Yanpei Shi
Swin-BERT: A Feature Fusion System designed for Speech-based Alzheimer's Dementia Detection
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Speech is usually used for constructing an automatic Alzheimer's dementia (AD) detection system, as the acoustic and linguistic abilities show a decline in people living with AD at the early stages. However, speech includes not only AD-related local and global information but also other information unrelated to cognitive status, such as age and gender. In this paper, we propose a speech-based system named Swin-BERT for automatic dementia detection. For the acoustic part, the shifted windows multi-head attention that proposed to extract local and global information from images, is used for designing our acoustic-based system. To decouple the effect of age and gender on acoustic feature extraction, they are used as an extra input of the designed acoustic system. For the linguistic part, the rhythm-related information, which varies significantly between people living with and without AD, is removed while transcribing the audio recordings into transcripts. To compensate for the removed rhythm-related information, the character-level transcripts are proposed to be used as the extra input of a word-level BERT-style system. Finally, the Swin-BERT combines the acoustic features learned from our proposed acoustic-based system with our linguistic-based system. The experiments are based on the two datasets provided by the international dementia detection challenges: the ADReSS and ADReSSo. The results show that both the proposed acoustic and linguistic systems can be better or comparable with previous research on the two datasets. Superior results are achieved by the proposed Swin-BERT system on the ADReSS and ADReSSo datasets, which are 85.58\% F-score and 87.32\% F-score respectively.
T-vectors: Weakly Supervised Speaker Identification Using Hierarchical Transformer Model
Oct 29, 2020



Abstract:Identifying multiple speakers without knowing where a speaker's voice is in a recording is a challenging task. This paper proposes a hierarchical network with transformer encoders and memory mechanism to address this problem. The proposed model contains a frame-level encoder and segment-level encoder, both of them make use of the transformer encoder block. The multi-head attention mechanism in the transformer structure could better capture different speaker properties when the input utterance contains multiple speakers. The memory mechanism used in the frame-level encoders can build a recurrent connection that better capture long-term speaker features. The experiments are conducted on artificial datasets based on the Switchboard Cellular part1 (SWBC) and Voxceleb1 datasets. In different data construction scenarios (Concat and Overlap), the proposed model shows better performance comparaing with four strong baselines, reaching 13.3% and 10.5% relative improvement compared with H-vectors and S-vectors. The use of memory mechanism could reach 10.6% and 7.7% relative improvement compared with not using memory mechanism.
Speaker Re-identification with Speaker Dependent Speech Enhancement
May 15, 2020



Abstract:While the use of deep neural networks has significantly boosted speaker recognition performance, it is still challenging to separate speakers in poor acoustic environments. Here speech enhancement methods have traditionally allowed improved performance. The recent works have shown that adapting speech enhancement can lead to further gains. This paper introduces a novel approach that cascades speech enhancement and speaker recognition. In the first step, a speaker embedding vector is generated , which is used in the second step to enhance the speech quality and re-identify the speakers. Models are trained in an integrated framework with joint optimisation. The proposed approach is evaluated using the Voxceleb1 dataset, which aims to assess speaker recognition in real world situations. In addition three types of noise at different signal-noise-ratios were added for this work. The obtained results show that the proposed approach using speaker dependent speech enhancement can yield better speaker recognition and speech enhancement performances than two baselines in various noise conditions.
Weakly Supervised Training of Hierarchical Attention Networks for Speaker Identification
May 15, 2020



Abstract:Identifying multiple speakers without knowing where a speaker's voice is in a recording is a challenging task. In this paper, a hierarchical attention network is proposed to solve a weakly labelled speaker identification problem. The use of a hierarchical structure, consisting of a frame-level encoder and a segment-level encoder, aims to learn speaker related information locally and globally. Speech streams are segmented into fragments. The frame-level encoder with attention learns features and highlights the target related frames locally, and output a fragment based embedding. The segment-level encoder works with a second attention layer to emphasize the fragments probably related to target speakers. The global information is finally collected from segment-level module to predict speakers via a classifier. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, artificial datasets based on Switchboard Cellular part1 (SWBC) and Voxceleb1 are constructed in two conditions, where speakers' voices are overlapped and not overlapped. Comparing to two baselines the obtained results show that the proposed approach can achieve better performances. Moreover, further experiments are conducted to evaluate the impact of utterance segmentation. The results show that a reasonable segmentation can slightly improve identification performances.
Supervised Speaker Embedding De-Mixing in Two-Speaker Environment
Jan 14, 2020
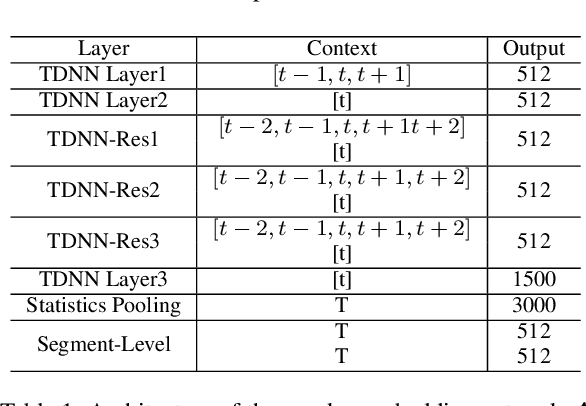


Abstract:In this work, a speaker embedding de-mixing approach is proposed. Instead of separating two-speaker signal in signal space like speech source separation, the proposed approach separates different speaker properties from two-speaker signal in embedding space. The proposed approach contains two steps. In step one, the clean speaker embeddings are learned and collected by a residual TDNN based network. In step two, the two-speaker signal and the embedding of one of the speakers are input to a speaker embedding de-mixing network. The de-mixing network is trained to generate the embedding of the other speaker of the by reconstruction loss. Speaker identification accuracy on the de-mixed speaker embeddings is used to evaluate the quality of the obtained embeddings. Experiments are done in two kind of data: artificial augmented two-speaker data (TIMIT) and real world recording of two-speaker data (MC-WSJ). Six diffident speaker embedding de-mixing architectures are investigated. Comparing with the speaker identification accuracy on the clean speaker embeddings (98.5%), the obtained results show that one of the speaker embedding de-mixing architectures obtain close performance, reaching 96.9% test accuracy on TIMIT when the SNR between the target speaker and interfering speaker is 5 dB. More surprisingly, we found choosing a simple subtraction as the embedding de-mixing function could obtain the second best performance, reaching 95.2% test accuracy.
Robust Speaker Recognition Using Speech Enhancement And Attention Model
Jan 14, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, a novel architecture for speaker recognition is proposed by cascading speech enhancement and speaker processing. Its aim is to improve speaker recognition performance when speech signals are corrupted by noise. Instead of individually processing speech enhancement and speaker recognition, the two modules are integrated into one framework by a joint optimisation using deep neural networks. Furthermore, to increase robustness against noise, a multi-stage attention mechanism is employed to highlight the speaker related features learned from context information in time and frequency domain. To evaluate speaker identification and verification performance of the proposed approach, we test it on the dataset of VoxCeleb1, one of mostly used benchmark datasets. Moreover, the robustness of our proposed approach is also tested on VoxCeleb1 data when being corrupted by three types of interferences, general noise, music, and babble, at different signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels. The obtained results show that the proposed approach using speech enhancement and multi-stage attention models outperforms two strong baselines not using them in most acoustic conditions in our experiments.
H-VECTORS: Utterance-level Speaker Embedding Using A Hierarchical Attention Model
Oct 19, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, a hierarchical attention network to generate utterance-level embeddings (H-vectors) for speaker identification is proposed. Since different parts of an utterance may have different contributions to speaker identities, the use of hierarchical structure aims to learn speaker related information locally and globally. In the proposed approach, frame-level encoder and attention are applied on segments of an input utterance and generate individual segment vectors. Then, segment level attention is applied on the segment vectors to construct an utterance representation. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, NIST SRE 2008 Part1 dataset is used for training, and two datasets, Switchboard Cellular part1 and CallHome American English Speech, are used to evaluate the quality of extracted utterance embeddings on speaker identification and verification tasks. In comparison with two baselines, X-vector, X-vector+Attention, the obtained results show that H-vectors can achieve a significantly better performance. Furthermore, the extracted utterance-level embeddings are more discriminative than the two baselines when mapped into a 2D space using t-SNE.
Contextual Joint Factor Acoustic Embeddings
Oct 16, 2019



Abstract:Embedding acoustic information into fixed length representations is of interest for a whole range of applications in speech and audio technology. We propose two novel unsupervised approaches to generate acoustic embeddings by modelling of acoustic context. The first approach is a contextual joint factor synthesis encoder, where the encoder in an encoder/decoder framework is trained to extract joint factors from surrounding audio frames to best generate the target output. The second approach is a contextual joint factor analysis encoder, where the encoder is trained to analyse joint factors from the source signal that correlates best with the neighbouring audio. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approaches compared to prior work, we chose two tasks - phone classification and speaker recognition - and test on different TIMIT data sets. Experimental results show that one of our proposed approaches outperforms phone classification baselines, yielding a classification accuracy of 74.1%. When using additional out-of-domain data for training, an additional 2-3% improvements can be obtained, for both for phone classification and speaker recognition tasks.
Improving Robustness In Speaker Identification Using A Two-Stage Attention Model
Sep 24, 2019



Abstract:In this paper a novel framework to tackle speaker recognition using a two-stage attention model is proposed. In recent years, the use of deep neural networks, such as time delay neural network (TDNN), and attention model have boosted speaker recognition performance. However, it is still a challenging task to tackle speaker recognition in severe acoustic environments. To build a robust speaker recognition system against noise, we employ a two-stage attention model and combine it with a TDNN model. In this framework, the attention mechanism is used in two aspects: embedding space and temporal space. The embedding attention model built in embedding space is to highlight the importance of each embedding element by weighting them using self attention. The frame attention model built in temporal space aims to find which frames are significant for speaker recognition. To evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of our approach, we use the TIMIT dataset and test our approach in the condition of five kinds of noise and different signal-noise-ratios (SNRs). In comparison with three strong baselines, CNN, TDNN and TDNN+attention, the experimental results show that the use of our approach outperforms them in different conditions. The correct recognition rate obtained using our approach can still reach 49.1%, better than any baselines, even if the noise is Gaussian white Noise and the SNR is 0dB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge