Shihao Li
Alibaba Inc
DiffPlace: Street View Generation via Place-Controllable Diffusion Model Enhancing Place Recognition
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Generative models have advanced significantly in realistic image synthesis, with diffusion models excelling in quality and stability. Recent multi-view diffusion models improve 3D-aware street view generation, but they struggle to produce place-aware and background-consistent urban scenes from text, BEV maps, and object bounding boxes. This limits their effectiveness in generating realistic samples for place recognition tasks. To address these challenges, we propose DiffPlace, a novel framework that introduces a place-ID controller to enable place-controllable multi-view image generation. The place-ID controller employs linear projection, perceiver transformer, and contrastive learning to map place-ID embeddings into a fixed CLIP space, allowing the model to synthesize images with consistent background buildings while flexibly modifying foreground objects and weather conditions. Extensive experiments, including quantitative comparisons and augmented training evaluations, demonstrate that DiffPlace outperforms existing methods in both generation quality and training support for visual place recognition. Our results highlight the potential of generative models in enhancing scene-level and place-aware synthesis, providing a valuable approach for improving place recognition in autonomous driving
Vibe AIGC: A New Paradigm for Content Generation via Agentic Orchestration
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:For the past decade, the trajectory of generative artificial intelligence (AI) has been dominated by a model-centric paradigm driven by scaling laws. Despite significant leaps in visual fidelity, this approach has encountered a ``usability ceiling'' manifested as the Intent-Execution Gap (i.e., the fundamental disparity between a creator's high-level intent and the stochastic, black-box nature of current single-shot models). In this paper, inspired by the Vibe Coding, we introduce the \textbf{Vibe AIGC}, a new paradigm for content generation via agentic orchestration, which represents the autonomous synthesis of hierarchical multi-agent workflows. Under this paradigm, the user's role transcends traditional prompt engineering, evolving into a Commander who provides a Vibe, a high-level representation encompassing aesthetic preferences, functional logic, and etc. A centralized Meta-Planner then functions as a system architect, deconstructing this ``Vibe'' into executable, verifiable, and adaptive agentic pipelines. By transitioning from stochastic inference to logical orchestration, Vibe AIGC bridges the gap between human imagination and machine execution. We contend that this shift will redefine the human-AI collaborative economy, transforming AI from a fragile inference engine into a robust system-level engineering partner that democratizes the creation of complex, long-horizon digital assets.
WaveMan: mmWave-Based Room-Scale Human Interaction Perception for Humanoid Robots
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Reliable humanoid-robot interaction (HRI) in household environments is constrained by two fundamental requirements, namely robustness to unconstrained user positions and preservation of user privacy. Millimeter-wave (mmWave) sensing inherently supports privacy-preserving interaction, making it a promising modality for room-scale HRI. However, existing mmWave-based interaction-sensing systems exhibit poor spatial generalization at unseen distances or viewpoints. To address this challenge, we introduce WaveMan, a spatially adaptive room-scale perception system that restores reliable human interaction sensing across arbitrary user positions. WaveMan integrates viewpoint alignment and spectrogram enhancement for spatial consistency, with dual-channel attention for robust feature extraction. Experiments across five participants show that, under fixed-position evaluation, WaveMan achieves the same cross-position accuracy as the baseline with five times fewer training positions. In random free-position testing, accuracy increases from 33.00% to 94.33%, enabled by the proposed method. These results demonstrate the feasibility of reliable, privacy-preserving interaction for household humanoid robots across unconstrained user positions.
DCG ReID: Disentangling Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle Re-Identification
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal vehicle Re-Identification (ReID) aims to leverage complementary information from RGB, Near Infrared (NIR), and Thermal Infrared (TIR) modalities to retrieve the same vehicle. The challenges of multi-modal vehicle ReID arise from the uncertainty of modality quality distribution induced by inherent discrepancies across modalities, resulting in distinct conflicting fusion requirements for data with balanced and unbalanced quality distributions. Existing methods handle all multi-modal data within a single fusion model, overlooking the different needs of the two data types and making it difficult to decouple the conflict between intra-class consistency and inter-modal heterogeneity. To this end, we propose Disentangle Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle ReID (DCG-ReID). Specifically, to disentangle heterogeneous quality-distributed modal data without mutual interference, we first design the Dynamic Confidence-based Disentangling Weighting (DCDW) mechanism: dynamically reweighting three-modal contributions via interaction-derived modal confidence to build a disentangled fusion framework. Building on DCDW, we develop two scenario-specific fusion strategies: (1) for balanced quality distributions, Collaboration Fusion Module (CFM) mines pairwise consensus features to capture shared discriminative information and boost intra-class consistency; (2) for unbalanced distributions, Guidance Fusion Module (GFM) implements differential amplification of modal discriminative disparities to reinforce dominant modality advantages, guide auxiliary modalities to mine complementary discriminative info, and mitigate inter-modal divergence to boost multi-modal joint decision performance. Extensive experiments on three multi-modal ReID benchmarks (WMVeID863, MSVR310, RGBNT100) validate the effectiveness of our method. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Optimization-Guided Diffusion for Interactive Scene Generation
Dec 11, 2025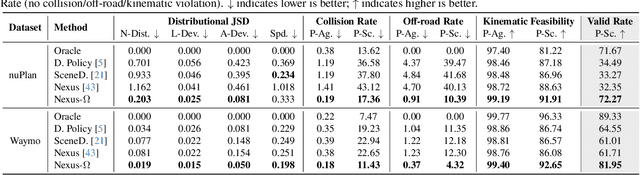
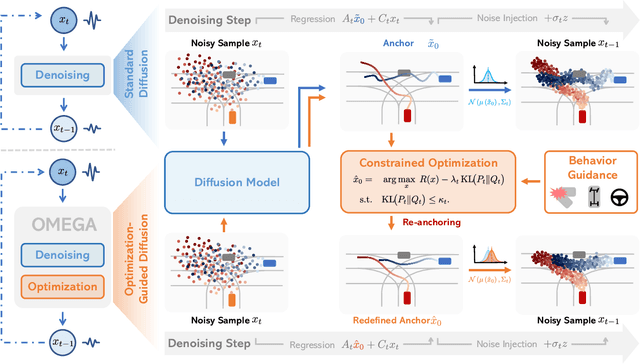
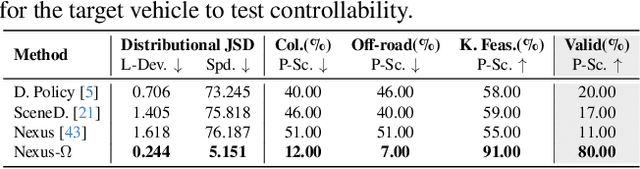
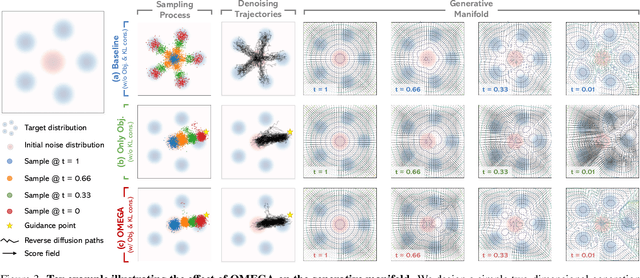
Abstract:Realistic and diverse multi-agent driving scenes are crucial for evaluating autonomous vehicles, but safety-critical events which are essential for this task are rare and underrepresented in driving datasets. Data-driven scene generation offers a low-cost alternative by synthesizing complex traffic behaviors from existing driving logs. However, existing models often lack controllability or yield samples that violate physical or social constraints, limiting their usability. We present OMEGA, an optimization-guided, training-free framework that enforces structural consistency and interaction awareness during diffusion-based sampling from a scene generation model. OMEGA re-anchors each reverse diffusion step via constrained optimization, steering the generation towards physically plausible and behaviorally coherent trajectories. Building on this framework, we formulate ego-attacker interactions as a game-theoretic optimization in the distribution space, approximating Nash equilibria to generate realistic, safety-critical adversarial scenarios. Experiments on nuPlan and Waymo show that OMEGA improves generation realism, consistency, and controllability, increasing the ratio of physically and behaviorally valid scenes from 32.35% to 72.27% for free exploration capabilities, and from 11% to 80% for controllability-focused generation. Our approach can also generate $5\times$ more near-collision frames with a time-to-collision under three seconds while maintaining the overall scene realism.
Natural Geometry of Robust Data Attribution: From Convex Models to Deep Networks
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Data attribution methods identify which training examples are responsible for a model's predictions, but their sensitivity to distributional perturbations undermines practical reliability. We present a unified framework for certified robust attribution that extends from convex models to deep networks. For convex settings, we derive Wasserstein-Robust Influence Functions (W-RIF) with provable coverage guarantees. For deep networks, we demonstrate that Euclidean certification is rendered vacuous by spectral amplification -- a mechanism where the inherent ill-conditioning of deep representations inflates Lipschitz bounds by over $10{,}000\times$. This explains why standard TRAK scores, while accurate point estimates, are geometrically fragile: naive Euclidean robustness analysis yields 0\% certification. Our key contribution is the Natural Wasserstein metric, which measures perturbations in the geometry induced by the model's own feature covariance. This eliminates spectral amplification, reducing worst-case sensitivity by $76\times$ and stabilizing attribution estimates. On CIFAR-10 with ResNet-18, Natural W-TRAK certifies 68.7\% of ranking pairs compared to 0\% for Euclidean baselines -- to our knowledge, the first non-vacuous certified bounds for neural network attribution. Furthermore, we prove that the Self-Influence term arising from our analysis equals the Lipschitz constant governing attribution stability, providing theoretical grounding for leverage-based anomaly detection. Empirically, Self-Influence achieves 0.970 AUROC for label noise detection, identifying 94.1\% of corrupted labels by examining just the top 20\% of training data.
MVU-Eval: Towards Multi-Video Understanding Evaluation for Multimodal LLMs
Nov 13, 2025
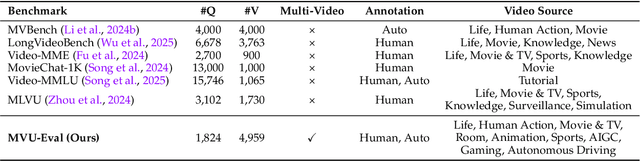
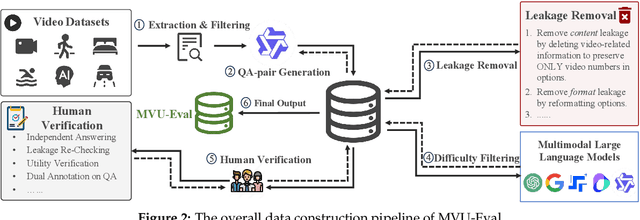
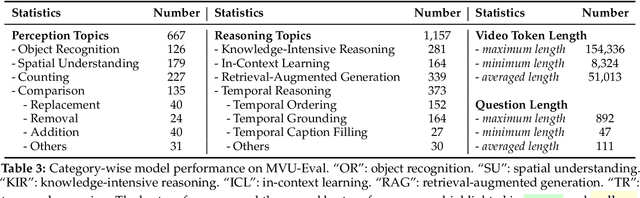
Abstract:The advent of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has expanded AI capabilities to visual modalities, yet existing evaluation benchmarks remain limited to single-video understanding, overlooking the critical need for multi-video understanding in real-world scenarios (e.g., sports analytics and autonomous driving). To address this significant gap, we introduce MVU-Eval, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating Multi-Video Understanding for MLLMs. Specifically, our MVU-Eval mainly assesses eight core competencies through 1,824 meticulously curated question-answer pairs spanning 4,959 videos from diverse domains, addressing both fundamental perception tasks and high-order reasoning tasks. These capabilities are rigorously aligned with real-world applications such as multi-sensor synthesis in autonomous systems and cross-angle sports analytics. Through extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art open-source and closed-source models, we reveal significant performance discrepancies and limitations in current MLLMs' ability to perform understanding across multiple videos. The benchmark will be made publicly available to foster future research.
Algorithm-Relative Trajectory Valuation in Policy Gradient Control
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:We study how trajectory value depends on the learning algorithm in policy-gradient control. Using Trajectory Shapley in an uncertain LQR, we find a negative correlation between Persistence of Excitation (PE) and marginal value under vanilla REINFORCE ($r\approx-0.38$). We prove a variance-mediated mechanism: (i) for fixed energy, higher PE yields lower gradient variance; (ii) near saddles, higher variance increases escape probability, raising marginal contribution. When stabilized (state whitening or Fisher preconditioning), this variance channel is neutralized and information content dominates, flipping the correlation positive ($r\approx+0.29$). Hence, trajectory value is algorithm-relative. Experiments validate the mechanism and show decision-aligned scores (Leave-One-Out) complement Shapley for pruning, while Shapley identifies toxic subsets.
Constrained Optimal Planning to Minimize Battery Degradation of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Jun 16, 2025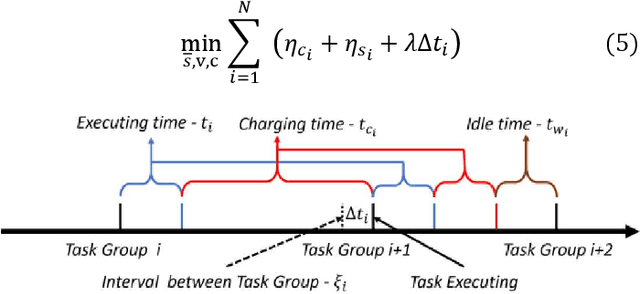
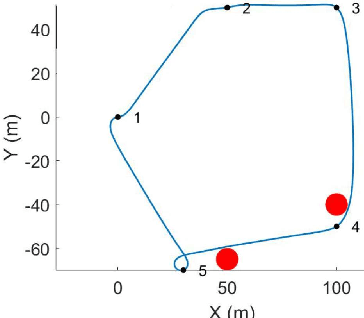
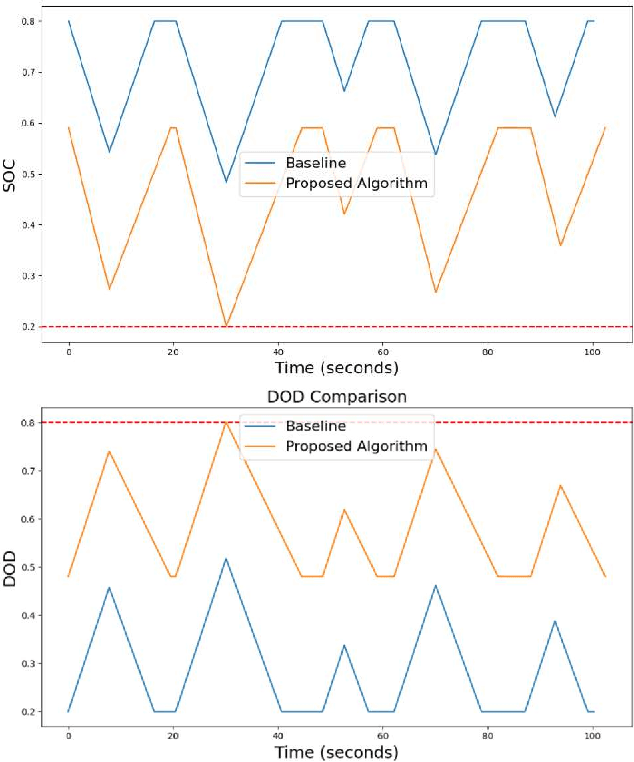
Abstract:This paper proposes an optimization framework that addresses both cycling degradation and calendar aging of batteries for autonomous mobile robot (AMR) to minimize battery degradation while ensuring task completion. A rectangle method of piecewise linear approximation is employed to linearize the bilinear optimization problem. We conduct a case study to validate the efficiency of the proposed framework in achieving an optimal path planning for AMRs while reducing battery aging.
Robust Optimal Task Planning to Maximize Battery Life
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a control-oriented optimization platform for autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), focusing on extending battery life while ensuring task completion. The requirement of fast AMR task planning while maintaining minimum battery state of charge, thus maximizing the battery life, renders a bilinear optimization problem. McCormick envelop technique is proposed to linearize the bilinear term. A novel planning algorithm with relaxed constraints is also developed to handle parameter uncertainties robustly with high efficiency ensured. Simulation results are provided to demonstrate the utility of the proposed methods in reducing battery degradation while satisfying task completion requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge