Shuai Lyu
CreBench: Human-Aligned Creativity Evaluation from Idea to Process to Product
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Human-defined creativity is highly abstract, posing a challenge for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to comprehend and assess creativity that aligns with human judgments. The absence of an existing benchmark further exacerbates this dilemma. To this end, we propose CreBench, which consists of two key components: 1) an evaluation benchmark covering the multiple dimensions from creative idea to process to products; 2) CreMIT (Creativity Multimodal Instruction Tuning dataset), a multimodal creativity evaluation dataset, consisting of 2.2K diverse-sourced multimodal data, 79.2K human feedbacks and 4.7M multi-typed instructions. Specifically, to ensure MLLMs can handle diverse creativity-related queries, we prompt GPT to refine these human feedbacks to activate stronger creativity assessment capabilities. CreBench serves as a foundation for building MLLMs that understand human-aligned creativity. Based on the CreBench, we fine-tune open-source general MLLMs, resulting in CreExpert, a multimodal creativity evaluation expert model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed CreExpert models achieve significantly better alignment with human creativity evaluation compared to state-of-the-art MLLMs, including the most advanced GPT-4V and Gemini-Pro-Vision.
SQL-o1: A Self-Reward Heuristic Dynamic Search Method for Text-to-SQL
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:The Text-to-SQL(Text2SQL) task aims to convert natural language queries into executable SQL queries. Thanks to the application of large language models (LLMs), significant progress has been made in this field. However, challenges such as model scalability, limited generation space, and coherence issues in SQL generation still persist. To address these issues, we propose SQL-o1, a Self-Reward-based heuristic search method designed to enhance the reasoning ability of LLMs in SQL query generation. SQL-o1 combines Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) for heuristic process-level search and constructs a Schema-Aware dataset to help the model better understand database schemas. Extensive experiments on the Bird and Spider datasets demonstrate that SQL-o1 improves execution accuracy by 10.8\% on the complex Bird dataset compared to the latest baseline methods, even outperforming GPT-4-based approaches. Additionally, SQL-o1 excels in few-shot learning scenarios and shows strong cross-model transferability. Our code is publicly available at:https://github.com/ShuaiLyu0110/SQL-o1.
TSVC:Tripartite Learning with Semantic Variation Consistency for Robust Image-Text Retrieval
Jan 19, 2025Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval maps data under different modality via semantic relevance. Existing approaches implicitly assume that data pairs are well-aligned and ignore the widely existing annotation noise, i.e., noisy correspondence (NC). Consequently, it inevitably causes performance degradation. Despite attempts that employ the co-teaching paradigm with identical architectures to provide distinct data perspectives, the differences between these architectures are primarily stemmed from random initialization. Thus, the model becomes increasingly homogeneous along with the training process. Consequently, the additional information brought by this paradigm is severely limited. In order to resolve this problem, we introduce a Tripartite learning with Semantic Variation Consistency (TSVC) for robust image-text retrieval. We design a tripartite cooperative learning mechanism comprising a Coordinator, a Master, and an Assistant model. The Coordinator distributes data, and the Assistant model supports the Master model's noisy label prediction with diverse data. Moreover, we introduce a soft label estimation method based on mutual information variation, which quantifies the noise in new samples and assigns corresponding soft labels. We also present a new loss function to enhance robustness and optimize training effectiveness. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets demonstrate that, even at increasing noise ratios, TSVC exhibits significant advantages in retrieval accuracy and maintains stable training performance.
MVREC: A General Few-shot Defect Classification Model Using Multi-View Region-Context
Dec 22, 2024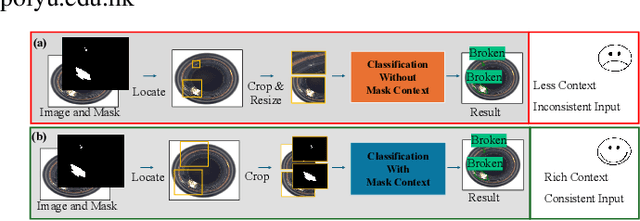
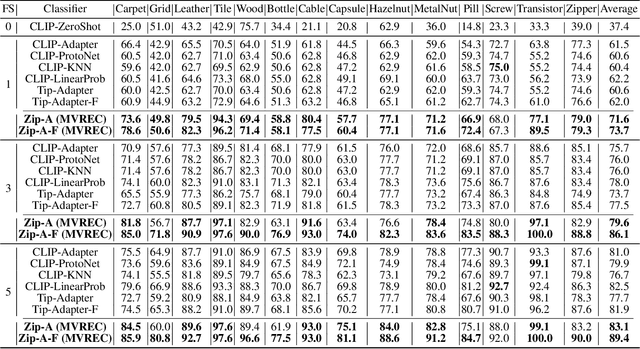
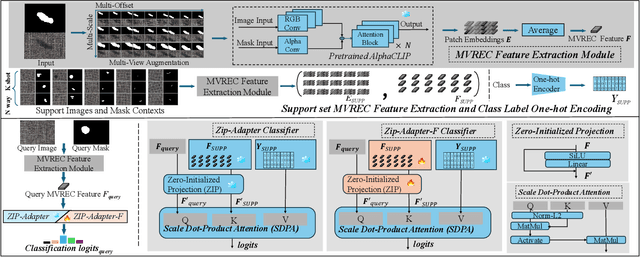
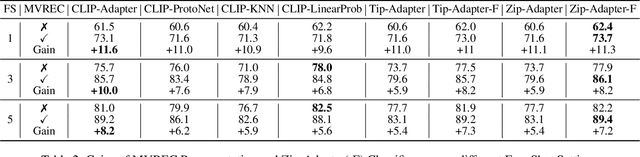
Abstract:Few-shot defect multi-classification (FSDMC) is an emerging trend in quality control within industrial manufacturing. However, current FSDMC research often lacks generalizability due to its focus on specific datasets. Additionally, defect classification heavily relies on contextual information within images, and existing methods fall short of effectively extracting this information. To address these challenges, we propose a general FSDMC framework called MVREC, which offers two primary advantages: (1) MVREC extracts general features for defect instances by incorporating the pre-trained AlphaCLIP model. (2) It utilizes a region-context framework to enhance defect features by leveraging mask region input and multi-view context augmentation. Furthermore, Few-shot Zip-Adapter(-F) classifiers within the model are introduced to cache the visual features of the support set and perform few-shot classification. We also introduce MVTec-FS, a new FSDMC benchmark based on MVTec AD, which includes 1228 defect images with instance-level mask annotations and 46 defect types. Extensive experiments conducted on MVTec-FS and four additional datasets demonstrate its effectiveness in general defect classification and its ability to incorporate contextual information to improve classification performance. Code: https://github.com/ShuaiLYU/MVREC
Improving Channel Resilience for Task-Oriented Semantic Communications: A Unified Information Bottleneck Approach
Apr 30, 2024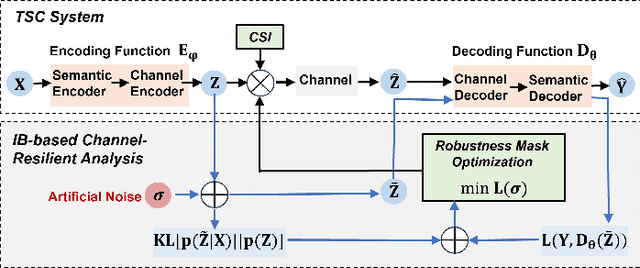
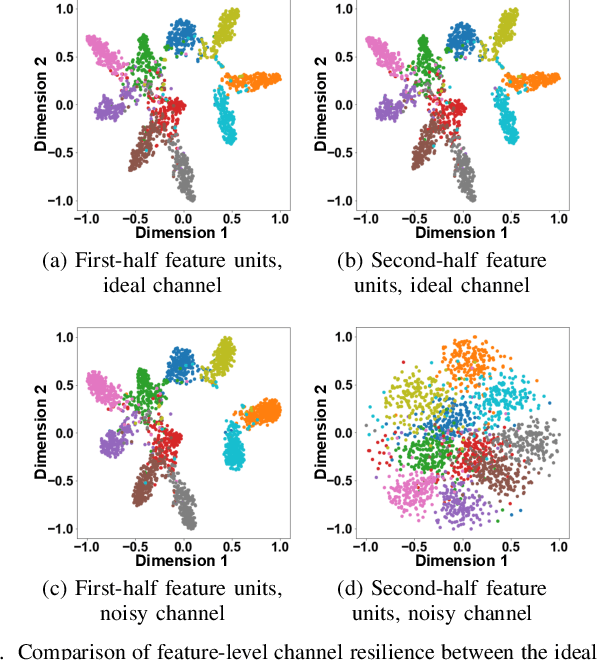
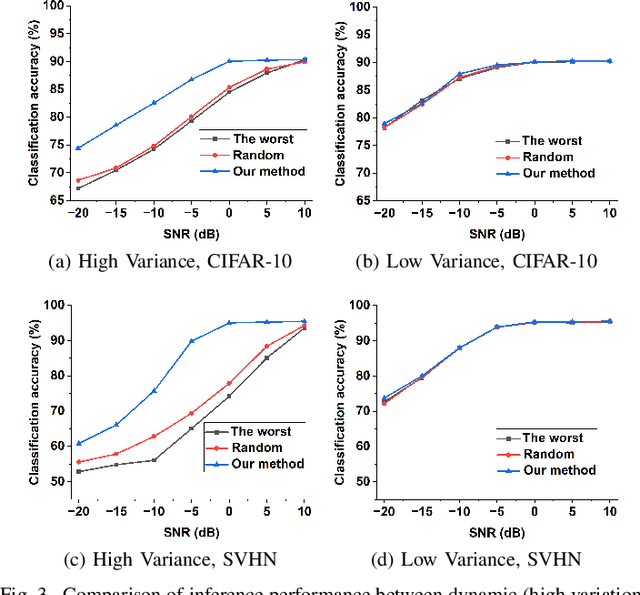
Abstract:Task-oriented semantic communications (TSC) enhance radio resource efficiency by transmitting task-relevant semantic information. However, current research often overlooks the inherent semantic distinctions among encoded features. Due to unavoidable channel variations from time and frequency-selective fading, semantically sensitive feature units could be more susceptible to erroneous inference if corrupted by dynamic channels. Therefore, this letter introduces a unified channel-resilient TSC framework via information bottleneck. This framework complements existing TSC approaches by controlling information flow to capture fine-grained feature-level semantic robustness. Experiments on a case study for real-time subchannel allocation validate the framework's effectiveness.
REB: Reducing Biases in Representation for Industrial Anomaly Detection
Aug 24, 2023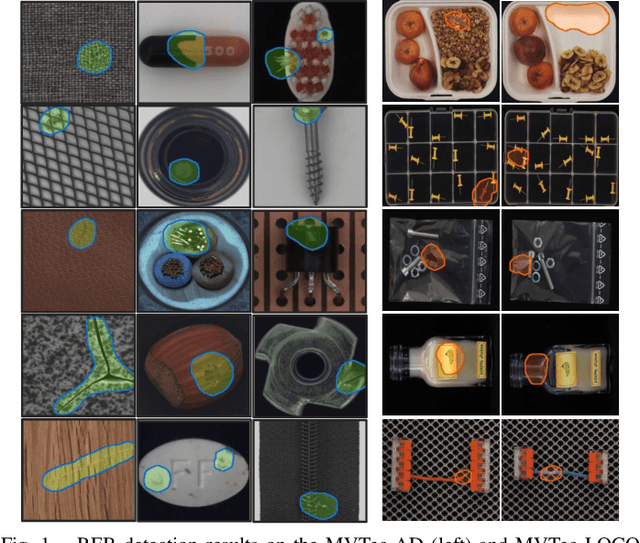
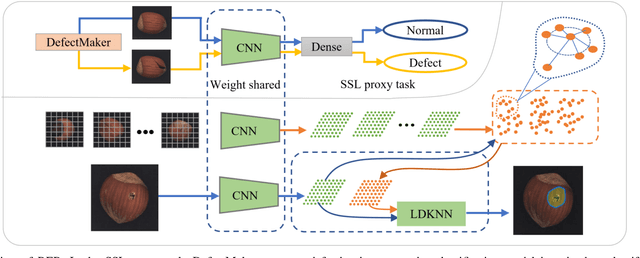
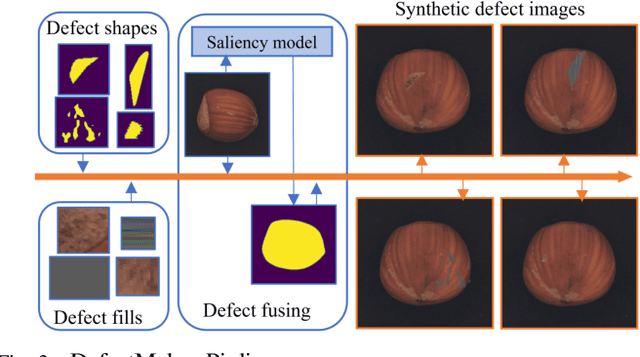
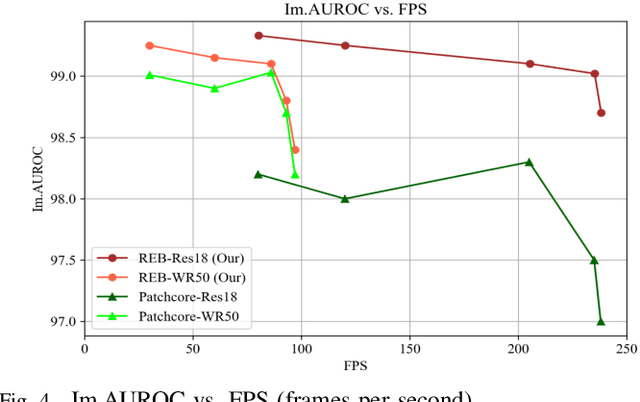
Abstract:Existing K-nearest neighbor (KNN) retrieval-based methods usually conduct industrial anomaly detection in two stages: obtain feature representations with a pre-trained CNN model and perform distance measures for defect detection. However, the features are not fully exploited as they ignore domain bias and the difference of local density in feature space, which limits the detection performance. In this paper, we propose Reducing Biases (REB) in representation by considering the domain bias of the pre-trained model and building a self-supervised learning task for better domain adaption with a defect generation strategy (DefectMaker) imitating the natural defects. Additionally, we propose a local density KNN (LDKNN) to reduce the local density bias and obtain effective anomaly detection. We achieve a promising result of 99.5\% AUROC on the widely used MVTec AD benchmark. We also achieve 88.0\% AUROC on the challenging MVTec LOCO AD dataset and bring an improvement of 4.7\% AUROC to the state-of-the-art result. All results are obtained with smaller backbone networks such as Vgg11 and Resnet18, which indicates the effectiveness and efficiency of REB for practical industrial applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge