Supervised Speaker Embedding De-Mixing in Two-Speaker Environment
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2020
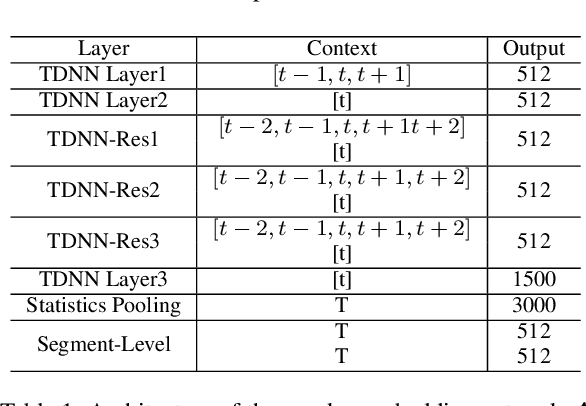


In this work, a speaker embedding de-mixing approach is proposed. Instead of separating two-speaker signal in signal space like speech source separation, the proposed approach separates different speaker properties from two-speaker signal in embedding space. The proposed approach contains two steps. In step one, the clean speaker embeddings are learned and collected by a residual TDNN based network. In step two, the two-speaker signal and the embedding of one of the speakers are input to a speaker embedding de-mixing network. The de-mixing network is trained to generate the embedding of the other speaker of the by reconstruction loss. Speaker identification accuracy on the de-mixed speaker embeddings is used to evaluate the quality of the obtained embeddings. Experiments are done in two kind of data: artificial augmented two-speaker data (TIMIT) and real world recording of two-speaker data (MC-WSJ). Six diffident speaker embedding de-mixing architectures are investigated. Comparing with the speaker identification accuracy on the clean speaker embeddings (98.5%), the obtained results show that one of the speaker embedding de-mixing architectures obtain close performance, reaching 96.9% test accuracy on TIMIT when the SNR between the target speaker and interfering speaker is 5 dB. More surprisingly, we found choosing a simple subtraction as the embedding de-mixing function could obtain the second best performance, reaching 95.2% test accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge