Yi Lei
Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China
Spark-Prover-X1: Formal Theorem Proving Through Diverse Data Training
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant promise in automated theorem proving, yet progress is often constrained by the scarcity of diverse and high-quality formal language data. To address this issue, we introduce Spark-Prover-X1, a 7B parameter model trained via an three-stage framework designed to unlock the reasoning potential of more accessible and moderately-sized LLMs. The first stage infuses deep knowledge through continuous pre-training on a broad mathematical corpus, enhanced by a suite of novel data tasks. Key innovation is a "CoT-augmented state prediction" task to achieve fine-grained reasoning. The second stage employs Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) within an expert iteration loop to specialize both the Spark-Prover-X1-7B and Spark-Formalizer-X1-7B models. Finally, a targeted round of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is applied to sharpen the prover's capabilities on the most challenging problems. To facilitate robust evaluation, particularly on problems from real-world examinations, we also introduce ExamFormal-Bench, a new benchmark dataset of 402 formal problems. Experimental results demonstrate that Spark-Prover achieves state-of-the-art performance among similarly-sized open-source models within the "Whole-Proof Generation" paradigm. It shows exceptional performance on difficult competition benchmarks, notably solving 27 problems on PutnamBench (pass@32) and achieving 24.0\% on CombiBench (pass@32). Our work validates that this diverse training data and progressively refined training pipeline provides an effective path for enhancing the formal reasoning capabilities of lightweight LLMs. Both Spark-Prover-X1-7B and Spark-Formalizer-X1-7B, along with the ExamFormal-Bench dataset, are made publicly available at: https://www.modelscope.cn/organization/iflytek, https://gitcode.com/ifly_opensource.
Predicting Nonlinear Interference for Short-Blocklength 4D Probabilistic Shaping
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:We derive a heuristic nonlinear interference model for 4D probabilistic shaping considering the polarization and time correlation of the 4D symbols. We demonstrate an average SNR prediction gap from split-step Fourier simulations of 0.15~dB.
On Shaping Gain of Multidimensional Constellation in Linear and Nonlinear Optical Fiber Channel
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Utilizing the multi-dimensional (MD) space for constellation shaping has been proven to be an effective approach for achieving shaping gains. Despite there exists a variety of MD modulation formats tailored for specific optical transmission scenarios, there remains a notable absence of a dependable comparison method for efficiently and promptly re-evaluating their performance in arbitrary transmission systems. In this paper, we introduce an analytical nonlinear interference (NLI) power model-based shaping gain estimation method to enable a fast performance evaluation of various MD modulation formats in coherent dual-polarization (DP) optical transmission system. In order to extend the applicability of this method to a broader set of modulation formats, we extend the established NLI model to take the 4D joint distribution into account and thus able to analyze the complex interactions of non-iid signaling in DP systems. With the help of the NLI model, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the state-of-the-art modulation formats and investigate their actual shaping gains in two types of optical fiber communication scenarios (multi-span and single-span). The numerical simulation shows that for arbitrary modulation formats, the NLI power and relative shaping gains in terms of signal-to-noise ratio can be more accurately estimated by capturing the statistics of MD symbols. Furthermore, the proposed method further validates the effectiveness of the reported NLI-tolerant modulation format in the literature, which reveals that the linear shaping gains and modulation-dependent NLI should be jointly considered for nonlinearity mitigation.
MPDS: A Movie Posters Dataset for Image Generation with Diffusion Model
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Movie posters are vital for captivating audiences, conveying themes, and driving market competition in the film industry. While traditional designs are laborious, intelligent generation technology offers efficiency gains and design enhancements. Despite exciting progress in image generation, current models often fall short in producing satisfactory poster results. The primary issue lies in the absence of specialized poster datasets for targeted model training. In this work, we propose a Movie Posters DataSet (MPDS), tailored for text-to-image generation models to revolutionize poster production. As dedicated to posters, MPDS stands out as the first image-text pair dataset to our knowledge, composing of 373k+ image-text pairs and 8k+ actor images (covering 4k+ actors). Detailed poster descriptions, such as movie titles, genres, casts, and synopses, are meticulously organized and standardized based on public movie synopsis, also named movie-synopsis prompt. To bolster poster descriptions as well as reduce differences from movie synopsis, further, we leverage a large-scale vision-language model to automatically produce vision-perceptive prompts for each poster, then perform manual rectification and integration with movie-synopsis prompt. In addition, we introduce a prompt of poster captions to exhibit text elements in posters like actor names and movie titles. For movie poster generation, we develop a multi-condition diffusion framework that takes poster prompt, poster caption, and actor image (for personalization) as inputs, yielding excellent results through the learning of a diffusion model. Experiments demonstrate the valuable role of our proposed MPDS dataset in advancing personalized movie poster generation. MPDS is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MPDS-373k-BD3B.
Multidimensional Voronoi Constellations vs. Short Blocklength Probabilistic Shaping: A Comparison for Multilevel Coding Approach
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Performance of concatenated multilevel coding with probabilistic shaping (PS) and Voronoi constellations (VCs) is analysed over AWGN channel. Numerical results show that VCs provide up to 1.3 dB SNR gains over PS-QAM with CCDM blocklength of 200.
Atmospheric Turbulence-Immune Free Space Optical Communication System based on Discrete-Time Analog Transmission
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:To effectively mitigate the influence of atmospheric turbulence, a novel discrete-time analog transmission free-space optical (DTAT-FSO) communication scheme is proposed. It directly maps information sources to discrete-time analog symbols via joint source-channel coding and modulation. Differently from traditional digital free space optical (TD-FSO) schemes, the proposed DTAT-FSO approach can automatically adapt to the variation of the channel state, with no need to adjust the specific modulation and coding scheme. The performance of the DTAT-FSO system was evaluated in both intensity modulation/direct detection (IM/DD) and coherent FSO systems for high-resolution image transmission. The results show that the DTAT-FSO reliably transmits images at low received optical powers (ROPs) and automatically enhances quality at high ROPs, while the TD-FSO experiences cliff and leveling effects when the channel state varies. With respect to the TD-FSO scheme, the DTAT-FSO scheme improved receiver sensitivity by 2.5 dB in the IM/DD FSO system and 0.8 dB in the coherent FSO system, and it achieved superior image fidelity under the same ROP. The automatic adaptation feature and improved performance of the DTAT-FSO suggest its potential for terrestrial, airborne, and satellite optical networks, addressing challenges posed by atmospheric turbulence.
DenseTrack: Drone-based Crowd Tracking via Density-aware Motion-appearance Synergy
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:Drone-based crowd tracking faces difficulties in accurately identifying and monitoring objects from an aerial perspective, largely due to their small size and close proximity to each other, which complicates both localization and tracking. To address these challenges, we present the Density-aware Tracking (DenseTrack) framework. DenseTrack capitalizes on crowd counting to precisely determine object locations, blending visual and motion cues to improve the tracking of small-scale objects. It specifically addresses the problem of cross-frame motion to enhance tracking accuracy and dependability. DenseTrack employs crowd density estimates as anchors for exact object localization within video frames. These estimates are merged with motion and position information from the tracking network, with motion offsets serving as key tracking cues. Moreover, DenseTrack enhances the ability to distinguish small-scale objects using insights from the visual-language model, integrating appearance with motion cues. The framework utilizes the Hungarian algorithm to ensure the accurate matching of individuals across frames. Demonstrated on DroneCrowd dataset, our approach exhibits superior performance, confirming its effectiveness in scenarios captured by drones.
Experimental Demonstration of 16D Voronoi Constellation with Two-Level Coding over 50km Four-Core Fiber
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:A 16-dimensional Voronoi constellation concatenated with multilevel coding is experimentally demonstrated over a 50km four-core fiber transmission system. The proposed scheme reduces the required launch power by 6dB and provides a 17dB larger operating range than 16QAM with BICM at the outer HD-FEC BER threshold.
Accent-VITS:accent transfer for end-to-end TTS
Dec 29, 2023


Abstract:Accent transfer aims to transfer an accent from a source speaker to synthetic speech in the target speaker's voice. The main challenge is how to effectively disentangle speaker timbre and accent which are entangled in speech. This paper presents a VITS-based end-to-end accent transfer model named Accent-VITS.Based on the main structure of VITS, Accent-VITS makes substantial improvements to enable effective and stable accent transfer.We leverage a hierarchical CVAE structure to model accent pronunciation information and acoustic features, respectively, using bottleneck features and mel spectrums as constraints.Moreover, the text-to-wave mapping in VITS is decomposed into text-to-accent and accent-to-wave mappings in Accent-VITS. In this way, the disentanglement of accent and speaker timbre becomes be more stable and effective.Experiments on multi-accent and Mandarin datasets show that Accent-VITS achieves higher speaker similarity, accent similarity and speech naturalness as compared with a strong baseline.
Multi-Speaker Expressive Speech Synthesis via Semi-supervised Contrastive Learning
Oct 26, 2023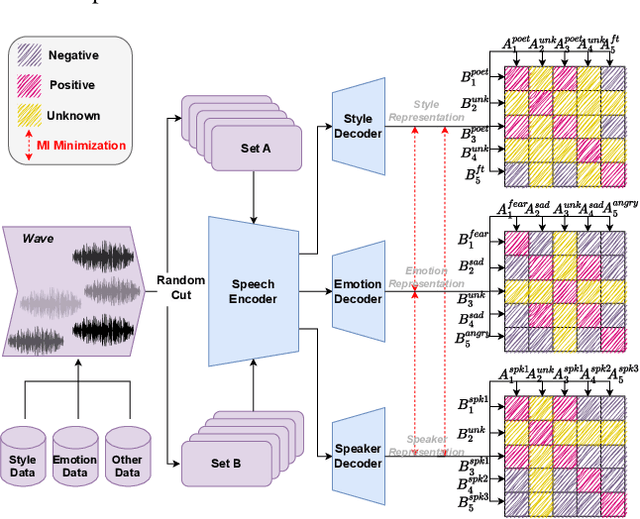
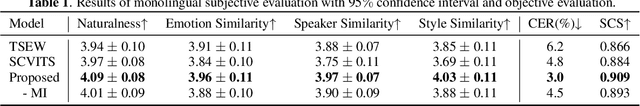
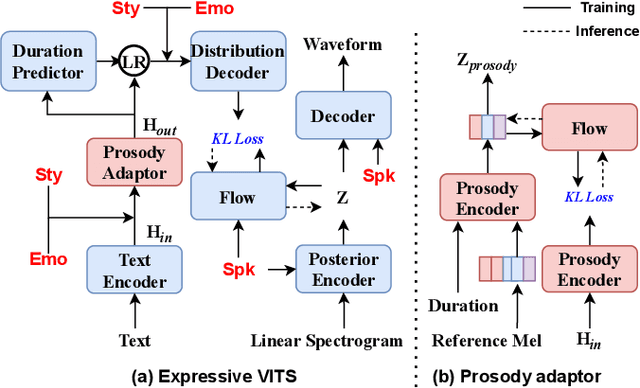
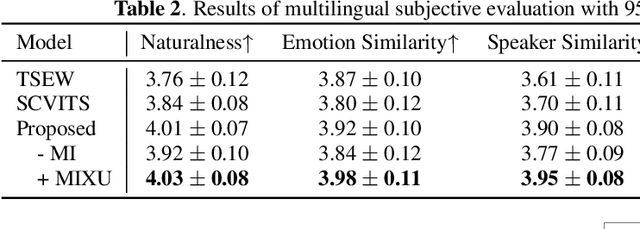
Abstract:This paper aims to build an expressive TTS system for multi-speakers, synthesizing a target speaker's speech with multiple styles and emotions. To this end, we propose a novel contrastive learning-based TTS approach to transfer style and emotion across speakers. Specifically, we construct positive-negative sample pairs at both utterance and category (such as emotion-happy or style-poet or speaker A) levels and leverage contrastive learning to better extract disentangled style, emotion, and speaker representations from speech. Furthermore, we introduce a semi-supervised training strategy to the proposed approach to effectively leverage multi-domain data, including style-labeled data, emotion-labeled data, and unlabeled data. We integrate the learned representations into an improved VITS model, enabling it to synthesize expressive speech with diverse styles and emotions for a target speaker. Experiments on multi-domain data demonstrate the good design of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge