Masahiro Masuda
Tensor Program Optimization with Probabilistic Programs
May 26, 2022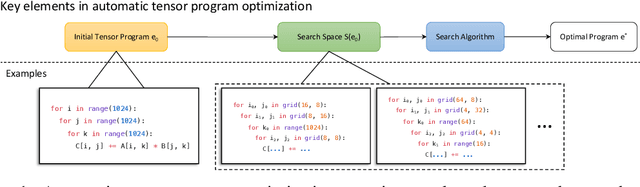
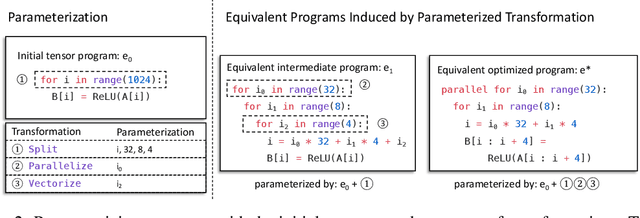
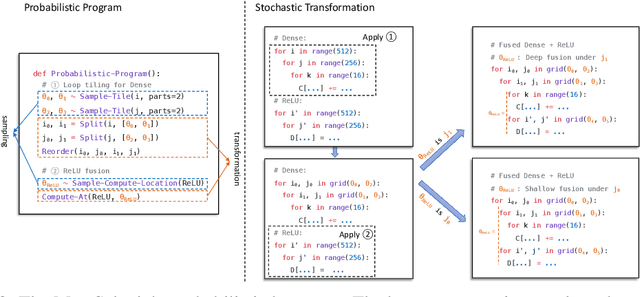
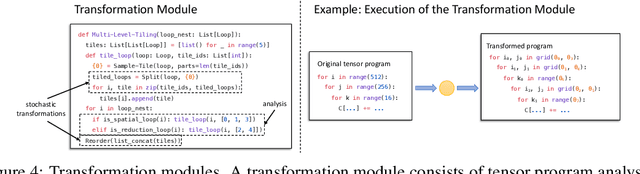
Abstract:Automatic optimization for tensor programs becomes increasingly important as we deploy deep learning in various environments, and efficient optimization relies on a rich search space and effective search. Most existing efforts adopt a search space which lacks the ability to efficiently enable domain experts to grow the search space. This paper introduces MetaSchedule, a domain-specific probabilistic programming language abstraction to construct a rich search space of tensor programs. Our abstraction allows domain experts to analyze the program, and easily propose stochastic choices in a modular way to compose program transformation accordingly. We also build an end-to-end learning-driven framework to find an optimized program for a given search space. Experimental results show that MetaSchedule can cover the search space used in the state-of-the-art tensor program optimization frameworks in a modular way. Additionally, it empowers domain experts to conveniently grow the search space and modularly enhance the system, which brings 48% speedup on end-to-end deep learning workloads.
Efficient Execution of Quantized Deep Learning Models: A Compiler Approach
Jun 18, 2020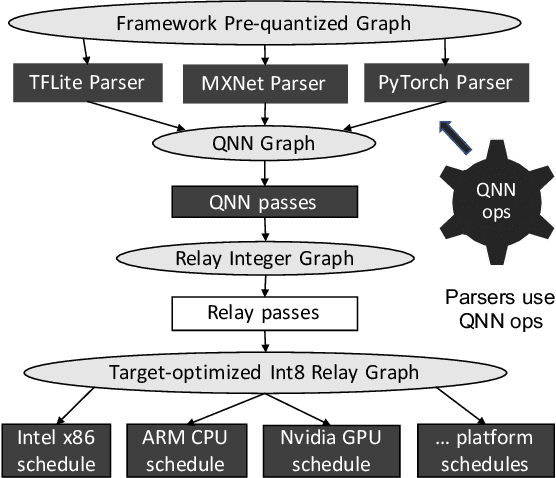
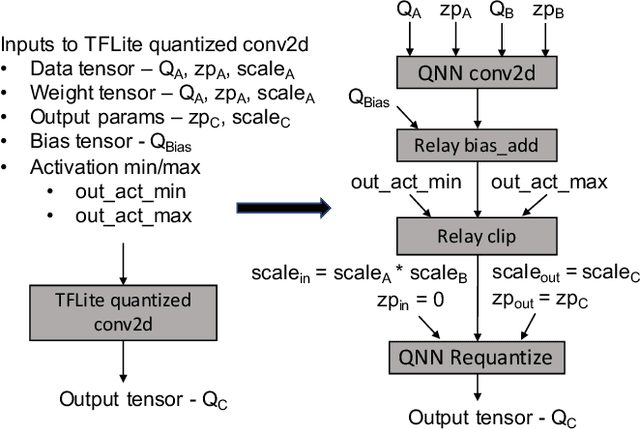
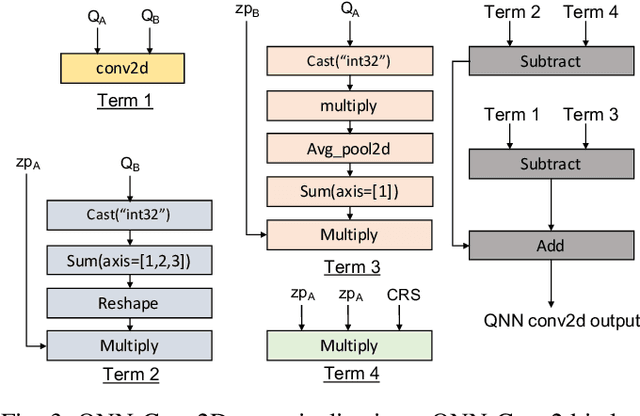
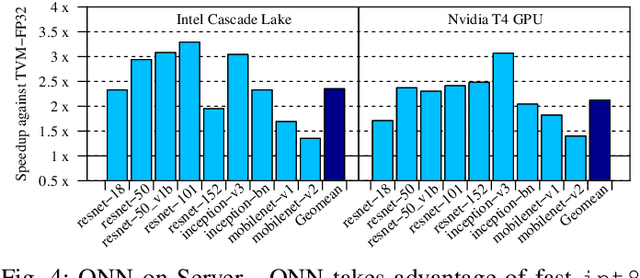
Abstract:A growing number of applications implement predictive functions using deep learning models, which require heavy use of compute and memory. One popular technique for increasing resource efficiency is 8-bit integer quantization, in which 32-bit floating point numbers (fp32) are represented using shorter 8-bit integer numbers. Although deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, TFLite, MXNet, and PyTorch enable developers to quantize models with only a small drop in accuracy, they are not well suited to execute quantized models on a variety of hardware platforms. For example, TFLite is optimized to run inference on ARM CPU edge devices but it does not have efficient support for Intel CPUs and Nvidia GPUs. In this paper, we address the challenges of executing quantized deep learning models on diverse hardware platforms by proposing an augmented compiler approach. A deep learning compiler such as Apache TVM can enable the efficient execution of model from various frameworks on various targets. Many deep learning compilers today, however, are designed primarily for fp32 computation and cannot optimize a pre-quantized INT8 model. To address this issue, we created a new dialect called Quantized Neural Network (QNN) that extends the compiler's internal representation with a quantization context. With this quantization context, the compiler can generate efficient code for pre-quantized models on various hardware platforms. As implemented in Apache TVM, we observe that the QNN-augmented deep learning compiler achieves speedups of 2.35x, 2.15x, 1.35x and 1.40x on Intel Xeon Cascade Lake CPUs, Nvidia Tesla T4 GPUs, ARM Raspberry Pi3 and Pi4 respectively against well optimized fp32 execution, and comparable performance to the state-of-the-art framework-specific solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge