Content-aware Balanced Spectrum Encoding in Masked Modeling for Time Series Classification
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2024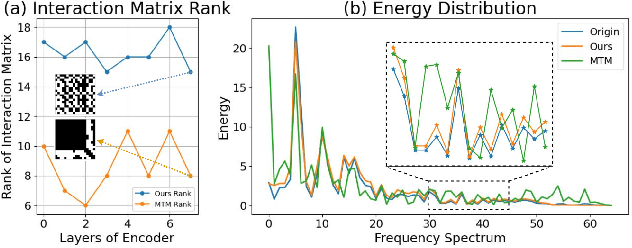
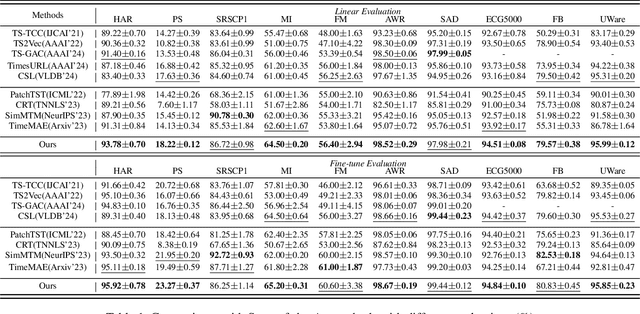
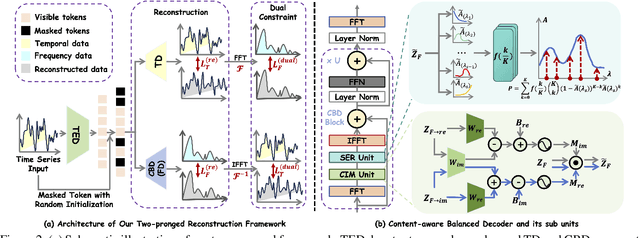
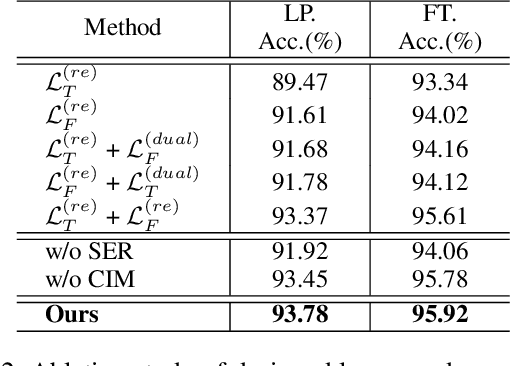
Due to the superior ability of global dependency, transformer and its variants have become the primary choice in Masked Time-series Modeling (MTM) towards time-series classification task. In this paper, we experimentally analyze that existing transformer-based MTM methods encounter with two under-explored issues when dealing with time series data: (1) they encode features by performing long-dependency ensemble averaging, which easily results in rank collapse and feature homogenization as the layer goes deeper; (2) they exhibit distinct priorities in fitting different frequency components contained in the time-series, inevitably leading to spectrum energy imbalance of encoded feature. To tackle these issues, we propose an auxiliary content-aware balanced decoder (CBD) to optimize the encoding quality in the spectrum space within masked modeling scheme. Specifically, the CBD iterates on a series of fundamental blocks, and thanks to two tailored units, each block could progressively refine the masked representation via adjusting the interaction pattern based on local content variations of time-series and learning to recalibrate the energy distribution across different frequency components. Moreover, a dual-constraint loss is devised to enhance the mutual optimization of vanilla decoder and our CBD. Extensive experimental results on ten time-series classification datasets show that our method nearly surpasses a bunch of baselines. Meanwhile, a series of explanatory results are showcased to sufficiently demystify the behaviors of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge