Haoxiang Yang
Large Neighborhood Search and Bitmask Dynamic Programming for Wireless Mobile Charging Electric Vehicle Routing Problems in Medical Transportation
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is critical to achieving sustainable transportation, but challenges such as limited driving range and insufficient charging infrastructure have hindered the widespread adoption of EVs, especially in time-sensitive logistics such as medical transportation. This paper presents a new model to break through this barrier by combining wireless mobile charging technology with optimization. We propose the Wireless Mobile Charging Electric Vehicle Routing Problem (WMC-EVRP), which enables Medical Transportation Electric Vehicles (MTEVs) to be charged while traveling via Mobile Charging Carts (MCTs). This eliminates the time wastage of stopping for charging and ensures uninterrupted operation of MTEVs for such time-sensitive transportation problems. However, in this problem, the decisions of these two types of heterogeneous vehicles are coupled with each other, which greatly increases the difficulty of vehicle routing optimizations. To address this complex problem, we develop a mathematical model and a tailored meta-heuristic algorithm that combines Bit Mask Dynamic Programming (BDP) and Large Neighborhood Search (LNS). The BDP approach efficiently optimizes charging strategies, while the LNS framework utilizes custom operators to optimize the MTEV routes under capacity and synchronization constraints. Our approach outperforms traditional solvers in providing solutions for medium and large instances. Using actual hospital locations in Singapore as data, we validated the practical applicability of the model through extensive experiments and provided important insights into minimizing costs and ensuring the timely delivery of healthcare services.
The Multi-Trip Time-Dependent Mix Vehicle Routing Problem for Hybrid Autonomous Shared Delivery Location and Traditional Door-to-Door Delivery Modes
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Rising labor costs and increasing logistical demands pose significant challenges to modern delivery systems. Automated Electric Vehicles (AEVs) could reduce reliance on delivery personnel and increase route flexibility, but their adoption is limited due to varying customer acceptance and integration complexities. Shared Distribution Locations (SDLs) offer an alternative to door-to-door (D2D) delivery by providing a wider delivery window and serving multiple community customers, thereby improving last-mile logistics through reduced delivery time, lower costs, and higher customer satisfaction.This paper introduces the Multi-Trip Time-Dependent Hybrid Vehicle Routing Problem (MTTD-MVRP), a challenging variant of the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) that combines Autonomous Electric Vehicles (AEVs) with conventional vehicles. The problem's complexity arises from factors such as time-dependent travel speeds, strict time windows, battery limitations, and driver labor constraints, while integrating both SDLs and D2D deliveries. To solve the MTTD-MVRP efficiently, we develop a tailored meta-heuristic based on Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search (ALNS) augmented with column generation (CG). This approach intensively explores the solution space using problem-specific operators and adaptively refines solutions, balancing high-quality outcomes with computational effort. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method delivers near-optimal solutions for large-scale instances within practical time limits.From a managerial perspective, our findings highlight the importance of integrating autonomous and human-driven vehicles in last-mile logistics. Decision-makers can leverage SDLs to reduce operational costs and carbon footprints while still accommodating customers who require or prefer D2D services.
VELoRA: A Low-Rank Adaptation Approach for Efficient RGB-Event based Recognition
Dec 28, 2024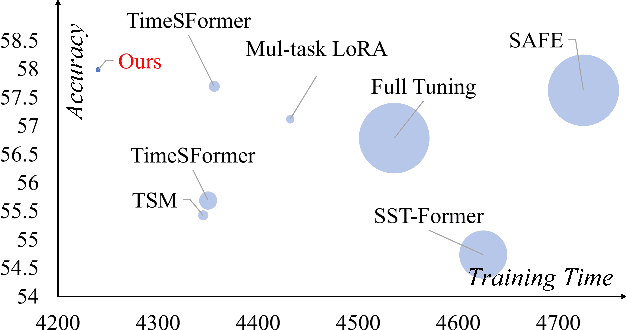
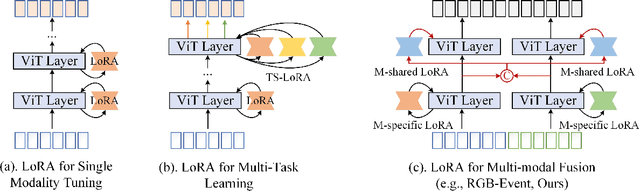
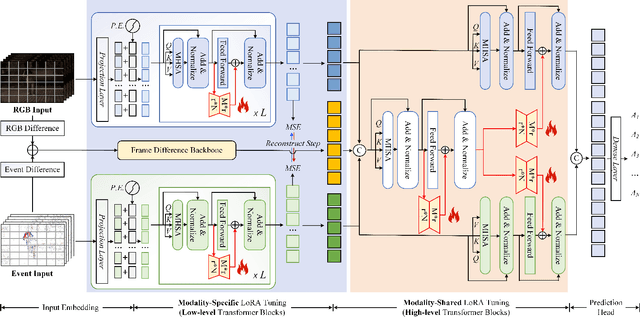
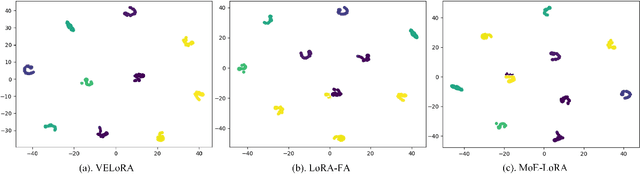
Abstract:Pattern recognition leveraging both RGB and Event cameras can significantly enhance performance by deploying deep neural networks that utilize a fine-tuning strategy. Inspired by the successful application of large models, the introduction of such large models can also be considered to further enhance the performance of multi-modal tasks. However, fully fine-tuning these models leads to inefficiency and lightweight fine-tuning methods such as LoRA and Adapter have been proposed to achieve a better balance between efficiency and performance. To our knowledge, there is currently no work that has conducted parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) for RGB-Event recognition based on pre-trained foundation models. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel PEFT strategy to adapt the pre-trained foundation vision models for the RGB-Event-based classification. Specifically, given the RGB frames and event streams, we extract the RGB and event features based on the vision foundation model ViT with a modality-specific LoRA tuning strategy. The frame difference of the dual modalities is also considered to capture the motion cues via the frame difference backbone network. These features are concatenated and fed into high-level Transformer layers for efficient multi-modal feature learning via modality-shared LoRA tuning. Finally, we concatenate these features and feed them into a classification head to achieve efficient fine-tuning. The source code and pre-trained models will be released on \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/VELoRA}.
State Space Model for New-Generation Network Alternative to Transformers: A Survey
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:In the post-deep learning era, the Transformer architecture has demonstrated its powerful performance across pre-trained big models and various downstream tasks. However, the enormous computational demands of this architecture have deterred many researchers. To further reduce the complexity of attention models, numerous efforts have been made to design more efficient methods. Among them, the State Space Model (SSM), as a possible replacement for the self-attention based Transformer model, has drawn more and more attention in recent years. In this paper, we give the first comprehensive review of these works and also provide experimental comparisons and analysis to better demonstrate the features and advantages of SSM. Specifically, we first give a detailed description of principles to help the readers quickly capture the key ideas of SSM. After that, we dive into the reviews of existing SSMs and their various applications, including natural language processing, computer vision, graph, multi-modal and multi-media, point cloud/event stream, time series data, and other domains. In addition, we give statistical comparisons and analysis of these models and hope it helps the readers to understand the effectiveness of different structures on various tasks. Then, we propose possible research points in this direction to better promote the development of the theoretical model and application of SSM. More related works will be continuously updated on the following GitHub: https://github.com/Event-AHU/Mamba_State_Space_Model_Paper_List.
Uncertainty-aware Bridge based Mobile-Former Network for Event-based Pattern Recognition
Jan 20, 2024Abstract:The mainstream human activity recognition (HAR) algorithms are developed based on RGB cameras, which are easily influenced by low-quality images (e.g., low illumination, motion blur). Meanwhile, the privacy protection issue caused by ultra-high definition (HD) RGB cameras aroused more and more people's attention. Inspired by the success of event cameras which perform better on high dynamic range, no motion blur, and low energy consumption, we propose to recognize human actions based on the event stream. We propose a lightweight uncertainty-aware information propagation based Mobile-Former network for efficient pattern recognition, which aggregates the MobileNet and Transformer network effectively. Specifically, we first embed the event images using a stem network into feature representations, then, feed them into uncertainty-aware Mobile-Former blocks for local and global feature learning and fusion. Finally, the features from MobileNet and Transformer branches are concatenated for pattern recognition. Extensive experiments on multiple event-based recognition datasets fully validated the effectiveness of our model. The source code of this work will be released at https://github.com/Event-AHU/Uncertainty_aware_MobileFormer.
Active Neural Mapping
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:We address the problem of active mapping with a continually-learned neural scene representation, namely Active Neural Mapping. The key lies in actively finding the target space to be explored with efficient agent movement, thus minimizing the map uncertainty on-the-fly within a previously unseen environment. In this paper, we examine the weight space of the continually-learned neural field, and show empirically that the neural variability, the prediction robustness against random weight perturbation, can be directly utilized to measure the instant uncertainty of the neural map. Together with the continuous geometric information inherited in the neural map, the agent can be guided to find a traversable path to gradually gain knowledge of the environment. We present for the first time an active mapping system with a coordinate-based implicit neural representation for online scene reconstruction. Experiments in the visually-realistic Gibson and Matterport3D environment demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge