Bingshen Mu
LLM-ForcedAligner: A Non-Autoregressive and Accurate LLM-Based Forced Aligner for Multilingual and Long-Form Speech
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Forced alignment (FA) predicts start and end timestamps for words or characters in speech, but existing methods are language-specific and prone to cumulative temporal shifts. The multilingual speech understanding and long-sequence processing abilities of speech large language models (SLLMs) make them promising for FA in multilingual, crosslingual, and long-form speech settings. However, directly applying the next-token prediction paradigm of SLLMs to FA results in hallucinations and slow inference. To bridge the gap, we propose LLM-ForcedAligner, reformulating FA as a slot-filling paradigm: timestamps are treated as discrete indices, and special timestamp tokens are inserted as slots into the transcript. Conditioned on the speech embeddings and the transcript with slots, the SLLM directly predicts the time indices at slots. During training, causal attention masking with non-shifted input and label sequences allows each slot to predict its own timestamp index based on itself and preceding context, with loss computed only at slot positions. Dynamic slot insertion enables FA at arbitrary positions. Moreover, non-autoregressive inference is supported, avoiding hallucinations and improving speed. Experiments across multilingual, crosslingual, and long-form speech scenarios show that LLM-ForcedAligner achieves a 69%~78% relative reduction in accumulated averaging shift compared with prior methods. The checkpoint and inference code will be released later.
dLLM-ASR: A Faster Diffusion LLM-based Framework for Speech Recognition
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems based on large language models (LLMs) achieve superior performance by leveraging pretrained LLMs as decoders, but their token-by-token generation mechanism leads to inference latency that grows linearly with sequence length. Meanwhile, discrete diffusion large language models (dLLMs) offer a promising alternative, enabling high-quality parallel sequence generation with pretrained decoders. However, directly applying native text-oriented dLLMs to ASR leads to a fundamental mismatch between open-ended text generation and the acoustically conditioned transcription paradigm required by ASR. As a result, it introduces unnecessary difficulty and computational redundancy, such as denoising from pure noise, inflexible generation lengths, and fixed denoising steps. We propose dLLM-ASR, an efficient dLLM-based ASR framework that formulates dLLM's decoding as a prior-guided and adaptive denoising process. It leverages an ASR prior to initialize the denoising process and provide an anchor for sequence length. Building upon this prior, length-adaptive pruning dynamically removes redundant tokens, while confidence-based denoising allows converged tokens to exit the denoising loop early, enabling token-level adaptive computation. Experiments demonstrate that dLLM-ASR achieves recognition accuracy comparable to autoregressive LLM-based ASR systems and delivers a 4.44$\times$ inference speedup, establishing a practical and efficient paradigm for ASR.
WenetSpeech-Wu: Datasets, Benchmarks, and Models for a Unified Chinese Wu Dialect Speech Processing Ecosystem
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Speech processing for low-resource dialects remains a fundamental challenge in developing inclusive and robust speech technologies. Despite its linguistic significance and large speaker population, the Wu dialect of Chinese has long been hindered by the lack of large-scale speech data, standardized evaluation benchmarks, and publicly available models. In this work, we present WenetSpeech-Wu, the first large-scale, multi-dimensionally annotated open-source speech corpus for the Wu dialect, comprising approximately 8,000 hours of diverse speech data. Building upon this dataset, we introduce WenetSpeech-Wu-Bench, the first standardized and publicly accessible benchmark for systematic evaluation of Wu dialect speech processing, covering automatic speech recognition (ASR), Wu-to-Mandarin translation, speaker attribute prediction, speech emotion recognition, text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis, and instruction-following TTS (instruct TTS). Furthermore, we release a suite of strong open-source models trained on WenetSpeech-Wu, establishing competitive performance across multiple tasks and empirically validating the effectiveness of the proposed dataset. Together, these contributions lay the foundation for a comprehensive Wu dialect speech processing ecosystem, and we open-source proposed datasets, benchmarks, and models to support future research on dialectal speech intelligence.
Efficient Scaling for LLM-based ASR
Aug 06, 2025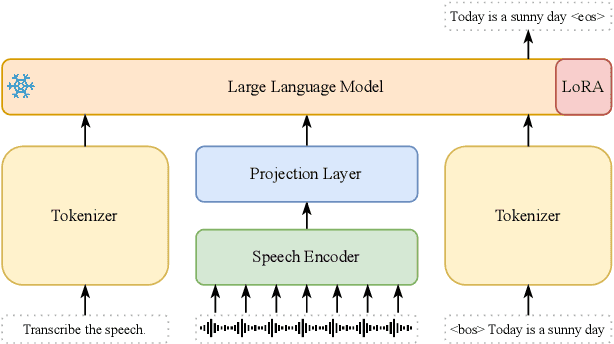
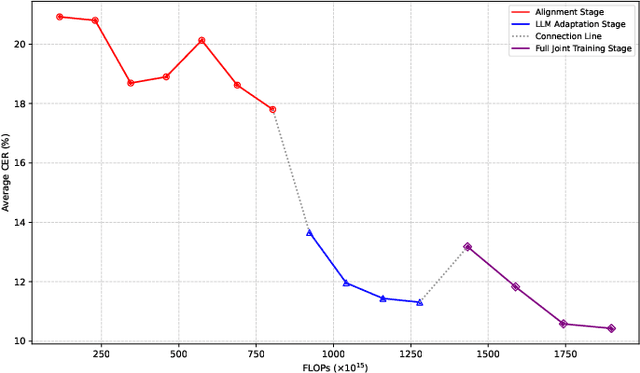
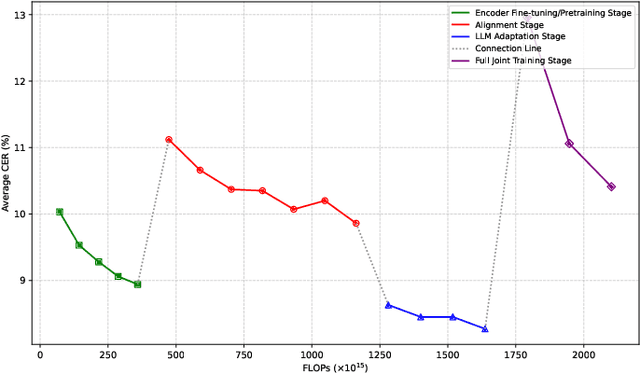
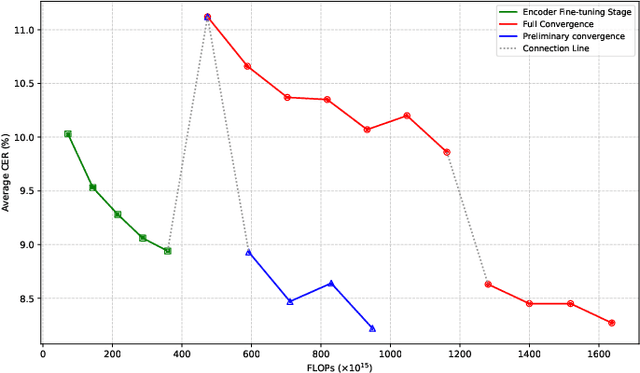
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) achieves strong performance but often incurs high computational costs. This work investigates how to obtain the best LLM-ASR performance efficiently. Through comprehensive and controlled experiments, we find that pretraining the speech encoder before integrating it with the LLM leads to significantly better scaling efficiency than the standard practice of joint post-training of LLM-ASR. Based on this insight, we propose a new multi-stage LLM-ASR training strategy, EFIN: Encoder First Integration. Among all training strategies evaluated, EFIN consistently delivers better performance (relative to 21.1% CERR) with significantly lower computation budgets (49.9% FLOPs). Furthermore, we derive a scaling law that approximates ASR error rates as a computation function, providing practical guidance for LLM-ASR scaling.
Weakly Supervised Data Refinement and Flexible Sequence Compression for Efficient Thai LLM-based ASR
May 28, 2025Abstract:Despite remarkable achievements, automatic speech recognition (ASR) in low-resource scenarios still faces two challenges: high-quality data scarcity and high computational demands. This paper proposes EThai-ASR, the first to apply large language models (LLMs) to Thai ASR and create an efficient LLM-based ASR system. EThai-ASR comprises a speech encoder, a connection module and a Thai LLM decoder. To address the data scarcity and obtain a powerful speech encoder, EThai-ASR introduces a self-evolving data refinement strategy to refine weak labels, yielding an enhanced speech encoder. Moreover, we propose a pluggable sequence compression module used in the connection module with three modes designed to reduce the sequence length, thus decreasing computational demands while maintaining decent performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EThai-ASR has achieved state-of-the-art accuracy in multiple datasets. We release our refined text transcripts to promote further research.
HDMoLE: Mixture of LoRA Experts with Hierarchical Routing and Dynamic Thresholds for Fine-Tuning LLM-based ASR Models
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in integrating Large Language Models (LLM) with automatic speech recognition (ASR) have performed remarkably in general domains. While supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of all model parameters is often employed to adapt pre-trained LLM-based ASR models to specific domains, it imposes high computational costs and notably reduces their performance in general domains. In this paper, we propose a novel parameter-efficient multi-domain fine-tuning method for adapting pre-trained LLM-based ASR models to multi-accent domains without catastrophic forgetting named \textit{HDMoLE}, which leverages hierarchical routing and dynamic thresholds based on combining low-rank adaptation (LoRA) with the mixer of experts (MoE) and can be generalized to any linear layer. Hierarchical routing establishes a clear correspondence between LoRA experts and accent domains, improving cross-domain collaboration among the LoRA experts. Unlike the static Top-K strategy for activating LoRA experts, dynamic thresholds can adaptively activate varying numbers of LoRA experts at each MoE layer. Experiments on the multi-accent and standard Mandarin datasets demonstrate the efficacy of HDMoLE. Applying HDMoLE to an LLM-based ASR model projector module achieves similar performance to full fine-tuning in the target multi-accent domains while using only 9.6% of the trainable parameters required for full fine-tuning and minimal degradation in the source general domain.
Unveiling the Potential of LLM-Based ASR on Chinese Open-Source Datasets
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated unparalleled effectiveness in various NLP tasks, and integrating LLMs with automatic speech recognition (ASR) is becoming a mainstream paradigm. Building upon this momentum, our research delves into an in-depth examination of this paradigm on a large open-source Chinese dataset. Specifically, our research aims to evaluate the impact of various configurations of speech encoders, LLMs, and projector modules in the context of the speech foundation encoder-LLM ASR paradigm. Furthermore, we introduce a three-stage training approach, expressly developed to enhance the model's ability to align auditory and textual information. The implementation of this approach, alongside the strategic integration of ASR components, enabled us to achieve the SOTA performance on the AISHELL-1, Test_Net, and Test_Meeting test sets. Our analysis presents an empirical foundation for future research in LLM-based ASR systems and offers insights into optimizing performance using Chinese datasets. We will publicly release all scripts used for data preparation, training, inference, and scoring, as well as pre-trained models and training logs to promote reproducible research.
MMGER: Multi-modal and Multi-granularity Generative Error Correction with LLM for Joint Accent and Speech Recognition
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Despite notable advancements in automatic speech recognition (ASR), performance tends to degrade when faced with adverse conditions. Generative error correction (GER) leverages the exceptional text comprehension capabilities of large language models (LLM), delivering impressive performance in ASR error correction, where N-best hypotheses provide valuable information for transcription prediction. However, GER encounters challenges such as fixed N-best hypotheses, insufficient utilization of acoustic information, and limited specificity to multi-accent scenarios. In this paper, we explore the application of GER in multi-accent scenarios. Accents represent deviations from standard pronunciation norms, and the multi-task learning framework for simultaneous ASR and accent recognition (AR) has effectively addressed the multi-accent scenarios, making it a prominent solution. In this work, we propose a unified ASR-AR GER model, named MMGER, leveraging multi-modal correction, and multi-granularity correction. Multi-task ASR-AR learning is employed to provide dynamic 1-best hypotheses and accent embeddings. Multi-modal correction accomplishes fine-grained frame-level correction by force-aligning the acoustic features of speech with the corresponding character-level 1-best hypothesis sequence. Multi-granularity correction supplements the global linguistic information by incorporating regular 1-best hypotheses atop fine-grained multi-modal correction to achieve coarse-grained utterance-level correction. MMGER effectively mitigates the limitations of GER and tailors LLM-based ASR error correction for the multi-accent scenarios. Experiments conducted on the multi-accent Mandarin KeSpeech dataset demonstrate the efficacy of MMGER, achieving a 26.72% relative improvement in AR accuracy and a 27.55% relative reduction in ASR character error rate, compared to a well-established standard baseline.
E-chat: Emotion-sensitive Spoken Dialogue System with Large Language Models
Jan 06, 2024



Abstract:This study focuses on emotion-sensitive spoken dialogue in human-machine speech interaction. With the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), dialogue systems can handle multimodal data, including audio. Recent models have enhanced the understanding of complex audio signals through the integration of various audio events. However, they are unable to generate appropriate responses based on emotional speech. To address this, we introduce the Emotional chat Model (E-chat), a novel spoken dialogue system capable of comprehending and responding to emotions conveyed from speech. This model leverages an emotion embedding extracted by a speech encoder, combined with LLMs, enabling it to respond according to different emotional contexts. Additionally, we introduce the E-chat200 dataset, designed explicitly for emotion-sensitive spoken dialogue. In various evaluation metrics, E-chat consistently outperforms baseline LLMs, demonstrating its potential in emotional comprehension and human-machine interaction.
Automatic channel selection and spatial feature integration for multi-channel speech recognition across various array topologies
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has shown remarkable progress, yet it still faces challenges in real-world distant scenarios across various array topologies each with multiple recording devices. The focal point of the CHiME-7 Distant ASR task is to devise a unified system capable of generalizing various array topologies that have multiple recording devices and offering reliable recognition performance in real-world environments. Addressing this task, we introduce an ASR system that demonstrates exceptional performance across various array topologies. First of all, we propose two attention-based automatic channel selection modules to select the most advantageous subset of multi-channel signals from multiple recording devices for each utterance. Furthermore, we introduce inter-channel spatial features to augment the effectiveness of multi-frame cross-channel attention, aiding it in improving the capability of spatial information awareness. Finally, we propose a multi-layer convolution fusion module drawing inspiration from the U-Net architecture to integrate the multi-channel output into a single-channel output. Experimental results on the CHiME-7 corpus with oracle segmentation demonstrate that the improvements introduced in our proposed ASR system lead to a relative reduction of 40.1% in the Macro Diarization Attributed Word Error Rates (DA-WER) when compared to the baseline ASR system on the Eval sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge