Yuhao Liang
E-chat: Emotion-sensitive Spoken Dialogue System with Large Language Models
Jan 06, 2024



Abstract:This study focuses on emotion-sensitive spoken dialogue in human-machine speech interaction. With the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), dialogue systems can handle multimodal data, including audio. Recent models have enhanced the understanding of complex audio signals through the integration of various audio events. However, they are unable to generate appropriate responses based on emotional speech. To address this, we introduce the Emotional chat Model (E-chat), a novel spoken dialogue system capable of comprehending and responding to emotions conveyed from speech. This model leverages an emotion embedding extracted by a speech encoder, combined with LLMs, enabling it to respond according to different emotional contexts. Additionally, we introduce the E-chat200 dataset, designed explicitly for emotion-sensitive spoken dialogue. In various evaluation metrics, E-chat consistently outperforms baseline LLMs, demonstrating its potential in emotional comprehension and human-machine interaction.
SA-Paraformer: Non-autoregressive End-to-End Speaker-Attributed ASR
Oct 07, 2023



Abstract:Joint modeling of multi-speaker ASR and speaker diarization has recently shown promising results in speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (SA-ASR).Although being able to obtain state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, most of the studies are based on an autoregressive (AR) decoder which generates tokens one-by-one and results in a large real-time factor (RTF). To speed up inference, we introduce a recently proposed non-autoregressive model Paraformer as an acoustic model in the SA-ASR model.Paraformer uses a single-step decoder to enable parallel generation, obtaining comparable performance to the SOTA AR transformer models. Besides, we propose a speaker-filling strategy to reduce speaker identification errors and adopt an inter-CTC strategy to enhance the encoder's ability in acoustic modeling. Experiments on the AliMeeting corpus show that our model outperforms the cascaded SA-ASR model by a 6.1% relative speaker-dependent character error rate (SD-CER) reduction on the test set. Moreover, our model achieves a comparable SD-CER of 34.8% with only 1/10 RTF compared with the SOTA joint AR SA-ASR model.
The second multi-channel multi-party meeting transcription challenge 2.0): A benchmark for speaker-attributed ASR
Sep 24, 2023



Abstract:With the success of the first Multi-channel Multi-party Meeting Transcription challenge (M2MeT), the second M2MeT challenge (M2MeT 2.0) held in ASRU2023 particularly aims to tackle the complex task of speaker-attributed ASR (SA-ASR), which directly addresses the practical and challenging problem of "who spoke what at when" at typical meeting scenario. We particularly established two sub-tracks. 1) The fixed training condition sub-track, where the training data is constrained to predetermined datasets, but participants can use any open-source pre-trained model. 2) The open training condition sub-track, which allows for the use of all available data and models. In addition, we release a new 10-hour test set for challenge ranking. This paper provides an overview of the dataset, track settings, results, and analysis of submitted systems, as a benchmark to show the current state of speaker-attributed ASR.
BA-SOT: Boundary-Aware Serialized Output Training for Multi-Talker ASR
May 23, 2023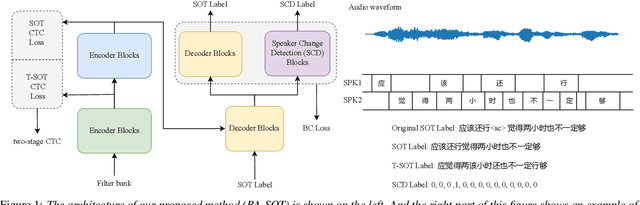
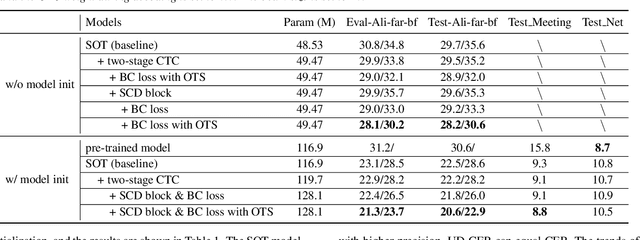
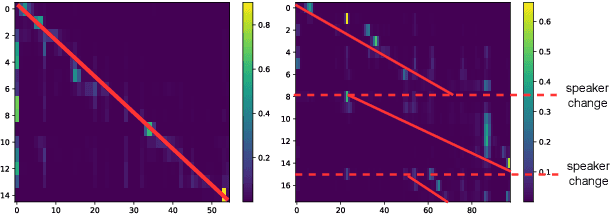
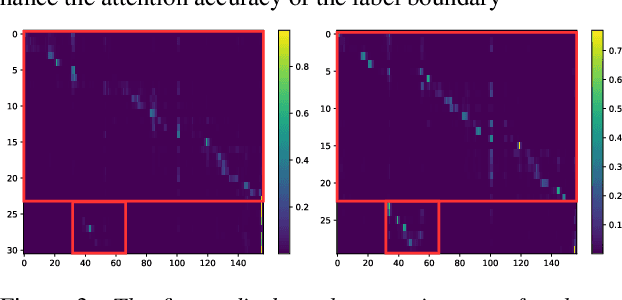
Abstract:The recently proposed serialized output training (SOT) simplifies multi-talker automatic speech recognition (ASR) by generating speaker transcriptions separated by a special token. However, frequent speaker changes can make speaker change prediction difficult. To address this, we propose boundary-aware serialized output training (BA-SOT), which explicitly incorporates boundary knowledge into the decoder via a speaker change detection task and boundary constraint loss. We also introduce a two-stage connectionist temporal classification (CTC) strategy that incorporates token-level SOT CTC to restore temporal context information. Besides typical character error rate (CER), we introduce utterance-dependent character error rate (UD-CER) to further measure the precision of speaker change prediction. Compared to original SOT, BA-SOT reduces CER/UD-CER by 5.1%/14.0%, and leveraging a pre-trained ASR model for BA-SOT model initialization further reduces CER/UD-CER by 8.4%/19.9%.
The NPU-ASLP System for The ISCSLP 2022 Magichub Code-Swiching ASR Challenge
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:This paper describes our NPU-ASLP system submitted to the ISCSLP 2022 Magichub Code-Switching ASR Challenge. In this challenge, we first explore several popular end-to-end ASR architectures and training strategies, including bi-encoder, language-aware encoder (LAE) and mixture of experts (MoE). To improve our system's language modeling ability, we further attempt the internal language model as well as the long context language model. Given the limited training data in the challenge, we further investigate the effects of data augmentation, including speed perturbation, pitch shifting, speech codec, SpecAugment and synthetic data from text-to-speech (TTS). Finally, we explore ROVER-based score fusion to make full use of complementary hypotheses from different models. Our submitted system achieves 16.87% on mix error rate (MER) on the test set and comes to the 2nd place in the challenge ranking.
MFCCA:Multi-Frame Cross-Channel attention for multi-speaker ASR in Multi-party meeting scenario
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Recently cross-channel attention, which better leverages multi-channel signals from microphone array, has shown promising results in the multi-party meeting scenario. Cross-channel attention focuses on either learning global correlations between sequences of different channels or exploiting fine-grained channel-wise information effectively at each time step. Considering the delay of microphone array receiving sound, we propose a multi-frame cross-channel attention, which models cross-channel information between adjacent frames to exploit the complementarity of both frame-wise and channel-wise knowledge. Besides, we also propose a multi-layer convolutional mechanism to fuse the multi-channel output and a channel masking strategy to combat the channel number mismatch problem between training and inference. Experiments on the AliMeeting, a real-world corpus, reveal that our proposed model outperforms single-channel model by 31.7\% and 37.0\% CER reduction on Eval and Test sets. Moreover, with comparable model parameters and training data, our proposed model achieves a new SOTA performance on the AliMeeting corpus, as compared with the top ranking systems in the ICASSP2022 M2MeT challenge, a recently held multi-channel multi-speaker ASR challenge.
NWPU-ASLP System for the VoicePrivacy 2022 Challenge
Sep 24, 2022



Abstract:This paper presents the NWPU-ASLP speaker anonymization system for VoicePrivacy 2022 Challenge. Our submission does not involve additional Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) model or x-vector pool. Our system consists of four modules, including feature extractor, acoustic model, anonymization module, and neural vocoder. First, the feature extractor extracts the Phonetic Posteriorgram (PPG) and pitch from the input speech signal. Then, we reserve a pseudo speaker ID from a speaker look-up table (LUT), which is subsequently fed into a speaker encoder to generate the pseudo speaker embedding that is not corresponding to any real speaker. To ensure the pseudo speaker is distinguishable, we further average the randomly selected speaker embedding and weighted concatenate it with the pseudo speaker embedding to generate the anonymized speaker embedding. Finally, the acoustic model outputs the anonymized mel-spectrogram from the anonymized speaker embedding and a modified version of HifiGAN transforms the mel-spectrogram into the anonymized speech waveform. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed anonymization system.
Boundary and Context Aware Training for CIF-based Non-Autoregressive End-to-end ASR
Apr 10, 2021Abstract:Continuous integrate-and-fire (CIF) based models, which use a soft and monotonic alignment mechanism, have been well applied in non-autoregressive (NAR) speech recognition and achieved competitive performance compared with other NAR methods. However, such an alignment learning strategy may also result in inaccurate acoustic boundary estimation and deceleration in convergence speed. To eliminate these drawbacks and improve performance further, we incorporate an additional connectionist temporal classification (CTC) based alignment loss and a contextual decoder into the CIF-based NAR model. Specifically, we use the CTC spike information to guide the leaning of acoustic boundary and adopt a new contextual decoder to capture the linguistic dependencies within a sentence in the conventional CIF model. Besides, a recently proposed Conformer architecture is also employed to model both local and global acoustic dependencies. Experiments on the open-source Mandarin corpora AISHELL-1 show that the proposed method achieves a comparable character error rate (CER) of 4.9% with only 1/24 latency compared with a state-of-the-art autoregressive (AR) Conformer model.
The Accented English Speech Recognition Challenge 2020: Open Datasets, Tracks, Baselines, Results and Methods
Feb 20, 2021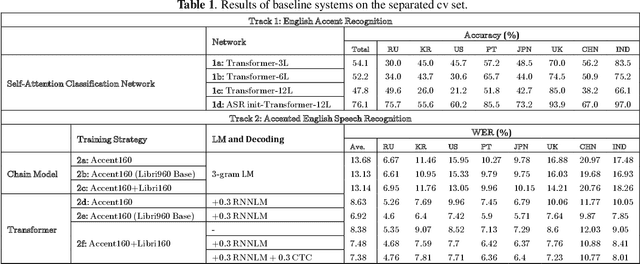
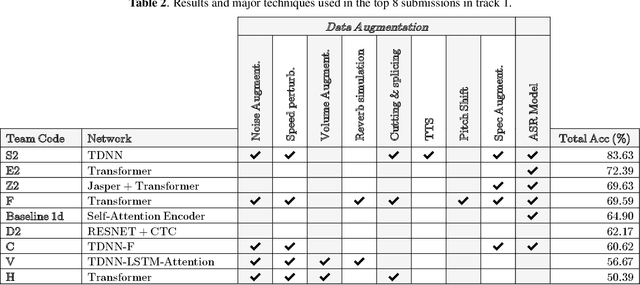
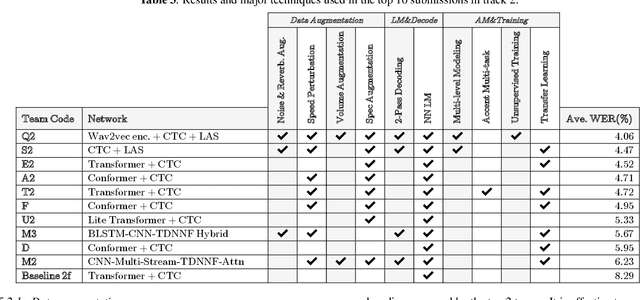
Abstract:The variety of accents has posed a big challenge to speech recognition. The Accented English Speech Recognition Challenge (AESRC2020) is designed for providing a common testbed and promoting accent-related research. Two tracks are set in the challenge -- English accent recognition (track 1) and accented English speech recognition (track 2). A set of 160 hours of accented English speech collected from 8 countries is released with labels as the training set. Another 20 hours of speech without labels is later released as the test set, including two unseen accents from another two countries used to test the model generalization ability in track 2. We also provide baseline systems for the participants. This paper first reviews the released dataset, track setups, baselines and then summarizes the challenge results and major techniques used in the submissions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge