Yuxiao Lin
HVD: Human Vision-Driven Video Representation Learning for Text-Video Retrieval
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:The success of CLIP has driven substantial progress in text-video retrieval. However, current methods often suffer from "blind" feature interaction, where the model struggles to discern key visual information from background noise due to the sparsity of textual queries. To bridge this gap, we draw inspiration from human cognitive behavior and propose the Human Vision-Driven (HVD) model. Our framework establishes a coarse-to-fine alignment mechanism comprising two key components: the Frame Features Selection Module (FFSM) and the Patch Features Compression Module (PFCM). FFSM mimics the human macro-perception ability by selecting key frames to eliminate temporal redundancy. Subsequently, PFCM simulates micro-perception by aggregating patch features into salient visual entities through an advanced attention mechanism, enabling precise entity-level matching. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate that HVD not only captures human-like visual focus but also achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Delving Deeper: Hierarchical Visual Perception for Robust Video-Text Retrieval
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Video-text retrieval (VTR) aims to locate relevant videos using natural language queries. Current methods, often based on pre-trained models like CLIP, are hindered by video's inherent redundancy and their reliance on coarse, final-layer features, limiting matching accuracy. To address this, we introduce the HVP-Net (Hierarchical Visual Perception Network), a framework that mines richer video semantics by extracting and refining features from multiple intermediate layers of a vision encoder. Our approach progressively distills salient visual concepts from raw patch-tokens at different semantic levels, mitigating redundancy while preserving crucial details for alignment. This results in a more robust video representation, leading to new state-of-the-art performance on challenging benchmarks including MSRVTT, DiDeMo, and ActivityNet. Our work validates the effectiveness of exploiting hierarchical features for advancing video-text retrieval. Our codes are available at https://github.com/boyun-zhang/HVP-Net.
MFCCA:Multi-Frame Cross-Channel attention for multi-speaker ASR in Multi-party meeting scenario
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Recently cross-channel attention, which better leverages multi-channel signals from microphone array, has shown promising results in the multi-party meeting scenario. Cross-channel attention focuses on either learning global correlations between sequences of different channels or exploiting fine-grained channel-wise information effectively at each time step. Considering the delay of microphone array receiving sound, we propose a multi-frame cross-channel attention, which models cross-channel information between adjacent frames to exploit the complementarity of both frame-wise and channel-wise knowledge. Besides, we also propose a multi-layer convolutional mechanism to fuse the multi-channel output and a channel masking strategy to combat the channel number mismatch problem between training and inference. Experiments on the AliMeeting, a real-world corpus, reveal that our proposed model outperforms single-channel model by 31.7\% and 37.0\% CER reduction on Eval and Test sets. Moreover, with comparable model parameters and training data, our proposed model achieves a new SOTA performance on the AliMeeting corpus, as compared with the top ranking systems in the ICASSP2022 M2MeT challenge, a recently held multi-channel multi-speaker ASR challenge.
A Comparative Study on Speaker-attributed Automatic Speech Recognition in Multi-party Meetings
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we conduct a comparative study on speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (SA-ASR) in the multi-party meeting scenario, a topic with increasing attention in meeting rich transcription. Specifically, three approaches are evaluated in this study. The first approach, FD-SOT, consists of a frame-level diarization model to identify speakers and a multi-talker ASR to recognize utterances. The speaker-attributed transcriptions are obtained by aligning the diarization results and recognized hypotheses. However, such an alignment strategy may suffer from erroneous timestamps due to the modular independence, severely hindering the model performance. Therefore, we propose the second approach, WD-SOT, to address alignment errors by introducing a word-level diarization model, which can get rid of such timestamp alignment dependency. To further mitigate the alignment issues, we propose the third approach, TS-ASR, which trains a target-speaker separation module and an ASR module jointly. By comparing various strategies for each SA-ASR approach, experimental results on a real meeting scenario corpus, AliMeeting, reveal that the WD-SOT approach achieves 10.7% relative reduction on averaged speaker-dependent character error rate (SD-CER), compared with the FD-SOT approach. In addition, the TS-ASR approach also outperforms the FD-SOT approach and brings 16.5% relative average SD-CER reduction.
Evaluation of Tree Based Regression over Multiple Linear Regression for Non-normally Distributed Data in Battery Performance
Nov 03, 2021



Abstract:Battery performance datasets are typically non-normal and multicollinear. Extrapolating such datasets for model predictions needs attention to such characteristics. This study explores the impact of data normality in building machine learning models. In this work, tree-based regression models and multiple linear regressions models are each built from a highly skewed non-normal dataset with multicollinearity and compared. Several techniques are necessary, such as data transformation, to achieve a good multiple linear regression model with this dataset; the most useful techniques are discussed. With these techniques, the best multiple linear regression model achieved an R^2 = 81.23% and exhibited no multicollinearity effect for the dataset used in this study. Tree-based models perform better on this dataset, as they are non-parametric, capable of handling complex relationships among variables and not affected by multicollinearity. We show that bagging, in the use of Random Forests, reduces overfitting. Our best tree-based model achieved accuracy of R^2 = 97.73%. This study explains why tree-based regressions promise as a machine learning model for non-normally distributed, multicollinear data.
BertGCN: Transductive Text Classification by Combining GCN and BERT
May 16, 2021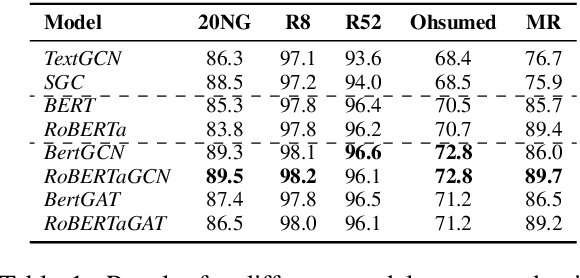

Abstract:In this work, we propose BertGCN, a model that combines large scale pretraining and transductive learning for text classification. BertGCN constructs a heterogeneous graph over the dataset and represents documents as nodes using BERT representations. By jointly training the BERT and GCN modules within BertGCN, the proposed model is able to leverage the advantages of both worlds: large-scale pretraining which takes the advantage of the massive amount of raw data and transductive learning which jointly learns representations for both training data and unlabeled test data by propagating label influence through graph convolution. Experiments show that BertGCN achieves SOTA performances on a wide range of text classification datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/ZeroRin/BertGCN.
Deep Sequential Feature Learning in Clinical Image Classification of Infectious Keratitis
Jun 04, 2020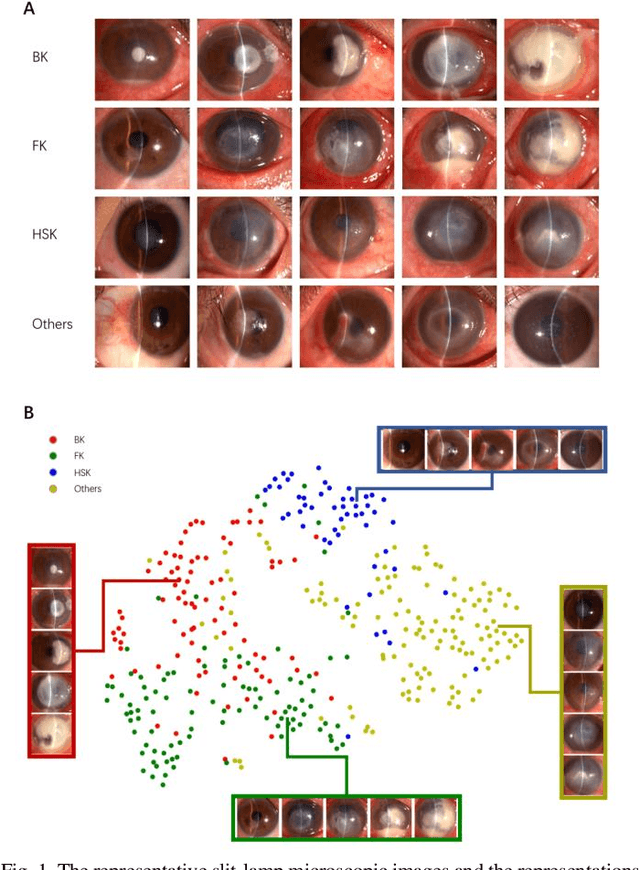
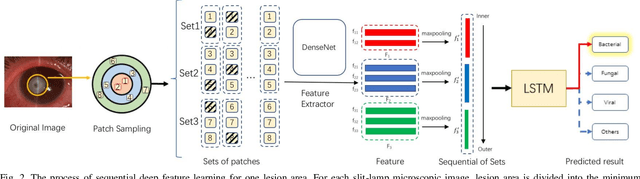
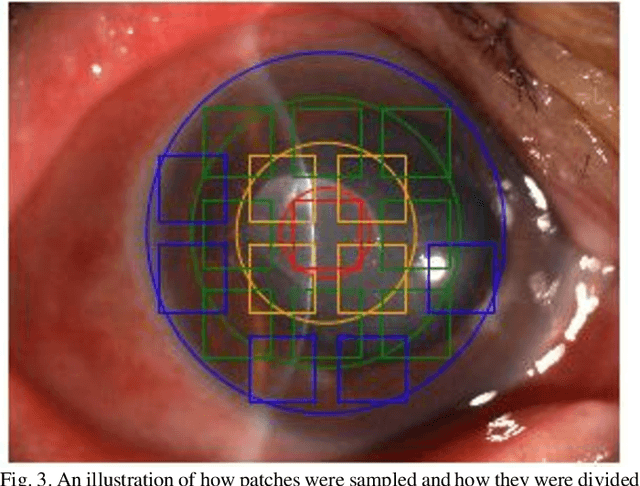
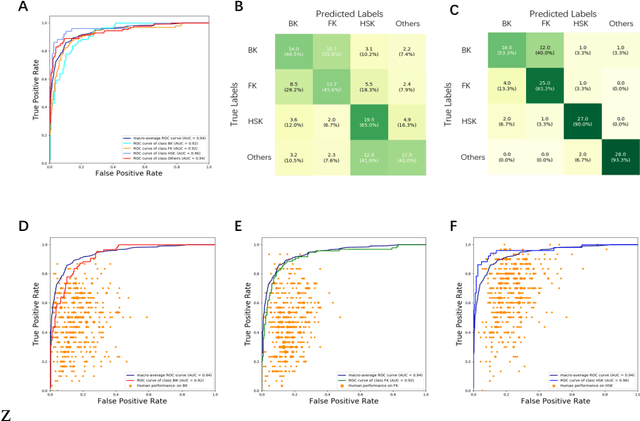
Abstract:Infectious keratitis is the most common entities of corneal diseases, in which pathogen grows in the cornea leading to inflammation and destruction of the corneal tissues. Infectious keratitis is a medical emergency, for which a rapid and accurate diagnosis is needed for speedy initiation of prompt and precise treatment to halt the disease progress and to limit the extent of corneal damage; otherwise it may develop sight-threatening and even eye-globe-threatening condition. In this paper, we propose a sequential-level deep learning model to effectively discriminate the distinction and subtlety of infectious corneal disease via the classification of clinical images. In this approach, we devise an appropriate mechanism to preserve the spatial structures of clinical images and disentangle the informative features for clinical image classification of infectious keratitis. In competition with 421 ophthalmologists, the performance of the proposed sequential-level deep model achieved 80.00% diagnostic accuracy, far better than the 49.27% diagnostic accuracy achieved by ophthalmologists over 120 test images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge