Zongyao Li
Object-Centric Framework for Video Moment Retrieval
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Most existing video moment retrieval methods rely on temporal sequences of frame- or clip-level features that primarily encode global visual and semantic information. However, such representations often fail to capture fine-grained object semantics and appearance, which are crucial for localizing moments described by object-oriented queries involving specific entities and their interactions. In particular, temporal dynamics at the object level have been largely overlooked, limiting the effectiveness of existing approaches in scenarios requiring detailed object-level reasoning. To address this limitation, we propose a novel object-centric framework for moment retrieval. Our method first extracts query-relevant objects using a scene graph parser and then generates scene graphs from video frames to represent these objects and their relationships. Based on the scene graphs, we construct object-level feature sequences that encode rich visual and semantic information. These sequences are processed by a relational tracklet transformer, which models spatio-temporal correlations among objects over time. By explicitly capturing object-level state changes, our framework enables more accurate localization of moments aligned with object-oriented queries. We evaluated our method on three benchmarks: Charades-STA, QVHighlights, and TACoS. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across all benchmarks.
KFS-Bench: Comprehensive Evaluation of Key Frame Sampling in Long Video Understanding
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:We propose KFS-Bench, the first benchmark for key frame sampling in long video question answering (QA), featuring multi-scene annotations to enable direct and robust evaluation of sampling strategies. Key frame sampling is crucial for efficient long-form video understanding. In long video QA, selecting informative frames enables multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to improve both accuracy and efficiency. KFS-Bench addresses the limitation of prior works that only indirectly assess frame selection quality via QA accuracy. By providing ground-truth annotations of multiple disjoint scenes required per question, KFS-Bench allows us to directly analyze how different sampling approaches capture essential content across an entire long video. Using KFS-Bench, we conduct a comprehensive study of key frame sampling methods and identify that not only sampling precision but also scene coverage and sampling balance are the key factors influencing QA performance. Regarding all the factors, we design a novel sampling quality metric that correlates with QA accuracy. Furthermore, we develop a novel key frame sampling method that leverages question-video relevance to balance sampling diversity against question-frame similarity, thereby improving coverage of relevant scenes. Our adaptively balanced sampling approach achieves superior performance in both key frame sampling and QA performance. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/NEC-VID/KFS-Bench.
Align-then-Slide: A complete evaluation framework for Ultra-Long Document-Level Machine Translation
Sep 04, 2025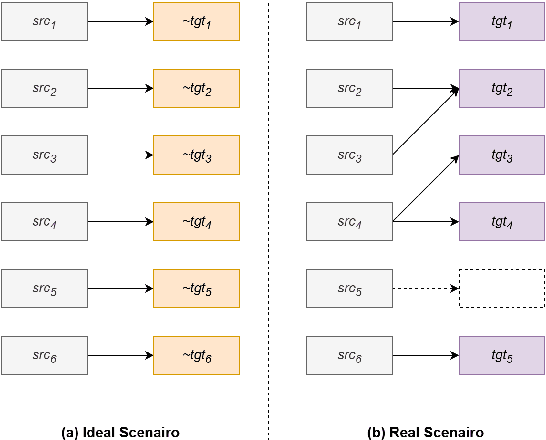
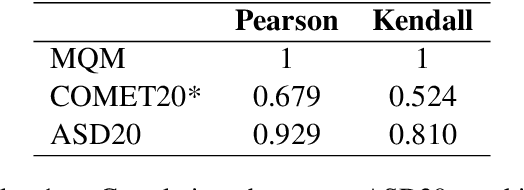
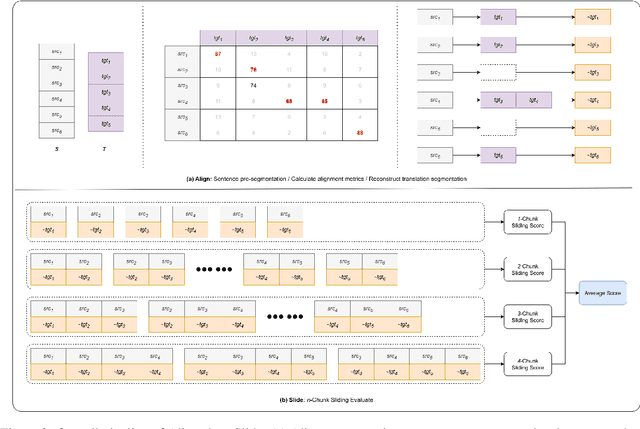
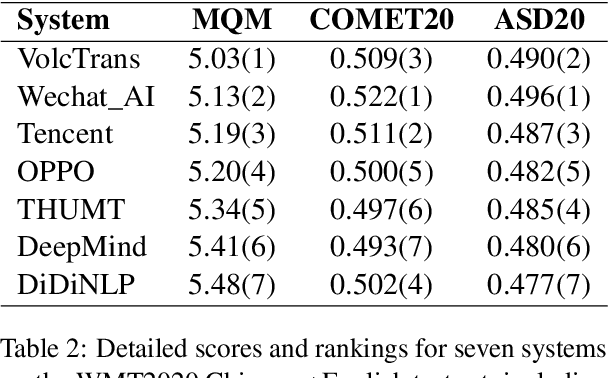
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have ushered in a new era for document-level machine translation (\textit{doc}-mt), yet their whole-document outputs challenge existing evaluation methods that assume sentence-by-sentence alignment. We introduce \textit{\textbf{Align-then-Slide}}, a complete evaluation framework for ultra-long doc-mt. In the Align stage, we automatically infer sentence-level source-target correspondences and rebuild the target to match the source sentence number, resolving omissions and many-to-one/one-to-many mappings. In the n-Chunk Sliding Evaluate stage, we calculate averaged metric scores under 1-, 2-, 3- and 4-chunk for multi-granularity assessment. Experiments on the WMT benchmark show a Pearson correlation of 0.929 between our method with expert MQM rankings. On a newly curated real-world test set, our method again aligns closely with human judgments. Furthermore, preference data produced by Align-then-Slide enables effective CPO training and its direct use as a reward model for GRPO, both yielding translations preferred over a vanilla SFT baseline. The results validate our framework as an accurate, robust, and actionable evaluation tool for doc-mt systems.
Generative Annotation for ASR Named Entity Correction
Aug 28, 2025

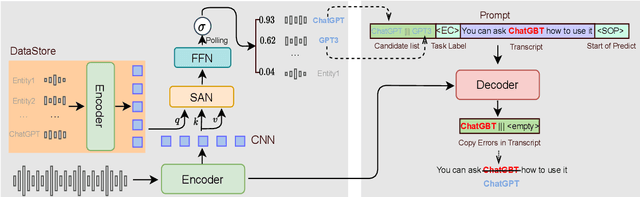

Abstract:End-to-end automatic speech recognition systems often fail to transcribe domain-specific named entities, causing catastrophic failures in downstream tasks. Numerous fast and lightweight named entity correction (NEC) models have been proposed in recent years. These models, mainly leveraging phonetic-level edit distance algorithms, have shown impressive performances. However, when the forms of the wrongly-transcribed words(s) and the ground-truth entity are significantly different, these methods often fail to locate the wrongly transcribed words in hypothesis, thus limiting their usage. We propose a novel NEC method that utilizes speech sound features to retrieve candidate entities. With speech sound features and candidate entities, we inovatively design a generative method to annotate entity errors in ASR transcripts and replace the text with correct entities. This method is effective in scenarios of word form difference. We test our method using open-source and self-constructed test sets. The results demonstrate that our NEC method can bring significant improvement to entity accuracy. We will open source our self-constructed test set and training data.
Automatic Evaluation Metrics for Document-level Translation: Overview, Challenges and Trends
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of deep learning technologies, the field of machine translation has witnessed significant progress, especially with the advent of large language models (LLMs) that have greatly propelled the advancement of document-level translation. However, accurately evaluating the quality of document-level translation remains an urgent issue. This paper first introduces the development status of document-level translation and the importance of evaluation, highlighting the crucial role of automatic evaluation metrics in reflecting translation quality and guiding the improvement of translation systems. It then provides a detailed analysis of the current state of automatic evaluation schemes and metrics, including evaluation methods with and without reference texts, as well as traditional metrics, Model-based metrics and LLM-based metrics. Subsequently, the paper explores the challenges faced by current evaluation methods, such as the lack of reference diversity, dependence on sentence-level alignment information, and the bias, inaccuracy, and lack of interpretability of the LLM-as-a-judge method. Finally, the paper looks ahead to the future trends in evaluation methods, including the development of more user-friendly document-level evaluation methods and more robust LLM-as-a-judge methods, and proposes possible research directions, such as reducing the dependency on sentence-level information, introducing multi-level and multi-granular evaluation approaches, and training models specifically for machine translation evaluation. This study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of automatic evaluation for document-level translation and offer insights into future developments.
Chain-of-Description: What I can understand, I can put into words
Feb 22, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel strategy defined as Chain-of-Description (CoD) Prompting, tailored for Multi-Modal Large Language Models. This approach involves having the model first provide a detailed description of the multi-modal input before generating an answer to the question. When applied to models such as Qwen2-Audio, Qwen2-VL, and Qwen2.5-VL, CoD Prompting significantly enhances performance compared to standard prompting methods. This is demonstrated by nearly a 4\% improvement in the speech category of the audio benchmark AIR-Bench-Chat and a 5.3\% improvement in the hard-level portion of the vision benchmark MMMU\_Pro. Our ablation study further validates the effectiveness of CoD Prompting.
Doc-Guided Sent2Sent++: A Sent2Sent++ Agent with Doc-Guided memory for Document-level Machine Translation
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:The field of artificial intelligence has witnessed significant advancements in natural language processing, largely attributed to the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). These models form the backbone of Agents designed to address long-context dependencies, particularly in Document-level Machine Translation (DocMT). DocMT presents unique challenges, with quality, consistency, and fluency being the key metrics for evaluation. Existing approaches, such as Doc2Doc and Doc2Sent, either omit sentences or compromise fluency. This paper introduces Doc-Guided Sent2Sent++, an Agent that employs an incremental sentence-level forced decoding strategy \textbf{to ensure every sentence is translated while enhancing the fluency of adjacent sentences.} Our Agent leverages a Doc-Guided Memory, focusing solely on the summary and its translation, which we find to be an efficient approach to maintaining consistency. Through extensive testing across multiple languages and domains, we demonstrate that Sent2Sent++ outperforms other methods in terms of quality, consistency, and fluency. The results indicate that, our approach has achieved significant improvements in metrics such as s-COMET, d-COMET, LTCR-$1_f$, and document-level perplexity (d-ppl). The contributions of this paper include a detailed analysis of current DocMT research, the introduction of the Sent2Sent++ decoding method, the Doc-Guided Memory mechanism, and validation of its effectiveness across languages and domains.
M-Ped: Multi-Prompt Ensemble Decoding for Large Language Models
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:With the widespread application of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), enhancing their performance has become a research hotspot. This paper presents a novel multi-prompt ensemble decoding approach designed to bolster the generation quality of LLMs by leveraging the aggregation of outcomes from multiple prompts. Given a unique input $X$, we submit $n$ variations of prompts with $X$ to LLMs in batch mode to decode and derive probability distributions. For each token prediction, we calculate the ensemble probability by averaging the $n$ probability distributions within the batch, utilizing this aggregated probability to generate the token. This technique is dubbed Inner-Batch Ensemble. To facilitate efficient batch inference, we implement a Left-Padding strategy to maintain uniform input lengths across the n prompts. Through extensive experimentation on diverse NLP tasks, including machine translation, code generation, and text simplification, we demonstrate the efficacy of our method in enhancing LLM performance. The results show substantial improvements in BLEU scores, pass@$k$ rates, and LENS metrics over conventional methods.
Context-aware and Style-related Incremental Decoding framework for Discourse-Level Literary Translation
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:This report outlines our approach for the WMT24 Discourse-Level Literary Translation Task, focusing on the Chinese-English language pair in the Constrained Track. Translating literary texts poses significant challenges due to the nuanced meanings, idiomatic expressions, and intricate narrative structures inherent in such works. To address these challenges, we leveraged the Chinese-Llama2 model, specifically enhanced for this task through a combination of Continual Pre-training (CPT) and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). Our methodology includes a novel Incremental Decoding framework, which ensures that each sentence is translated with consideration of its broader context, maintaining coherence and consistency throughout the text. This approach allows the model to capture long-range dependencies and stylistic elements, producing translations that faithfully preserve the original literary quality. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in both sentence-level and document-level BLEU scores, underscoring the effectiveness of our proposed framework in addressing the complexities of document-level literary translation.
Multilingual Transfer and Domain Adaptation for Low-Resource Languages of Spain
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:This article introduces the submission status of the Translation into Low-Resource Languages of Spain task at (WMT 2024) by Huawei Translation Service Center (HW-TSC). We participated in three translation tasks: spanish to aragonese (es-arg), spanish to aranese (es-arn), and spanish to asturian (es-ast). For these three translation tasks, we use training strategies such as multilingual transfer, regularized dropout, forward translation and back translation, labse denoising, transduction ensemble learning and other strategies to neural machine translation (NMT) model based on training deep transformer-big architecture. By using these enhancement strategies, our submission achieved a competitive result in the final evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge