicly available at:https://github.com/ShuaiLyu0110/SQL-o1.
TSVC:Tripartite Learning with Semantic Variation Consistency for Robust Image-Text Retrieval
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval maps data under different modality via semantic relevance. Existing approaches implicitly assume that data pairs are well-aligned and ignore the widely existing annotation noise, i.e., noisy correspondence (NC). Consequently, it inevitably causes performance degradation. Despite attempts that employ the co-teaching paradigm with identical architectures to provide distinct data perspectives, the differences between these architectures are primarily stemmed from random initialization. Thus, the model becomes increasingly homogeneous along with the training process. Consequently, the additional information brought by this paradigm is severely limited. In order to resolve this problem, we introduce a Tripartite learning with Semantic Variation Consistency (TSVC) for robust image-text retrieval. We design a tripartite cooperative learning mechanism comprising a Coordinator, a Master, and an Assistant model. The Coordinator distributes data, and the Assistant model supports the Master model's noisy label prediction with diverse data. Moreover, we introduce a soft label estimation method based on mutual information variation, which quantifies the noise in new samples and assigns corresponding soft labels. We also present a new loss function to enhance robustness and optimize training effectiveness. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets demonstrate that, even at increasing noise ratios, TSVC exhibits significant advantages in retrieval accuracy and maintains stable training performance.
Universal Actions for Enhanced Embodied Foundation Models
Jan 17, 2025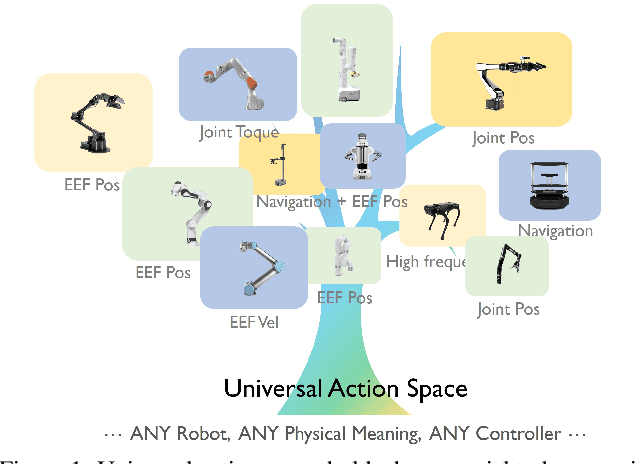

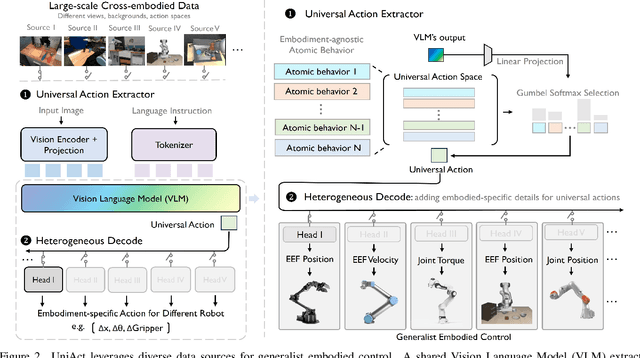
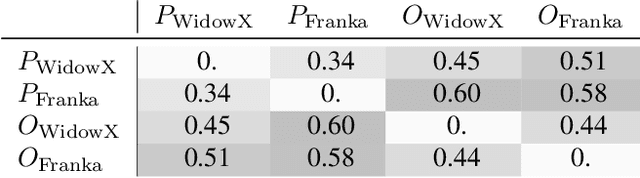
Abstract:Training on diverse, internet-scale data is a key factor in the success of recent large foundation models. Yet, using the same recipe for building embodied agents has faced noticeable difficulties. Despite the availability of many crowd-sourced embodied datasets, their action spaces often exhibit significant heterogeneity due to distinct physical embodiment and control interfaces for different robots, causing substantial challenges in developing embodied foundation models using cross-domain data. In this paper, we introduce UniAct, a new embodied foundation modeling framework operating in a tokenized Universal Action Space. Our learned universal actions capture the generic atomic behaviors across diverse robots by exploiting their shared structural features, and enable enhanced cross-domain data utilization and cross-embodiment generalizations by eliminating the notorious heterogeneity. The universal actions can be efficiently translated back to heterogeneous actionable commands by simply adding embodiment-specific details, from which fast adaptation to new robots becomes simple and straightforward. Our 0.5B instantiation of UniAct outperforms 14X larger SOTA embodied foundation models in extensive evaluations on various real-world and simulation robots, showcasing exceptional cross-embodiment control and adaptation capability, highlighting the crucial benefit of adopting universal actions. Project page: https://github.com/2toinf/UniAct
FGU3R: Fine-Grained Fusion via Unified 3D Representation for Multimodal 3D Object Detection
Jan 08, 2025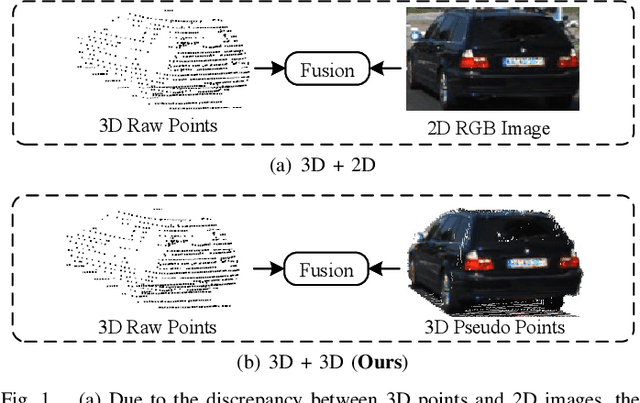
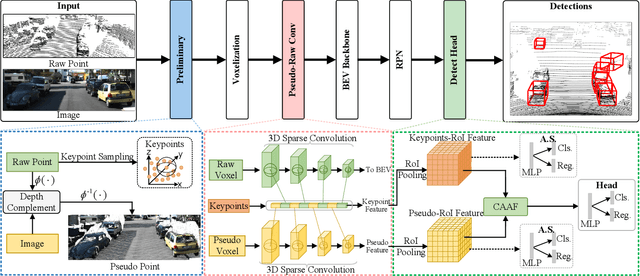

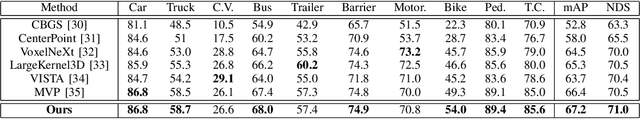
Abstract:Multimodal 3D object detection has garnered considerable interest in autonomous driving. However, multimodal detectors suffer from dimension mismatches that derive from fusing 3D points with 2D pixels coarsely, which leads to sub-optimal fusion performance. In this paper, we propose a multimodal framework FGU3R to tackle the issue mentioned above via unified 3D representation and fine-grained fusion, which consists of two important components. First, we propose an efficient feature extractor for raw and pseudo points, termed Pseudo-Raw Convolution (PRConv), which modulates multimodal features synchronously and aggregates the features from different types of points on key points based on multimodal interaction. Second, a Cross-Attention Adaptive Fusion (CAAF) is designed to fuse homogeneous 3D RoI (Region of Interest) features adaptively via a cross-attention variant in a fine-grained manner. Together they make fine-grained fusion on unified 3D representation. The experiments conducted on the KITTI and nuScenes show the effectiveness of our proposed method.
RevGNN: Negative Sampling Enhanced Contrastive Graph Learning for Academic Reviewer Recommendation
Jul 30, 2024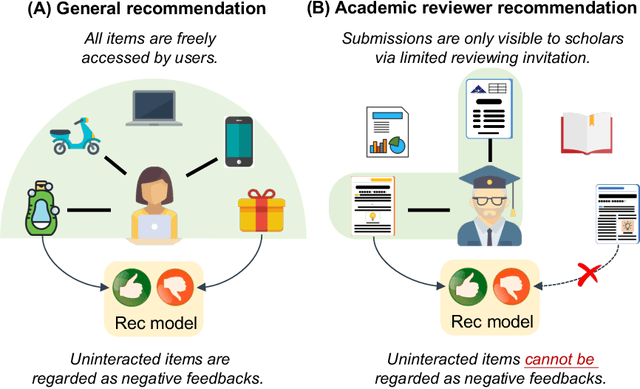
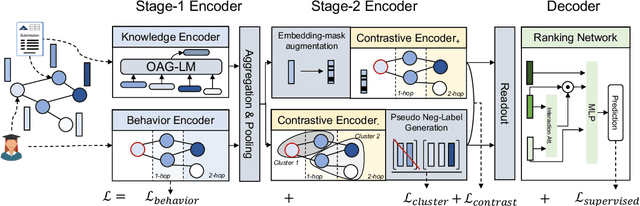
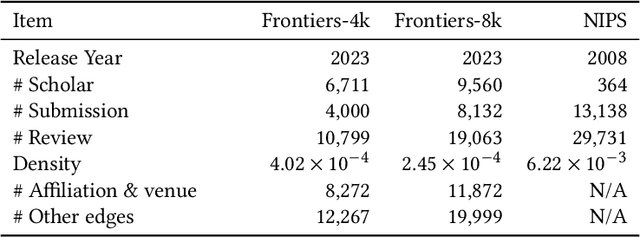
Abstract:Acquiring reviewers for academic submissions is a challenging recommendation scenario. Recent graph learning-driven models have made remarkable progress in the field of recommendation, but their performance in the academic reviewer recommendation task may suffer from a significant false negative issue. This arises from the assumption that unobserved edges represent negative samples. In fact, the mechanism of anonymous review results in inadequate exposure of interactions between reviewers and submissions, leading to a higher number of unobserved interactions compared to those caused by reviewers declining to participate. Therefore, investigating how to better comprehend the negative labeling of unobserved interactions in academic reviewer recommendations is a significant challenge. This study aims to tackle the ambiguous nature of unobserved interactions in academic reviewer recommendations. Specifically, we propose an unsupervised Pseudo Neg-Label strategy to enhance graph contrastive learning (GCL) for recommending reviewers for academic submissions, which we call RevGNN. RevGNN utilizes a two-stage encoder structure that encodes both scientific knowledge and behavior using Pseudo Neg-Label to approximate review preference. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that RevGNN outperforms all baselines across four metrics. Additionally, detailed further analyses confirm the effectiveness of each component in RevGNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge