Sukwon Yun
I2MoE: Interpretable Multimodal Interaction-aware Mixture-of-Experts
May 25, 2025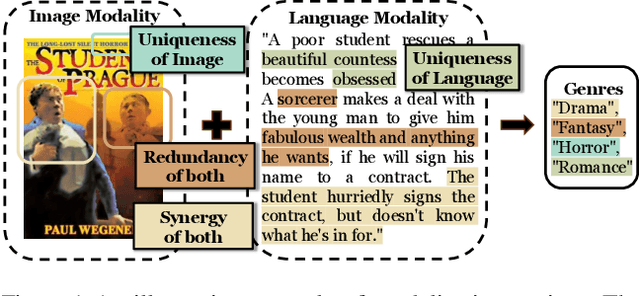
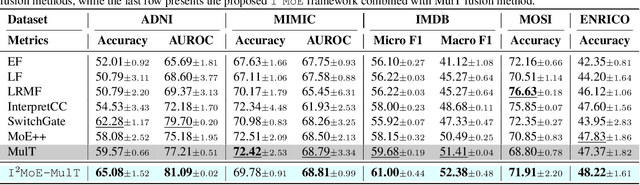

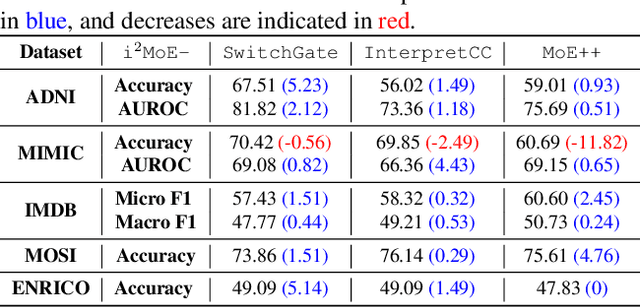
Abstract:Modality fusion is a cornerstone of multimodal learning, enabling information integration from diverse data sources. However, vanilla fusion methods are limited by (1) inability to account for heterogeneous interactions between modalities and (2) lack of interpretability in uncovering the multimodal interactions inherent in the data. To this end, we propose I2MoE (Interpretable Multimodal Interaction-aware Mixture of Experts), an end-to-end MoE framework designed to enhance modality fusion by explicitly modeling diverse multimodal interactions, as well as providing interpretation on a local and global level. First, I2MoE utilizes different interaction experts with weakly supervised interaction losses to learn multimodal interactions in a data-driven way. Second, I2MoE deploys a reweighting model that assigns importance scores for the output of each interaction expert, which offers sample-level and dataset-level interpretation. Extensive evaluation of medical and general multimodal datasets shows that I2MoE is flexible enough to be combined with different fusion techniques, consistently improves task performance, and provides interpretation across various real-world scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/Raina-Xin/I2MoE.
Efficient MAP Estimation of LLM Judgment Performance with Prior Transfer
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:LLM ensembles are widely used for LLM judges. However, how to estimate their accuracy, especially in an efficient way, is unknown. In this paper, we present a principled maximum a posteriori (MAP) framework for an economical and precise estimation of the performance of LLM ensemble judgment. We first propose a mixture of Beta-Binomial distributions to model the judgment distribution, revising from the vanilla Binomial distribution. Next, we introduce a conformal prediction-driven approach that enables adaptive stopping during iterative sampling to balance accuracy with efficiency. Furthermore, we design a prior transfer mechanism that utilizes learned distributions on open-source datasets to improve estimation on a target dataset when only scarce annotations are available. Finally, we present BetaConform, a framework that integrates our distribution assumption, adaptive stopping, and the prior transfer mechanism to deliver a theoretically guaranteed distribution estimation of LLM ensemble judgment with minimum labeled samples. BetaConform is also validated empirically. For instance, with only 10 samples from the TruthfulQA dataset, for a Llama ensembled judge, BetaConform gauges its performance with error margin as small as 3.37%.
$\textit{Agents Under Siege}$: Breaking Pragmatic Multi-Agent LLM Systems with Optimized Prompt Attacks
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Most discussions about Large Language Model (LLM) safety have focused on single-agent settings but multi-agent LLM systems now create novel adversarial risks because their behavior depends on communication between agents and decentralized reasoning. In this work, we innovatively focus on attacking pragmatic systems that have constrains such as limited token bandwidth, latency between message delivery, and defense mechanisms. We design a $\textit{permutation-invariant adversarial attack}$ that optimizes prompt distribution across latency and bandwidth-constraint network topologies to bypass distributed safety mechanisms within the system. Formulating the attack path as a problem of $\textit{maximum-flow minimum-cost}$, coupled with the novel $\textit{Permutation-Invariant Evasion Loss (PIEL)}$, we leverage graph-based optimization to maximize attack success rate while minimizing detection risk. Evaluating across models including $\texttt{Llama}$, $\texttt{Mistral}$, $\texttt{Gemma}$, $\texttt{DeepSeek}$ and other variants on various datasets like $\texttt{JailBreakBench}$ and $\texttt{AdversarialBench}$, our method outperforms conventional attacks by up to $7\times$, exposing critical vulnerabilities in multi-agent systems. Moreover, we demonstrate that existing defenses, including variants of $\texttt{Llama-Guard}$ and $\texttt{PromptGuard}$, fail to prohibit our attack, emphasizing the urgent need for multi-agent specific safety mechanisms.
Symbolic Mixture-of-Experts: Adaptive Skill-based Routing for Heterogeneous Reasoning
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Combining existing pre-trained expert LLMs is a promising avenue for scalably tackling large-scale and diverse tasks. However, selecting experts at the task level is often too coarse-grained, as heterogeneous tasks may require different expertise for each instance. To enable adaptive instance-level mixing of pre-trained LLM experts, we propose Symbolic-MoE, a symbolic, text-based, and gradient-free Mixture-of-Experts framework. Symbolic-MoE takes a fine-grained approach to selection by emphasizing skills, e.g., algebra in math or molecular biology in biomedical reasoning. We propose a skill-based recruiting strategy that dynamically selects the most relevant set of expert LLMs for diverse reasoning tasks based on their strengths. Each selected expert then generates its own reasoning, resulting in k outputs from k experts, which are then synthesized into a final high-quality response by an aggregator chosen based on its ability to integrate diverse reasoning outputs. We show that Symbolic-MoE's instance-level expert selection improves performance by a large margin but -- when implemented naively -- can introduce a high computational overhead due to the need for constant model loading and offloading. To address this, we implement a batch inference strategy that groups instances based on their assigned experts, loading each model only once. This allows us to integrate 16 expert models on 1 GPU with a time cost comparable to or better than prior multi-agent baselines using 4 GPUs. Through extensive evaluations on diverse benchmarks (MMLU-Pro, GPQA, AIME, and MedMCQA), we demonstrate that Symbolic-MoE outperforms strong LLMs like GPT4o-mini, as well as multi-agent approaches, with an absolute average improvement of 8.15% over the best multi-agent baseline. Moreover, Symbolic-MoE removes the need for expensive multi-round discussions, outperforming discussion baselines with less computation.
Subgraph Federated Learning for Local Generalization
Mar 06, 2025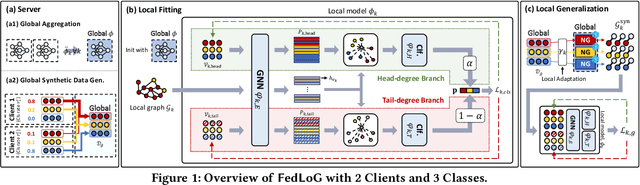
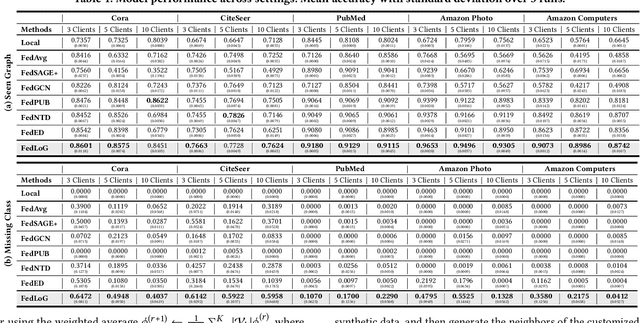
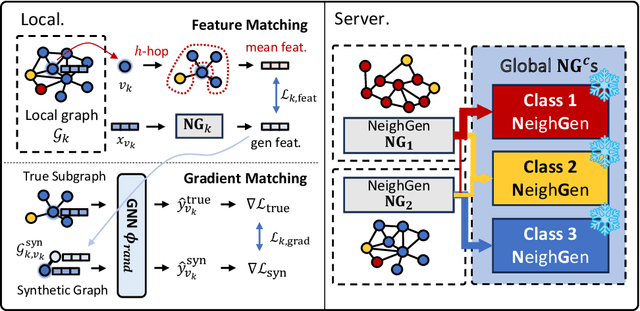
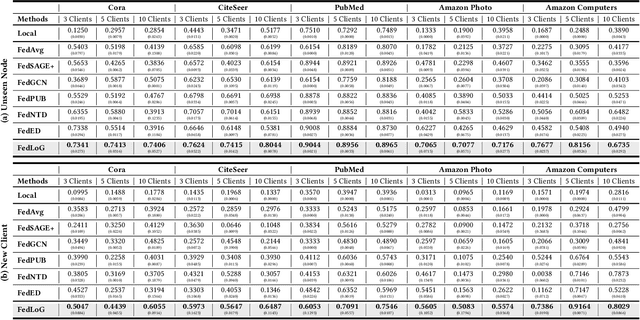
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) on graphs enables collaborative model training to enhance performance without compromising the privacy of each client. However, existing methods often overlook the mutable nature of graph data, which frequently introduces new nodes and leads to shifts in label distribution. Since they focus solely on performing well on each client's local data, they are prone to overfitting to their local distributions (i.e., local overfitting), which hinders their ability to generalize to unseen data with diverse label distributions. In contrast, our proposed method, FedLoG, effectively tackles this issue by mitigating local overfitting. Our model generates global synthetic data by condensing the reliable information from each class representation and its structural information across clients. Using these synthetic data as a training set, we alleviate the local overfitting problem by adaptively generalizing the absent knowledge within each local dataset. This enhances the generalization capabilities of local models, enabling them to handle unseen data effectively. Our model outperforms baselines in our proposed experimental settings, which are designed to measure generalization power to unseen data in practical scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/sung-won-kim/FedLoG
GRNFormer: A Biologically-Guided Framework for Integrating Gene Regulatory Networks into RNA Foundation Models
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Foundation models for single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) have shown promising capabilities in capturing gene expression patterns. However, current approaches face critical limitations: they ignore biological prior knowledge encoded in gene regulatory relationships and fail to leverage multi-omics signals that could provide complementary regulatory insights. In this paper, we propose GRNFormer, a new framework that systematically integrates multi-scale Gene Regulatory Networks (GRNs) inferred from multi-omics data into RNA foundation model training. Our framework introduces two key innovations. First, we introduce a pipeline for constructing hierarchical GRNs that capture regulatory relationships at both cell-type-specific and cell-specific resolutions. Second, we design a structure-aware integration framework that addresses the information asymmetry in GRNs through two technical advances: (1) A graph topological adapter using multi-head cross-attention to weight regulatory relationships dynamically, and (2) a novel edge perturbation strategy that perturb GRNs with biologically-informed co-expression links to augment graph neural network training. Comprehensive experiments have been conducted on three representative downstream tasks across multiple model architectures to demonstrate the effectiveness of GRNFormer. It achieves consistent improvements over state-of-the-art (SoTA) baselines: $3.6\%$ increase in drug response prediction correlation, $9.6\%$ improvement in single-cell drug classification AUC, and $1.1\%$ average gain in gene perturbation prediction accuracy.
Training Robust Graph Neural Networks by Modeling Noise Dependencies
Feb 27, 2025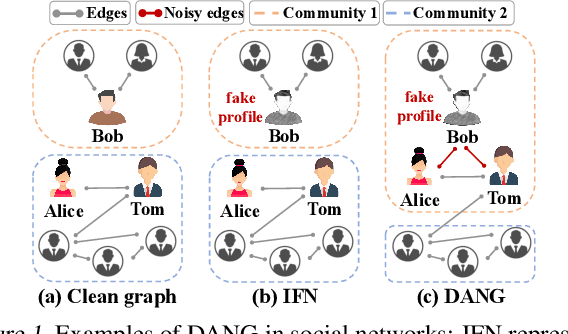
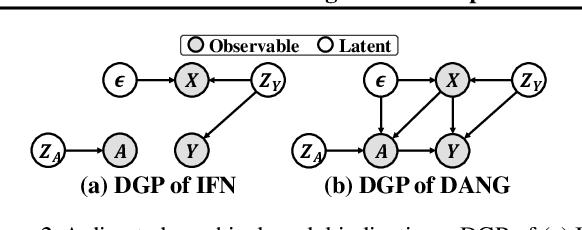
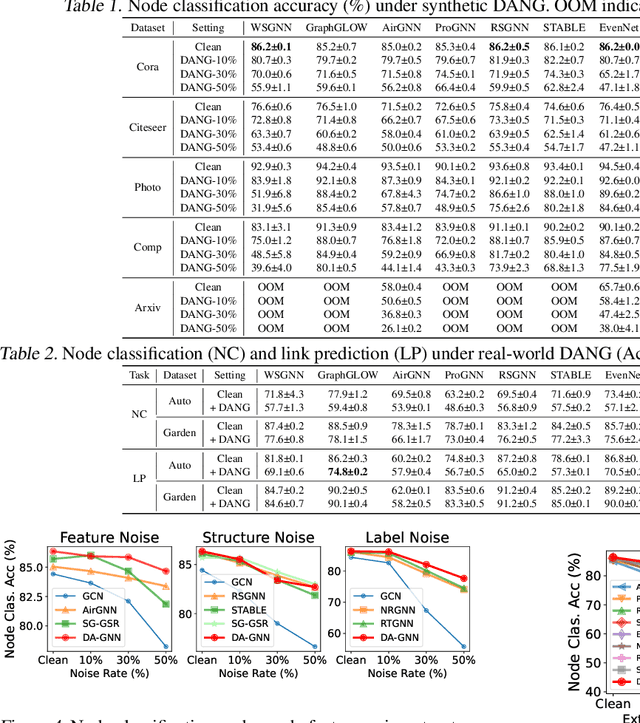
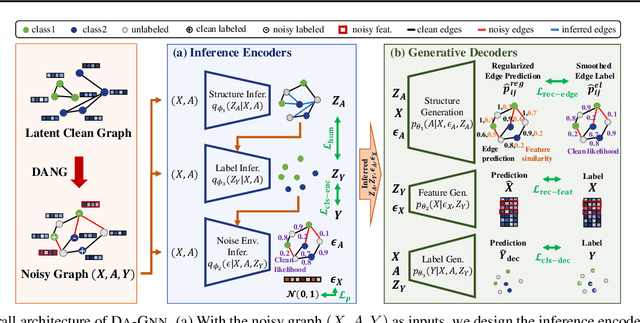
Abstract:In real-world applications, node features in graphs often contain noise from various sources, leading to significant performance degradation in GNNs. Although several methods have been developed to enhance robustness, they rely on the unrealistic assumption that noise in node features is independent of the graph structure and node labels, thereby limiting their applicability. To this end, we introduce a more realistic noise scenario, dependency-aware noise on graphs (DANG), where noise in node features create a chain of noise dependencies that propagates to the graph structure and node labels. We propose a novel robust GNN, DA-GNN, which captures the causal relationships among variables in the data generating process (DGP) of DANG using variational inference. In addition, we present new benchmark datasets that simulate DANG in real-world applications, enabling more practical research on robust GNNs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DA-GNN consistently outperforms existing baselines across various noise scenarios, including both DANG and conventional noise models commonly considered in this field.
Flex-MoE: Modeling Arbitrary Modality Combination via the Flexible Mixture-of-Experts
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Multimodal learning has gained increasing importance across various fields, offering the ability to integrate data from diverse sources such as images, text, and personalized records, which are frequently observed in medical domains. However, in scenarios where some modalities are missing, many existing frameworks struggle to accommodate arbitrary modality combinations, often relying heavily on a single modality or complete data. This oversight of potential modality combinations limits their applicability in real-world situations. To address this challenge, we propose Flex-MoE (Flexible Mixture-of-Experts), a new framework designed to flexibly incorporate arbitrary modality combinations while maintaining robustness to missing data. The core idea of Flex-MoE is to first address missing modalities using a new missing modality bank that integrates observed modality combinations with the corresponding missing ones. This is followed by a uniquely designed Sparse MoE framework. Specifically, Flex-MoE first trains experts using samples with all modalities to inject generalized knowledge through the generalized router ($\mathcal{G}$-Router). The $\mathcal{S}$-Router then specializes in handling fewer modality combinations by assigning the top-1 gate to the expert corresponding to the observed modality combination. We evaluate Flex-MoE on the ADNI dataset, which encompasses four modalities in the Alzheimer's Disease domain, as well as on the MIMIC-IV dataset. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of Flex-MoE highlighting its ability to model arbitrary modality combinations in diverse missing modality scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/flex-moe.
PortLLM: Personalizing Evolving Large Language Models with Training-Free and Portable Model Patches
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) increasingly shape the AI landscape, fine-tuning pretrained models has become more popular than in the pre-LLM era for achieving optimal performance in domain-specific tasks. However, pretrained LLMs such as ChatGPT are periodically evolved, i.e., model parameters are frequently updated), making it challenging for downstream users with limited resources to keep up with fine-tuning the newest LLMs for their domain application. Even though fine-tuning costs have nowadays been reduced thanks to the innovations of parameter-efficient fine-tuning such as LoRA, not all downstream users have adequate computing for frequent personalization. Moreover, access to fine-tuning datasets, particularly in sensitive domains such as healthcare, could be time-restrictive, making it crucial to retain the knowledge encoded in earlier fine-tuned rounds for future adaptation. In this paper, we present PortLLM, a training-free framework that (i) creates an initial lightweight model update patch to capture domain-specific knowledge, and (ii) allows a subsequent seamless plugging for the continual personalization of evolved LLM at minimal cost. Our extensive experiments cover seven representative datasets, from easier question-answering tasks {BoolQ, SST2} to harder reasoning tasks {WinoGrande, GSM8K}, and models including {Mistral-7B, Llama2, Llama3.1, and Gemma2}, validating the portability of our designed model patches and showcasing the effectiveness of our proposed framework. For instance, PortLLM achieves comparable performance to LoRA fine-tuning with reductions of up to 12.2x in GPU memory usage. Finally, we provide theoretical justifications to understand the portability of our model update patches, which offers new insights into the theoretical dimension of LLMs' personalization.
Cut the Crap: An Economical Communication Pipeline for LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language model (LLM)-powered agents have shown that collective intelligence can significantly outperform individual capabilities, largely attributed to the meticulously designed inter-agent communication topologies. Though impressive in performance, existing multi-agent pipelines inherently introduce substantial token overhead, as well as increased economic costs, which pose challenges for their large-scale deployments. In response to this challenge, we propose an economical, simple, and robust multi-agent communication framework, termed $\texttt{AgentPrune}$, which can seamlessly integrate into mainstream multi-agent systems and prunes redundant or even malicious communication messages. Technically, $\texttt{AgentPrune}$ is the first to identify and formally define the \textit{communication redundancy} issue present in current LLM-based multi-agent pipelines, and efficiently performs one-shot pruning on the spatial-temporal message-passing graph, yielding a token-economic and high-performing communication topology. Extensive experiments across six benchmarks demonstrate that $\texttt{AgentPrune}$ \textbf{(I)} achieves comparable results as state-of-the-art topologies at merely $\$5.6$ cost compared to their $\$43.7$, \textbf{(II)} integrates seamlessly into existing multi-agent frameworks with $28.1\%\sim72.8\%\downarrow$ token reduction, and \textbf{(III)} successfully defend against two types of agent-based adversarial attacks with $3.5\%\sim10.8\%\uparrow$ performance boost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge